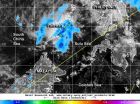
(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Gillian's eye was starting to "close" or become cloud-filled when NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the Southern Indian Ocean on March 23.
On March 23, Gillian's maximum sustained winds peaked near 140 knots/161.1 mph/259.3 kph making it a Category 5 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. Fortunately, Gillian pulled away from Indonesia, so all of the regional warnings were canceled on March 23.
At 06:45 UTC on March 23, NASA's Aqua satellite flew overhead and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument captured a visible image of the storm. In the image, Gillian's eye had already started to fill in with clouds and was surrounded by a thick band of thunderstorms wrapping around the center of circulation.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that satellite data also showed that convection along the northwest quadrant has started to contract and convection in the southeastern quadrant has continued to stretch out. Whenever a storm elongates, it can't maintain its speed and strength, much like a tire going flat.
By 09:00 UTC/5 a.m. EDT on March 24, Gillian's strength had waned as maximum sustained winds dropped to 120 knots/138.1 mph/222.2 kph. At that time it was centered near 17.2 south latitude and 103.5 east longitude, about 672 nautical miles/773.3 miles/1,245 km west-northwest of Learmonth, Australia. Gillian was moving toward the south at 10 knots/11.5 mph/ 18.5 kph and generating seas around 40 feet high.
JTWC noted that upper-level northwesterly wind shear has been increasing and is now strong, blowing as high as 30 knots/35.5 mph/55.5 kph. The wind shear is weakening the tropical cyclone. In addition, there is a mid-level trough (elongated area of low pressure) approaching Gillian, and that's creating the sinking or subsidence of air, so that thunderstorms (that make up a tropical cyclone) are unable to develop.
JTWC expects Gillian to continue weakening while tracking south for another couple of days before turning to the west.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA spots Tropical Cyclone Gillian's eye closing
2014-03-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Computer models solve geologic riddle millions of years in the making
2014-03-24
An international team of scientists that included USC's Meghan Miller used computer modeling to reveal, for the first time, how giant swirls form during the collision of tectonic plates – with subduction zones stuttering and recovering after continental fragments slam into them.
The team's 3D models suggest a likely answer to a question that has long plagued geologists: why do long, curving mountain chains form along some subduction zones – where two tectonic plates collide, pushing one down into the mantle?
Based on the models, the researchers found that parts of the ...
Motor learning: Lining up our sights
2014-03-24
Neurologists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have studied the role of the vestibular system, which controls balance, in optimizing how we direct our gaze. The results could lead to more effective rehabilitation of patients with vestibular or cerebellar dysfunction.
When we shift the direction of our gaze, head and eye movements are normally highly coordinated with each other. Indeed, from the many possible combinations of speed and duration for such movements, the brain chooses the one that minimizes the error in reaching the intended line of sight. ...
Glatt Kosher for Passover Seders At Talia's Steakhouse & Bar, A Manhattan Kosher Restaurant - Chol Hamoed and Yom Tov Meals Are Also Available at Talia's During This Popular Jewish Holiday
2014-03-24
If you are looking for a relaxing and stress-free way to celebrate Passover with your loved ones without spending the whole day in the kitchen, consider what has become a tradition for Passover at the popular New York City Glatt Kosher restaurant, Talia's Steakhouse & Bar, located on the Upper West Side of Manhattan, NYC.
For over eleven years, Talia's Steakhouse & Bar has been serving the kosher community of the NY Metro area. As the premier Glatt kosher establishment in Manhattan, Talia's is proud to announce that, once again, it will conduct four prepaid ...
Leukemia caused by chromosome catastrophe
2014-03-24
Researchers have found that people born with a rare abnormality of their chromosomes have a 2,700-fold increased risk of a rare childhood leukaemia. In this abnormality, two specific chromosomes are fused together but become prone to catastrophic shattering.
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, or ALL, is the most common childhood cancer. Scientists previously found that a small subset of ALL patients have repeated sections of chromosome 21 in the genomes of their leukaemia cells. This form of ALL – iAMP21 ALL – requires more intensive treatment than many other types of ALL. ...
Small number of counties leads the way in reducing smoking rates in the US
2014-03-24
SEATTLE — Nationally, smoking rates have decreased since 1996, but the declines have been driven by a relatively small share of counties across the US, according to new research from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington.
The study, "Cigarette smoking prevalence in US counties: 1996-2012," was published March 24 in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Population Health Metrics.
Total cigarette smoking prevalence – the percentage of the population that smokes – has not decreased significantly in all counties but, because ...
Increased awareness about skin cancer needed for minorities
2014-03-24
DETROIT – More awareness about skin cancer is needed for minorities because they believe they are at low risk of developing it, says Henry Ford Hospital dermatologist Diane Jackson-Richards, M.D.
Research has shown that minorities are diagnosed at a more advanced stage of skin cancer and have lower chances of survival than Caucasians. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer among African Americans and Asian Indians, and the second most common skin cancer in Hispanics, East Asians and Caucasians, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
"We need to intensify ...
Researchers improve performance of III-V nanowire solar cells on graphene
2014-03-24
Imagine a field of small wires—standing at attention like a tiny field of wheat—gathering the Sun's rays as the first step in solar energy conversion.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have achieved new levels of performance for seed-free and substrate-free arrays of nanowires from class of materials called III-V (three-five) directly on graphene. These compound semiconductors hold particular promise for applications involving light, such as solar cells or lasers.
"Over the past two decades, research in the field of semiconductor nanowires ...
NASA sees Tropical Depression 04W's remnants affecting Palawan
2014-03-24
Tropical Depression 04W formed in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean on March 23 and marched across the southern Philippines. NASA's TRMM satellite spotted moderate rainfall occurring near Palawan the next day from the storm's remnants.
Formerly known as System 94W, the tropical low organized into Tropical Depression 04W (TD04W) on Sunday, March 23. TD04W then crossed through the southern and central Philippines on March 22 and 23, moving from east to west through Mindanao and Visayas. At 04:32 UTC/12:32 a.m. EDT the depression had maximum sustained winds near 20 knots/23.0 ...
World's first light-activated antimicrobial surface that also works in the dark
2014-03-24
Researchers at UCL have developed a new antibacterial material which has potential for cutting hospital acquired infections. The combination of two simple dyes with nanoscopic particles of gold is deadly to bacteria when activated by light - even under modest indoor lighting. And in a first for this type of substance, it also shows impressive antibacterial properties in total darkness.
The research, from by Sacha Noimark and Ivan Parkin (both UCL Chemistry) and Elaine Allan (UCL Eastman Dental Institute), is published today in the journal Chemical Science.
Hospital-acquired ...
NTU scientists discover material that can be solar cell by day, light panel by night
2014-03-24
In future, when your mobile or tablet runs out of battery, you could just recharge it by putting it out in the sun.
Nanyang Technological University (NTU) scientists have developed a next-generation solar cell material which can also emit light, in addition to converting light to electricity.
This solar cell is developed from Perovskite, a promising material that could hold the key to creating high-efficiency, inexpensive solar cells. The new cells not only glow when electricity passes through them, but they can also be customised to emit different colours.
Picture ...