(Press-News.org) DETROIT – More awareness about skin cancer is needed for minorities because they believe they are at low risk of developing it, says Henry Ford Hospital dermatologist Diane Jackson-Richards, M.D.
Research has shown that minorities are diagnosed at a more advanced stage of skin cancer and have lower chances of survival than Caucasians. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer among African Americans and Asian Indians, and the second most common skin cancer in Hispanics, East Asians and Caucasians, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
"We need to intensify our awareness efforts for minorities so they fully understand the dangers of sun exposure and what they can do to reduce their risk of skin cancer," says Jackson-Richards, director of Henry Ford's Multicultural Dermatology Clinic in Detroit.
"Our minority populations have this perception that they are at low risk and little can be done to prevent it. The reality is that skin cancer is a significant health concern for minorities. With early detection and treatment, though, skin cancer is highly curable."
Dr. Jackson-Richards will discuss these issues Monday during a presentation of "Skin of Color" at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in Denver.
Dr. Jackson-Richards says "we must educate African Americans, Hispanics and other minorities that prevention guidelines are effective at reducing their risk of skin cancer." In Hispanic communities, fewer sunscreen products are available than in non-Hispanic communities, she says.
INFORMATION:
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States, the Foundation says, and more new cases are diagnosed each year than the combined incidence of breast, prostate, lung and colon cancers.
Common risk factors for skin cancer include a personal or family history, 50 or more moles, history of excessive sun exposure, diseases that suppress the immune system and a past history of skin cancer.
People can reduce their risk of developing skin cancer by:
Avoiding sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun's rays are the strongest.
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher generously. Re-apply every 2 hours.
Wear protective clothing – long-sleeved shirt and pants, wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses.
Avoiding tanning beds and tanning.
Seeing your physician for a skin exam every year.
Water, snow and sand increase your cancer of sunburn.
Increased awareness about skin cancer needed for minorities
2014-03-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers improve performance of III-V nanowire solar cells on graphene
2014-03-24
Imagine a field of small wires—standing at attention like a tiny field of wheat—gathering the Sun's rays as the first step in solar energy conversion.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have achieved new levels of performance for seed-free and substrate-free arrays of nanowires from class of materials called III-V (three-five) directly on graphene. These compound semiconductors hold particular promise for applications involving light, such as solar cells or lasers.
"Over the past two decades, research in the field of semiconductor nanowires ...
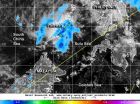
NASA sees Tropical Depression 04W's remnants affecting Palawan
2014-03-24
Tropical Depression 04W formed in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean on March 23 and marched across the southern Philippines. NASA's TRMM satellite spotted moderate rainfall occurring near Palawan the next day from the storm's remnants.
Formerly known as System 94W, the tropical low organized into Tropical Depression 04W (TD04W) on Sunday, March 23. TD04W then crossed through the southern and central Philippines on March 22 and 23, moving from east to west through Mindanao and Visayas. At 04:32 UTC/12:32 a.m. EDT the depression had maximum sustained winds near 20 knots/23.0 ...
World's first light-activated antimicrobial surface that also works in the dark
2014-03-24
Researchers at UCL have developed a new antibacterial material which has potential for cutting hospital acquired infections. The combination of two simple dyes with nanoscopic particles of gold is deadly to bacteria when activated by light - even under modest indoor lighting. And in a first for this type of substance, it also shows impressive antibacterial properties in total darkness.
The research, from by Sacha Noimark and Ivan Parkin (both UCL Chemistry) and Elaine Allan (UCL Eastman Dental Institute), is published today in the journal Chemical Science.
Hospital-acquired ...
NTU scientists discover material that can be solar cell by day, light panel by night
2014-03-24
In future, when your mobile or tablet runs out of battery, you could just recharge it by putting it out in the sun.
Nanyang Technological University (NTU) scientists have developed a next-generation solar cell material which can also emit light, in addition to converting light to electricity.
This solar cell is developed from Perovskite, a promising material that could hold the key to creating high-efficiency, inexpensive solar cells. The new cells not only glow when electricity passes through them, but they can also be customised to emit different colours.
Picture ...
'RoboClam' replicates a clam's ability to burrow while using little energy
2014-03-24
The Atlantic razor clam uses very little energy to burrow into undersea soil at high speed. Now a detailed insight into how the animal digs has led to the development of a robotic clam that can perform the same trick.
The device, known as "RoboClam," could be used to dig itself into the ground to bury anchors or destroy underwater mines, according to its developer, Amos Winter, the Robert N. Noyce Career Development Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT.
Despite its rigid shell, the Atlantic razor clam (Ensis directus) can move through soil at a speed ...
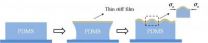
A new concept for manufacturing wrinkling patterns on hard-nano-film/soft-matter-substrate
2014-03-24
Wrinkling is a common phenomenon for thin stiff film adhered on soft substrate. Various wrinkling phenomenon has been reported previously. Wu Dan, Yin Yajun, Xie Huimin,et al from Tsinghua University proposed a new method to control wrinkling and buckling of thin stiff film on soft substrate. It is found that the curve pattern on the soft substrate has obvious influence on the wrinkling distribution of the thin film/soft substrate. Their work, entitled "Controlling the surface buckling wrinkles by patterning the material system of hard-nano-film/soft-matter-substrate", ...
Psychiatric complications in women with PCOS often linked to menstrual irr
2014-03-24
(NEW YORK, NY, March 24, 2014) – Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormone imbalance that causes infertility, obesity, and excessive facial hair in women, can also lead to severe mental health issues including anxiety, depression, and eating disorders. A study supervised by Columbia University School of Nursing professor Nancy Reame, MSN, PhD, FAAN, and published in the Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research, identifies the PCOS complications that may be most responsible for psychiatric problems. While weight gain and unwanted body hair can be distressing, irregular ...
Statins could ease coughing in lung disease patients, study finds
2014-03-24
Common cholesterol-lowering drugs could provide relief to patients suffering from a chronic lung disease, a study has shown.
The drugs – known as statins – were found to help alleviate the chronic coughing associated with the disease for some patients.
Statins are commonly prescribed for people at risk of heart attack because they can reduce cholesterol levels, but scientists are increasingly finding that they also have anti-inflammatory effects.
Researchers at the University of Edinburgh have shown the therapeutic potential of statins to treat patients with an inflammatory ...
Gene implicated in progression and relapse of deadly breast cancer finding points to potential Achilles' heel in triple negative breast cancer
2014-03-24
NEW YORK – (March 24, 2014) – Scientists from Weill Cornell Medical College and Houston Methodist have found that a gene previously unassociated with breast cancer plays a pivotal role in the growth and progression of the triple negative form of the disease, a particularly deadly strain that often has few treatment options. Their research, published in this week's Nature, suggests that targeting the gene may be a new approach to treating the disease.
About 42,000 new cases of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) are diagnosed in the United States each year, about 20 ...
Like being inside a star
2014-03-24
Some experiments are really difficult to perform in practice. To gain a detailed understanding of the behaviour of molecular hydrogen (H2), for example, we would have to produce such high pressures as those occurring within the core of gaseous planets like Jupiter and Saturn or inside stars. If such conditions cannot be created, an alternative method is to simulate them on the computer, but the model has to be accurate. A group of research scientists from the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA) in Trieste used a simulation model that is far more accurate than ...