(Press-News.org) The study found a 'stop mechanism' that determined brain signals telling the individual to stop drinking water when no longer thirsty, and the brain effects of drinking more water than required.
Researcher Professor Derek Denton from the Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry and Health Sciences at the University of Melbourne said the study provided insight into the human instincts that determine survival behaviour and are also of medical importance.
"Different areas of the brain involved in emotional decision-making were activated when people drank water after becoming thirsty and when study participants followed instructions to keep drinking when no longer thirsty."
"The brain regions determining the signals to stop drinking have not previously been recognised in this context. It identifies an important component in regulation and this 'stop mechanism' may prevent complications from excessive water intake," he said.
Overdrinking can reduce the salt concentration of the blood that can result in the swelling of the brain, a potentially fatal condition. Also known as polydipsia, it has been found in some patients with schizophrenia and in some marathon runners.
Professor Denton believes the findings could be applied to other aspects of human gratification.
"This is a study of elements of gratification and how the body programs accurate behaviour. In revealing aspects of gratification control, the data are relevant to study the gratification of other instincts, such as food intake, salt intake and sexual behaviour," he said.
The study used magnetic resonance imaging to scan two physiological conditions of the brain, starting with scanning brain regions during the experience of thirst. Participants were then removed from the scanner and asked to drink to satiation or 'overdrink' and returned for further scanning.INFORMATION:
The study was done in collaboration with the Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute and Monash Biomedical Imaging.
Last drinks: Brain's mechanism knows when to stop
2014-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Two spine surgeons are 3 times safer than 1
2014-03-26
Seattle, WA—A new team approach has improved safety—reducing rates of major complications by two thirds—for complex spinal reconstructive surgery for spinal deformity in adult Group Health patients at Virginia Mason Hospital & Seattle Medical Center. An article in the March issue of Spine Deformity gives a detailed description of the standardized protocol before, during, and after the surgery, stressing the new approach's three main features:
Two spine surgeons in the operating room
A live preoperative screening conference
Monitoring bleeding during the operation
The ...
ATHENA desktop human 'body' could reduce need for animal drug tests
2014-03-26
Creating surrogate human organs, coupled with insights from highly sensitive mass spectrometry technologies, a new project is on the brink of revolutionizing the way we screen new drugs and toxic agents.
ATHENA, the Advanced Tissue-engineered Human Ectypal Network Analyzer project team, is developing four human organ constructs – liver, heart, lung and kidney – that are based on a significantly miniaturized platform. Each organ component will be about the size of a smartphone screen, and the whole ATHENA "body" of interconnected organs would fit neatly on a desk.
"By ...
Life expectancy gains elude overweight teens
2014-03-26
Washington, DC—Although people live longer today than they did 50 years ago, people who were overweight and obese as teenagers aren't experiencing the same gains as other segments of the population, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
The life expectancy of the average American born in 2011 was 78.7 years, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The average lifespan has increased by more than a decade since 1950, but rising obesity rates threaten to take a toll on ...
Sugary drinks weigh heavily on teenage obesity
2014-03-26
New research shows sugary drinks are the worst offenders in the fight against youth obesity and recommends that B.C. schools fully implement healthy eating guidelines to reduce their consumption.
Data from the 2008 Adolescent Health survey among 11,000 grade seven to 12 students in British Columbia schools indicates sugary drinks like soda increased the odds of obesity more than other foods such as pizza, french fries, chips and candies.
The study, published today in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, found that students in schools ...
Research: Less invasive technique possible in vulvar cancer treatment
2014-03-26
A team of researchers from Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island commanded a national stage to present the results of a study evaluating the use of sentinel lymph node dissection in women with vulvar malignancies, and then follow the patients for complications and recurrence.
The team – Drs. Richard G. Moore, Dario Roque, Carolyn McCourt, Ashley Stuckey, Paul A. DiSIlvestro, James Sung, Margaret Steinhoff, Cornelius Granai III, and Katina Robison – presented their work at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncologists (SGO) in Tampa. The oral presentation ...
Lack of coronin 1 protein causes learning deficits and aggressive behavior
2014-03-26
This news release is available in German.
Organisms must be able to sense signals from the outside and translate these into biochemical cues in order to adequately respond to their environment. This capability is also required to process information that reaches the brain. Within the brain, stimulation of neurons activates genes that are required, for example for learning and memory. In collaboration with an international and interdisciplinary team the research group led by Prof. Jean Pieters from the Biozentrum, University of Basel, has now uncovered the role of ...
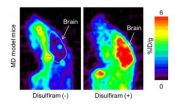
Using PET scanning to evaluate therapies of Menkes disease
2014-03-26
Scientists at the RIKEN Center for Life Science Technologies have used PET imaging to visualize the distribution in the body of copper, which is deregulated in Menkes disease, a genetic disorder, using a mouse model. This study lays the groundwork for PET imaging studies on human Menkes disease patients to identify new therapy options.
Menkes disease, though rare, is a fearsome genetic disorder. Most affected babies die within the first few years of life. The disease is caused by an inborn fault in the body's ability to absorb copper. The standard treatment today for ...
Diabetes: Good self-management helps to reduce mortality
2014-03-26
Scientists of the Institute of Health Economics and Health Care Management (IGM) and of the Institute of Epidemiology II (EPI II) at Helmholtz Zentrum München (HMGU), together with colleagues of the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) in Düsseldorf, investigated the association between self-management behavior and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. HMGU and the DDZ are partners in the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD).
High self-management index – low mortality
340 study participants with type 2 diabetes were interviewed with regard to their patient behavior ...
Real-life CSI: What can investigators really tell from gunshot residue?
2014-03-26
The popular TV series "CSI" is fiction, but every day, real-life investigators and forensic scientists collect and analyze evidence to determine what happened at crime scenes. In a study published in the ACS journal Analytical Chemistry, scientists say they have developed a more rapid and accurate method that could allow crime scene investigators to tell what kind of ammunition was shot from a gun based on the residue it left behind.
Igor K. Lednev and Justin Bueno point out that when someone fires a gun, burnt particles from the bullet spray out of the weapon onto a ...
Electroacupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels and hUCB-MSCs for cerebral ischemia
2014-03-26
Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation is a novel means of treating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, and can promote angiogenesis and neurological functional recovery. Acupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels also has positive effects as a treatment for cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Therefore, Prof. Haibo Yu and co-workers from Affiliated Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine in China hypothesized that electro-acupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels plus mesenchymal stem cell transplantation may have better therapeutic ...