(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
Subtle interactions of electrons and light make them so valuable for technology: ultra-thin systems of semiconductor layers can turn electrical voltage into light. But they can also be used the other way around and serve as light detectors. Until now, it has been hard to couple light into these layered semiconductor systems. Scientists at Vienna University of Technology solved this problem. They used metamaterials, which are able to manipulate light in the terahertz range due to their special microscopic structure.
Customized Semiconductor Layers
"Ultra-thin layered semiconductor systems have the great advantage, that their electronic properties can be very precisely tuned", says Professor Karl Unterrainer (TU Vienna). By selecting suitable materials, by tuning the thickness of the layers and the geometry of the device, the behaviour of the electrons in the system can be influenced. That way, quantum cascade lasers can be built, in which the electrons jump from layer to layer and emit a photon with each jump. Also, light detectors can be created, with a selective sensitivity to one particular wavelength.
The problem, however, is that quantum physics prohibits photons with a certain directions of oscillation (polarization) from interacting with the electrons of the semiconductor system. Light which hits the layered surface head-on, cannot influence the electron in the semiconductor. Therefore a method is required to rotate the polarization of the incident light, so that it can be detected in the semicionductor layers.
An Artificial Butterfly
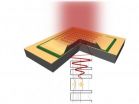
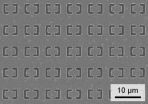
This can be done with an unusual method – with metamaterials. A metamaterial has an ordered geometric structure with a periodicity smaller than the wavelength of the incident light. The light is scattered according to the structure's geometry, some wavelengths may be absorbed, others reflected. The intriguing play of colours on a butterfly's wings comes from exactly this kind of effects. Metamaterials on top of a semiconductor structure are able to rotate the polarization of the incoming light so that it can interact with the electrons inside.
The light used in the experiment has a considerably longer wavelength than visible light: It is radiation in the terahertz- or infrared regime, with a wavelength of about a tenth of a millimetre. This kind of radiation has important technological applications, for instance for next-generation computer technology, but it is difficult to work with these kind of waves.
A Detector on a Chip
The discovery made at Vienna University of Technology now opens up the possibility of integrating a light detector for terahertz radiation into a chip. "With conventional fabrication methods, large arrays of such detectors can be built", Unterrainer explains. They do not take up much space: Layers with a thickness in the order of magnitude of nanometers are enough to detect light – the detector is more than a thousand times thinner than the wavelength of the light which is being detected.
INFORMATION:
Further Information:
Prof. Karl Unterrainer
Photonics Institute
Vienna University of Technology
Gusshausstraße 25-29, 1040 Wien
T: +43-1-58801-38730
karl.unterrainer@tuwien.ac.at
Dipl.-Ing. Michael Krall
Photonics Institute
Vienna University of Technology
Gusshausstraße 25-29, 1040 Wien
T: +43-1-58801-38737
michael.krall@tuwien.ac.at
Ultra-thin light detectors
A new, extremely thin kind of light detectors was created at Vienna University of Technology; 2 very different technologies were combined for the first time: metamaterials and quantum cascade structures
2014-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Simple blood test may predict if a child will become obese
2014-03-27
Researchers at the Universities of Southampton, Plymouth and Exeter used the test to assess the levels of epigenetic switches in the PGC1a gene – a gene that regulates fat storage in the body.
Epigenetic switches take place through a chemical change called DNA methylation, which controls how genes work and is set during early life.
The Southampton team found that the test, when carried out on children at five years old, differentiates between children with a high body fat and those with a low body fat when they were older. Results showed that a rise in DNA methylation ...
Predicting oil changes in industrial applications without interrupting operations
2014-03-27
This news release is available in German.
Predictive maintenance of hard-to-access plants, no unnecessary oil changes, no unnecessary laboratory costs and less environmental impact. These are just some of the benefits offered by a new system that can monitor the condition of lubricating oils, hydraulic oils and other fluids in industrial installations without interrupting ongoing operations. The method was developed by engineers from Saarbrücken in collaboration with project partners. The compact sensor system is available as a portable unit or can be built into ...
Democratizing data visualization
2014-03-27
In 2007, members of the Haystack Group in MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory released a set of Web development tools called "Exhibit." Exhibit lets novices quickly put together interactive data visualizations, such as maps with sortable data embedded in them; sortable tables that automatically pull in updated data from other sites; and sortable displays of linked thumbnail images.
In April, at the Association for Computing Machinery's Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Haystack members will present an in-depth study of the ways ...
Students on field course bag new spider species
2014-03-27
As a spin-off (pun intended) of their Tropical Biodiversity course in Malaysian Borneo, a team of biology students discover a new spider species, build a makeshift taxonomy lab, write a joint publication and send it off to a major taxonomic journal.
Discovering a new spider species was not what she had anticipated when she signed up for her field course in Tropical Biodiversity, says Elisa Panjang, a Malaysian master's student from Universiti Malaysia Sabah. She is one of twenty students following the course, organised by Naturalis Biodiversity Center in The Netherlands, ...
The first insects were not yet able to smell well
2014-03-27
This news release is available in German. An insect's sense of smell is vital to its survival. Only if it can trace even tiny amounts of odor molecules is it is able to find food sources, communicate with conspecifics, or avoid enemies. According to scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, many proteins involved in the highly sensitive odor perception of insects emerged rather late in the evolutionary process. The very complex olfactory system of modern insects is therefore not an adaptation to a terrestrial environment when ancient ...
One gene, many tissues
2014-03-27
Genes are the "code" for building the biological elements that form an organism. The DNA that makes up genes contains the instructions to synthesise proteins, but it's wrong to think that, for a given gene, these instructions are always the same for all parts of the organisms. In actual fact, the gene varies depending on the tissue where it is located (cerebral cortex, cerebellum, olfactory epithelium, etc.); in particular, what varies is the point in the "string" of code at which protein synthesis starts. This complexity complicates the work of scientists considerably, ...
How size splits cells
2014-03-27
One of the scientists who revealed how plants "do maths" can now reveal how cells take measurements of size. Size is important to cells as it determines when they divide.
In a paper published in eLife, Professor Martin Howard from the John Innes Centre and colleagues from the US, Germany and Singapore discovered that cells measure their surface area using a particular protein, cdr2p. The finding challenges a previous model suggesting that another protein called pom1p senses a cell's length.
"Many cell types have been shown to reach a size threshold before they commit ...
Natural plant compounds may assist chemotherapy
2014-03-27
Auckland, New Zealand. 27 March 2014...Researchers at Plant & Food Research have identified plant compounds present in carrots and parsley that may one day support more effective delivery of chemotherapy treatments.
Scientists at Plant & Food Research, working together with researchers at The University of Auckland and the National Cancer Institute of The Netherlands, have discovered specific plant compounds able to inhibit transport mechanisms in the body that select what compounds are absorbed into the body,and eventually into cells. These same transport mechanisms ...
Smoke-free air policies seem to protect the heart
2014-03-27
WASHINGTON (March 27, 2014) — A new study on the impact of Michigan's statewide smoking ban adds to mounting evidence that policies prohibiting tobacco smoking in workplaces and other public spaces may substantially improve public health by reducing heart disease and death, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
Studies on previous indoor smoking bans have consistently shown a major decrease in hospital admissions for heart attacks after smoke-free laws went into effect. Secondhand smoke exposure is ...
The heart responds differently to exercise in men vs. women
2014-03-27
WASHINGTON (March 27, 2014) — The formula for peak exercise heart rate that doctors have used for decades in tests to diagnose heart conditions may be flawed because it does not account for differences between men and women, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
The simple formula of "220 minus age" has been widely used to calculate the maximum number of heart beats per minute a person can achieve. Many people use it to derive their target heart rate during a workout. Doctors use it to determine how ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] Ultra-thin light detectorsA new, extremely thin kind of light detectors was created at Vienna University of Technology; 2 very different technologies were combined for the first time: metamaterials and quantum cascade structures