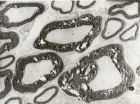
(Press-News.org) Percutaneous microballoon compression of the trigeminal ganglion is a brand new operative technique for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. However, it is unclear how the procedure mediates pain relief, and there are no standardized criteria, such as compression pressure, compression time or balloon shape, for the procedure. In particular, the links between compression duration and postoperative complications and pain recurrence are still under debate. An extended duration of compression would cause irreversible injury and drastic demyelination, and paresthesia and numbness with discomfort would ensue. In comparison, a short compression time may reduce postoperative complications. However, the rate of pain relief diminishes and the recurrence rate elevates. This may require a second operation and increase psychological and economic burdens on the patient. However, it remains a challenge to define optimal compression time, guarantee operative success, and reduce the complication rate and X-ray exposure. Dr. Fuyong Li and co-workers from Shengjing Hospital, China Medical University in China established an animal model of trigeminal neuralgia using percutaneous microballoon compression on the trigeminal ganglion, with the aim of observing changes in the trigeminal ganglion and the demyelination of myelinated nerve fibers under a compression pressure of 1,005 ± 150 mmHg for 2 or 5 minutes. After percutaneous microballoon compression, the large-diameter myelinated nerves displayed axonal swelling, rupture and demyelination under the electron microscope. Fragmentation of myelin and formation of digestion chambers were more evident after 5 minutes of compression. Image analyzer results showed that the diameter of trigeminal ganglion cells remained unaltered after compression. These experimental findings indicate that a 2-minute period of compression can suppress pain transduction, but long-term compression is ideal for patients with recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. The relevant paper has been published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 2, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: " Optimal duration of percutaneous microballoon compression for treatment of trigeminal nerve injury " by Fuyong Li1, Shuai Han2, Yi Ma3, Fuxin Yi4, Xinmin Xu3, Yunhui Liu1 (1 Department of Neurosurgery, Shengjing Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China; 2 Department of Neurosurgery, the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China; 3 Second Department of Neurosurgery, the People's Hospital of Liaoning Province, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China; 4 First Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital, Liaoning Medical College, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China)
Li FY, Han S, Ma Y, Yi FX, Xu XM, Liu YH. Optimal duration of percutaneous microballoon compression for treatment of trigeminal nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(2):179-189.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Optimal duration of percutaneous microballoon compression for trigeminal nerve injury
2014-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Concerning number of kids have elevated cholesterol
2014-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2014) — Roughly one out of three kids screened for high cholesterol between the ages of 9 and 11 has borderline or high cholesterol, potentially placing them at greater risk for future cardiovascular disease, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
In one of the largest studies of outpatient pediatric clinic visits to date, researchers examined the medical records of 12,712 children who had screening for cholesterol levels as part of a routine physical exam within the Texas Children's ...
Number of babies mom has may play role in future cardiovascular health
2014-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2014) — Women who give birth to four or more children are much more likely to have evidence of plaque in their heart or thickening of their arteries – early signs of cardiovascular disease – compared with those having fewer pregnancies, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
While earlier studies have shown an association between several aspects of pregnancy – physiological changes, complications, number of pregnancies – and future heart disease risk, many questions remain about ...
Eating fruits and vegetables linked to healthier arteries later in life
2014-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2014) — Women who ate a diet high in fresh fruits and vegetables as young adults were much less likely to have plaque build-up in their arteries 20 years later compared with those who consumed lower amounts of these foods, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session. This new finding reinforces the importance of developing healthy eating habits early in life.
Previous studies have found that middle-aged adults whose diet consists of a high proportion of fruits and vegetables are less ...
TV linked to poor snacking habits, cardiovascular risk in middle schoolers
2014-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2014) — Middle school kids who park themselves in front of the TV for two hours or more each day are more likely to consume junk food and have risk factors for cardiovascular disease, even compared to those who spend an equal amount of time on the computer or playing video games, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
"While too much of both types of screen time encourages sedentary behavior, our study suggests high TV time in particular is associated with poorer food choices ...
Marriage linked to lower heart risks in study of 3.5+ million adults
2014-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2014) — People who are married have lower rates of several cardiovascular diseases compared with those who are single, divorced or widowed, according to research to be presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session. The relationship between marriage and lower odds of vascular diseases is especially pronounced before age 50.
"These findings certainly shouldn't drive people to get married, but it's important to know that decisions regarding who one is with, why, and why not may have important implications for vascular ...
Revolutionary solar cells double as lasers
2014-03-28
Commercial silicon-based solar cells - such as those seen on the roofs of houses across the country - operate at about 20% efficiency for converting the Sun's rays into electrical energy. It's taken over 20 years to achieve that rate of efficiency.
A relatively new type of solar cell based on a perovskite material - named for scientist Lev Perovski, who first discovered materials with this structure in the Ural Mountains in the 19th century - was recently pioneered by an Oxford research team led by Professor Henry Snaith.
Perovskite solar cells, the source of huge excitement ...
Research suggests autumn is ending later in the northern hemisphere
2014-03-28
A study by the University of Southampton suggests that on average the end of Autumn is taking place later in the year and Spring is starting slightly earlier.
A team of researchers examined satellite imagery covering the northern hemisphere over a 25 year period (1982 - 2006), and looked for any seasonal changes in vegetation by making a measure of its 'greenness'. They examined in detail, at daily intervals, the growth cycle of the vegetation – identifying physical changes such as leaf cover, colour and growth.
The project was led by University of Southampton Professor ...
UEA research shows gastric surgery halves risk of heart attack in obese people
2014-03-28
Obese people who have stomach surgery to help them lose weight will halve their risk of heart attack according to new research from a team of doctors at the University of East Anglia, University of Manchester and University of Aberdeen.
The procedures, known as bariatric surgery, involve techniques such as gastric banding, which are available on the National Health Service (NHS) in the UK for selected patients.
New research published today in the International Journal of Cardiology reviewed data from 14 studies involving more than 29,000 patients who underwent bariatric ...
Great earthquakes, water under pressure, high risk
2014-03-28
The largest earthquakes occur where oceanic plates move beneath continents. Obviously, water trapped in the boundary between both plates has a dominant influence on the earthquake rupture process. Analyzing the great Chile earthquake of February, 27th, 2010, a group of scientists from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences and from Liverpool University found that the water pressure in the pores of the rocks making up the plate boundary zone takes the key role (Nature Geoscience, 28.03.2014).
The stress build-up before an earthquake and the magnitude of subsequent ...
Call for more awareness of sexual dysfunction in lung cancer patients
2014-03-28
Geneva, Switzerland, 28 March 2014 -- Many lung cancer patients suffer difficulties with sexual expression and intimacy, yet for too long the topic has been ignored by doctors and researchers, experts have said at the 4th European Lung Cancer Conference (ELCC).
"It's time that doctors and scientists paid more attention to this important issue," said Stephane Droupy from the University Hospital of Nimes, France, speaking at a special session on sexual dysfunction after lung cancer treatment at ELCC.
Researchers have estimated that sexual dysfunction affects between 40 ...