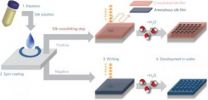
(Press-News.org) MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, MASS. -- Tufts University engineers have demonstrated that it is possible to generate nanostructures from silk in an environmentally friendly process that uses water as a developing agent and standard fabrication techniques. This approach provides a green alternative to the toxic materials commonly used in nanofabrication while delivering fabrication quality comparable to conventional synthetic polymers. Nanofabrication is at the heart of manufacture of semi-conductors and other electronic and photonic devices.
The paper describing this work, "All Water-based Electron Beam Lithography Using Silk as a Positive, Negative and Biofunctional Resist," appears in Nature Nanotechnology, published online March 23 in advance of print publication.
"In a world that strives to reduce toxic footprints associated with manufacturing, our laboratory is exploring biopolymers, and silk in particular, as a candidate material to replace plastics in many high-technology applications," said Frank C. Doble Professor of Biomedical Engineering Fiorenzo Omenetto, Ph.D., senior researcher on the work.
Nanofabrication involves high-resolution patterning with features so small that they have at least one dimension no larger than 100 nanometers (nm)—the size of particles filtered out by surgical masks. Nanoscale fabrication is usually obtained depositing thin films of customized polymers, called "resists," onto silicon wafers. Each resist layer is successively patterned by using light or electrons (via electron beam lithography) to expose the part of the resist not covered by a mask. Subsequently, positive resists are dissolved when subjected to a developer while negative resists remain behind after development. The composition and configuration of the layers determine the properties of the structure.
Developing a resist typically requires toxic chemicals, which need careful, and costly, handling and disposal. Significant advances have been made using "green" resists that can be developed with water, but these techniques have lacked the desired precision and scalability.
"In contrast, our process is entirely water-based, starting with the silk aqueous solution and ending with simple development of the exposed silk film in water, and the resolution achieved was comparable to one of the commonly used synthetic polymers," said Omenetto, who holds a professorship in the Department of Physics at Tufts School of Arts and Sciences in addition to his appointment in the School of Engineering. "A variety of manufacturing industries, high-tech companies and academic labs could ultimately benefit from clean rooms that are also green."
For this work, the Tufts engineers fabricated nanoscale photonic lattices using both neat silk and functionalized silk doped with quantum dots, green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) or horseradish peroxidase (HRP).
"By showing that biomolecules of the enzyme HRP remained active after the electron beam nanofabrication process, we demonstrated the feasibility of fabricating biologically active silk sensing devices, something not currently available," said Benedetto Marelli, Ph.D. Marelli is a post-doctoral associate in Omenetto's laboratory and a lead co-author on the paper with former Omenetto post doctoral associate Sunghwan Kim, Ph.D., now a professor in Ajou, Korea.
This research builds on previous work by Omenetto and his collaborators at the Tufts School of Engineering. In the past, they had shown that silk could be nanofabricated, but those processes required starting with other nanosized materials. This is the first time that silk has been fabricated to begin the nanofabrication manufacturing chain.
INFORMATION:
The work was supported by the National Science Foundation (DMR-1242240), ONR (N00014-13-1-0596) and AFOSR (FA9950-10-1-0172).
"All-water-based electron-beam lithography using silk as a resist," Sunghwan Kim, Benedetto Marelli, Mark A. Brenckle, Alexander N. Mitropoulos, Eun-Seok Gil, Konstantinos Tsioris, Hu Tao, David L. Kaplan, & Fiorenzo G. Omenetto, Nature Nanotechnology, doi:10.1038/nnano.2014.47, published online 23 March 2014.
Located on Tufts' Medford/Somerville campus, the Tufts University School of Engineering offers a rigorous engineering education in a unique environment that blends the intellectual and technological resources of a world-class research university with the strengths of a top-ranked liberal arts college. Close partnerships with Tufts' excellent undergraduate, graduate and professional schools, coupled with a long tradition of collaboration, provide a strong platform for interdisciplinary education and scholarship. The School of Engineering's mission is to educate engineers committed to the innovative and ethical application of science and technology in addressing the most pressing societal needs, to develop and nurture twenty-first century leadership qualities in its students, faculty, and alumni, and to create and disseminate transformational new knowledge and technologies that further the well-being and sustainability of society in such cross-cutting areas as human health, environmental sustainability, alternative energy, and the human-technology interface. For more information, visit http://engineering.tufts.edu.
Fabricating nanostructures with silk could make clean rooms green rooms
2014-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Safety and immunogenicity of 2 doses of the HPV-16/18 AS04 adjuvanted vaccine Cervarix
2014-03-28
A recent study in the journal Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, showed that two doses of the HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine Cervarix (GlaxoSmithKline) are non-inferior to three-doses in the current schedule.
Since high coverage and compliance rates can be difficult to achieve with the current three-dose HPV vaccineregimen, several studies have looked at the possibility of reducing the number of doses. Proof-of-principle that a two-dose schedule can provide sufficient protection against cervical cancer came initially from a study performed in Costa Rica in 2011. ...
Repeated hUCB injections may improve prognosis of children with deadly inherited disorder
2014-03-28
Putnam Valley, NY. (Mar. 28 2014) – New insight has been gained into treating an inherited disorder that creates serious neurological and behavioral disabilities in children and usually leads to death in the teen years.
In a recent study into the effects of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells (hUCB MNCs) when they are injected to counter the symptoms and progression of Sanfilippo syndrome type III B (MPS III B), researchers found that repeated injections into laboratory mice modeled with the disorder had clear benefits for the mice receiving multiple injections ...
Rainbow-catching waveguide could revolutionize energy technologies
2014-03-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. – More efficient photovoltaic cells. Improved radar and stealth technology. A new way to recycle waste heat generated by machines into energy.
All may be possible due to breakthrough photonics research at the University at Buffalo.
The work, published March 28 in the journal Scientific Reports, explores the use of a nanoscale microchip component called a "multilayered waveguide taper array" that improves the chip's ability to trap and absorb light.
Unlike current chips, the waveguide tapers (the thimble-shaped structures above) slow and ultimately absorb ...
Gene may predict if further cancer treatments are needed
2014-03-28
DALLAS – March 28, 2014 – UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers are developing a new predictive tool that could help patients with breast cancer and certain lung cancers decide whether follow-up treatments are likely to help.
Dr. Jerry Shay, Vice Chairman and Professor of Cell Biology at UT Southwestern, led a three-year study on the effects of irradiation in a lung cancer-susceptible mouse model. When his team looked at gene expression changes in the mice, then applied them to humans with early stage cancer, the results revealed a breakdown of which patients have ...
Erectile dysfunction can be reversed without medication
2014-03-28
Men suffering from sexual dysfunction can be successful at reversing their problem, by focusing on lifestyle factors and not just relying on medication, according to research at the University of Adelaide.
In a new paper published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, researchers highlight the incidence of erectile dysfunction and lack of sexual desire among Australian men aged 35-80 years.
Over a five-year period, 31% of the 810 men involved in the study developed some form of erectile dysfunction.
"Sexual relations are not only an important part of people's wellbeing. ...
NUS researchers developed world's first fluorescent sensor to detect date rape drug
2014-03-28
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed the world's first fluorescent sensor to identify the presence of a drug known as GHB that is commonly used to spike beverages. When the sensor is mixed with a sample of a beverage containing GHB, the mixture changes colour in less than 30 seconds, making detection of the drug fast and easy.
This simple mix-and-see discovery, led by Professor Chang Young-Tae of the Department of Chemistry at the NUS Faculty of Science, is a novel scientific breakthrough that contributes towards prevention ...
More male fish 'feminized' by pollution on the Basque coast
2014-03-28
The UPV/EHU's Cell Biology in Environmental Toxicology group has conducted research using thick-lipped grey mullet and has analysed specimens in six zones: Arriluze and Gernika in 2007 and 2008, and since then, Santurtzi, Plentzia, Ondarroa, Deba and Pasaia. The acquisition of feminine features by male fish has been detected, to a greater or lesser extent, in all the estuaries, not only in the characteristics of the gonads of the specimens analysed but also in various molecular markers. According to Miren P. Cajaraville, director of the research group, the results show ...
Fingerprint of dissolved glycine in the Terahertz range explained
2014-03-28
Chemists at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) have, for the first time, completely analysed the fingerprint region of the Terahertz spectrum of a biologically relevant molecule in water, in this case, an amino acid. By combining spectroscopy and molecular-dynamics simulations, they rendered the motion of the most basic amino acid, glycine, visible in an aqueous solution. Their results have disproved the long-standing theory that frequencies in the Terahertz range provide no information regarding the amino acid's motion. The team led by Prof Dr Martina Havenith-Newen and ...
Aspartic acid in the hippocampus: A biomarker for postoperative cognitive dysfunction
2014-03-28
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction is the deterioration of cognitive performance after anesthesia and surgery, and manifests as impairments in short-term memory, concentration, language comprehension, and social integration skills. Previous studies have shown that the occurrence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction is affected by many factors, including advanced age, low educational level, pre-existing cognitive impairment, alcohol abuse, and severity of coexisting illness. However, the real cause for postoperative cognitive dysfunction is still unclear. Metabolite changes ...
Ancient African cattle first domesticated in Middle East, MU study reveals
2014-03-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Geneticist and anthropologists previously suspected that ancient Africans domesticated cattle native to the African continent nearly 10,000 years ago. Now, a team of University of Missouri researchers has completed the genetic history of 134 cattle breeds from around the world. In the process of completing this history, they found that ancient domesticated African cattle originated in the "Fertile Crescent," a region that covered modern day Iraq, Jordan, Syria and Israel.
Lead researcher Jared Decker, an assistant professor of animal science in the MU ...