(Press-News.org) Evidence from Disneyland suggests that human creativity may have evolved not in response to sexual selection as some scientists believe but as a way to help parents bond with their children and to pass on traditions and cultural knowledge, a new study published in the inaugural issue of the International Journal of Tourism Anthropology suggests.
Evolutionary psychologist Geoffrey Miller of the University of New Mexico has suggested that human creativity, storytelling, humor, wit, music, fantasy, and morality, all evolved as forms of courtship behavior. He used evidence drawn from the Southern California tourist industry to underpin his argument. The work offers an explanation as to why the human brain is so much bigger relative to body size than that of other apes - sexual selection for greater intellect. Intriguingly, Miller has referred to the mind as "amusement park".
Now, anthropologists Craig Palmer of the University of Missouri, Columbia, and Kathryn Coe of the University of Arizona beg to differ. Although Miller talks of the mind in such terms, he fails to include in his analysis the most famous amusement park in the world, Disneyland. Palmer and Coe suggest that this is one of the most dense concentrations in the world of exactly those aspects of culture - art, creativity, storytelling, humor, wit, music, fantasy, and morality - that Miller claims evolved as courtship displays.
Writing in the IJTA, Palmer and Coe suggest that Miller's hypothesis cannot account for the fact that Disneyland is fundamentally devoted to children. They reason that Disneyland and other similar amusement parks, support an alternative hypothesis that the creative aspects of the human brain may have evolved in the context of parents influencing their offspring, and offspring responding to their parents, not in the context of courtship.
The researchers do concede that some tourism is related to courtship, and not just "honeymoon" tourism and that it often involves art, creativity, storytelling, humor, wit, music, fantasy, and morality as part of the attractions. The team argues, however, that "The brain circuitry involved in both the generation of, and response to, these traits was selected for because it enabled parents to increase their fitness by increasing their ability to influence their offspring." The human brain increased in size through evolution as cultural traditions accumulated over numerous generations. "Traditions can last much longer than a generation or two and that the massive accumulation of traditional behavior is unique to our species as is the large brain," the team concludes.
INFORMATION:
"Parenting, courtship, Disneyland and the human brain" in Int. J. Tourism Anthropology, 2010, 1, 1-14
Brain size and a trip to Disneyland
How parental concerns could increase the size of our creative brains
2010-11-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New way of predicting dominant seasonal flu strain
2010-11-16
HOUSTON -- (Nov. 15, 2010) -- Rice University scientists have found a way to predict rapidly whether a new strain of the influenza virus should be included in the annual seasonal flu vaccine. While it sometimes takes new flu strains up to three years to become dominant worldwide, the new method can predict whether they will become dominant as little as two weeks after the sequence first appears in the GenBank database, the National Institutes of Health's collection of all publicly available DNA sequences.
"We studied a new strain of the virus that evolved in British Columbia ...
Child/teen sexual and physical abuse linked to fibroids in premenopausal women
2010-11-16
(Boston) - Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have found that both physical and sexual abuse history were positively associated with a higher incidence of uterine fibroids later in life. These findings currently appear on-line in the journal Epidemiology.
Uterine leiomyomas, also known as fibroids or myomas, are benign, hormone-dependent tumors that are clinically symptomatic in 20 percent of reproductive age women. Fibroids contribute to a third of hysterectomies in the US, increase risk of infertility, spontaneous abortion and pelvic ...
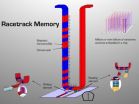
Racetrack memory
2010-11-16
Annoyed by how long it took his computer to boot up, Kläui began to think about an alternative. Hard disks are cheap and can store enormous quantities of data, but they are slow; every time a computer boots up, 2-3 minutes are lost while information is transferred from the hard disk into RAM (random access memory). The global cost in terms of lost productivity and energy consumption runs into the hundreds of millions of dollars a day.
Like the tried and true VHS videocassette, the proposed solution involves data recorded on magnetic tape. But the similarity ends there; ...
When video games get problematic so do smoking, drug use and aggression
2010-11-16
A new study on gaming and health in adolescents, conducted by researchers at Yale School of Medicine, found some significant gender differences linked to gaming as well as important health risks associated with problematic gaming. Published today in the journal Pediatrics, the study is among the first and largest to examine possible health links to gaming and problematic gaming in a community sample of adolescents.
Rani Desai, associate professor of psychiatry and epidemiology and public health at Yale, and colleagues anonymously surveyed 4,028 adolescents about their ...
New treatment for lung cancer shows promise
2010-11-16
Arlington, Va. — A new inhalable dry powder treatment for lung cancer shows a significant increase in survival rates and is far less invasive than current treatment options, which frequently include radiation and surgery. This research is being presented at the 2010 International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) Pharmaceutical Sciences World Congress (PSWC) in association with the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) Annual Meeting and Exposition in New Orleans, La., Nov. 14-18.
Lung cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the U.S., accounting ...
New tech to help protect bridges, other infrastructure from scour
2010-11-16
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a sensor that allows engineers to assess the scour potential of soils at various depths and on-site for the first time – a technology that will help evaluate the safety of civil infrastructure before and after storm events. Scour, or erosion of soil around structures due to water flow, is responsible for a wide range of critical infrastructure failures – from unstable bridges to the levees that gave way in the wake of Hurricane Katrina.
"The 'in situ scour evaluation probe' (ISEP) is the first technology ...
Where did you get those eyes and that brain?
2010-11-16
Philadelphia, PA, 15 November 2010 - A family history of Alzheimer's disease significantly increases the risk for developing this disorder, but a new study in Biological Psychiatry suggests that which of your parents has the disease is very important.
Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia in late-life, affecting over 5 million elderly in the United States alone. In order to develop preventative treatments, it is necessary to identify those individuals who are at highest risk for developing Alzheimer's.
Although individuals with a parental history of Alzheimer's ...
Study: Teleworkers more satisfied than office-based employees
2010-11-16
Employees who telecommute the majority of the work week are more satisfied with their jobs compared to those working mostly in the office because working remotely alleviates more stress than it creates, according to a new study by a communication researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee (UWM).
The study, conducted by Kathryn Fonner, UWM assistant professor of communication, and Michael Roloff, a professor of communication studies at Northwestern University, compared the advantages and disadvantages of each work arrangement. A paper outlining the results appears ...
Prostate cancer treatment linked to higher rate of colon cancer, study finds
2010-11-16
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Men treated with hormone-based therapy for prostate cancer faced a 30 percent to 40 percent higher risk of colorectal cancer, compared to patients who did not receive this treatment, according to a new study.
The study looked at use of androgen deprivation therapy, a common type of treatment for prostate cancer that involves blocking the male hormone testosterone through either surgical removal of the testicles or a series of injections. It's been shown to benefit men with advanced cancers, but its benefit for less-advanced disease is unclear. Still, ...
Robo-op marks new world first for heart procedure
2010-11-16
The world's first remote heart procedure, using a robotic arm alongside 3-D mapping, is due to take place at Glenfield Hospital in Leicester.
It comes six months after Dr Andre Ng carried out the first ever remote catheter ablation procedure using the Amigo Robotic Catheter System.
Dr Ng, is senior lecturer at the University of Leicester and consultant cardiologist and electrophysiologist at Glenfield Hospital.
On Tuesday 16 November, Dr Ng will be carrying out another "world first" using the robotic arm in combination with advanced 3-dimensional mapping to fix ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Brain size and a trip to DisneylandHow parental concerns could increase the size of our creative brains