(Press-News.org) The human mind tends to devalue future rewards compared to immediate ones – a phenomenon that often leads to favoring immediate gratification over long-term wellbeing. As a consequence, patience has long been recognized to be a virtue. And indeed, the inability to resist temptation underlies a host of problems ranging from credit card debt and inadequate savings to unhealthy eating and drug addiction.
The prevailing view for reducing costly impatience has emphasized the use of willpower. Emotions were to be tamped down in order to avoid irrational impulses for immediate gain. But as Northeastern University psychologist David DeSteno notes, "Emotions exist to serve adaptive purposes, so the idea that emotions would always be a hindrance to long-term success makes little sense."
In a potentially landmark study forthcoming in the journal Psychological Science, a team of researchers from Northeastern University, the University of California, Riverside, and Harvard Kennedy School challenge the conventional view by demonstrating that feelings of gratitude automatically reduce financial impatience.
THE STUDY
Impatience was assessed using a set of decisions pitting desire for instant gratification against waiting for larger, future rewards. For example, participants chose between receiving $54 now or $80 in 30 days. To increase the stakes, participants had the chance to obtain one of the financial rewards they selected. But before making these decisions, participants were randomly assigned to one of three conditions in which they wrote about an event from their past that made them feel (a) grateful, (b) happy, or (c) neutral, depending on condition.
Although participants feeling neutral and happy showed a strong preference for immediate payouts, those feeling grateful showed more patience. For example, they required $63 immediately to forgo receiving $85 in three months, whereas neutral and happy people required only $55 to forgo the future gain. What's more, the degree of patience exhibited was directly related to the amount of gratitude any individual felt. Positive feelings alone were not enough to enhance patience, as happy participants were just as impatient as those in the neutral condition. The influence of gratitude, possibly due to its ties to a sense of fulfillment and a need to "pay back" in the future, was quite specific.
The implications of this finding are profound. "Showing that emotion can foster self-control and discovering a way to reduce impatience with a simple gratitude exercise opens up tremendous possibilities for reducing a wide range of societal ills from impulse buying and insufficient saving to obesity and smoking," says Assistant Professor Ye Li from the University of California, Riverside School of Business Administration. Harvard Kennedy School Professor Jennifer Lerner underscored that economic impatience is one of the most common and troubling tendencies in human decision making.
INFORMATION: END
Can gratitude reduce costly impatience?
2014-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Periodic puns: Chemistry jokes just in time for April Fools' Day (video)
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON, March 31, 2014 — It's almost April Fools' Day, and the American Chemical Society's (ACS') Reactions video series is celebrating with an episode featuring our favorite chemistry jokes. Which two elements look cute together? Why is father water concerned about his "iced out" son? What do you get when you combine sulfur, tungsten and silver? Get all the punchlines in the latest Reactions episode, available at: http://youtu.be/C5RZRkhk0OM.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions.
INFORMATION:
The American Chemical ...
New Penn-designed gel allows for targeted therapy after heart attack
2014-03-31
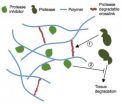
Combatting the tissue degrading enzymes that cause lasting damage following a heart attack is tricky. Each patient responds to a heart attack differently and damage can vary from one part of the heart muscle to another, but existing treatments can't be fine-tuned to deal with this variation.
University of Pennsylvania researchers have developed a way to address this problem via a material that can be applied directly to the damaged heart tissue. The potentially dangerous enzymes break down this gel-like material, releasing enzyme inhibitors contained within. This responsive, ...
New Zealand physicists split and collide ultracold atom clouds
2014-03-31
VIDEO:
Physicists from New Zealands' University of Otago have pushed the frontiers of quantum technology by developing a steerable 'optical tweezers' unit that uses intense laser beams to precisely split minute...
Click here for more information.
Physicists at New Zealand's University of Otago have pushed the frontiers of quantum technology by developing a steerable 'optical tweezers' unit that uses intense laser beams to precisely split minute clouds of ultracold atoms and to ...
Childhood virus may increase type 1 diabetes risk
2014-03-31
The study, published today in PLOS Pathogens, explored the ways the rotavirus infection contributes to autoimmune disease in mice, and researchers believe the breakthrough could be relevant to human infection with rotavirus.
The research found that it may be the "bystander effect" that causes the rotavirus infection to accelerate the onset of type 1 diabetes.
The "bystander effect" suggests that the virus provokes a strong activation of the immune system, which then spills over, allowing the immune system to attack not only the viral intruder but some of the body's ...
Role of type-2 astrocytes on the repair of spinal cord injury
2014-03-31
Increasing expression of bone morphogenetic proteins at the lesion site of the central nervous system possibly induces oligodendrocyte precursor cells to differentiate into type-2 astrocytes. While the restriction of oligodendrocyte differentiation could affect remyelination, it remains poorly understood how type-2 astrocytes regulate regeneration and functional recovery. Thus, examining the effects of type-2 astrocytes on neuronal growth is helpful in understanding the possible influential factors of oligodendrocyte precursor cells on axonal regeneration and remyelination, ...
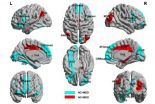
Resting-state functional connectivity as an auxillary diagnosis of depression
2014-03-31
According to a paper published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 2, 2014), both depressive patients and healthy controls presented typical small-world attributes, and compared with healthy controls, characteristic path length was significantly shorter in depressive patients, suggesting development toward randomization. Patients with depression showed apparently abnormal node attributes at key areas in cortical-striatal-pallidal-thalamic circuits. In addition, right hippocampus and right thalamus were closely linked with the severity of depression. An artificial ...
How does acupuncture at Baihui and Dazhui reduce brain cell apoptosis in heroin readdicts?
2014-03-31
Acupuncture has therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemia, dementia, epilepsy and other brain diseases, and also functions to repair the nervous system. Dazhui (GV14) and Baihui (GV20) are the preferred acupoints for treatment. However, whether acupuncture can treat addiction and prevent readdiction through changes to brain cell ultrastructure remains unknown. A research team from Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China pointed out that cell apoptosis was observed in the hippocampus and frontal lobe of heroin readdicted rats by electron microscopy, and ...
Metformin does not improve heart function in patients without diabetes
2014-03-31
Although some research has suggested that metformin, a medication often used in the treatment of diabetes, may have favorable effects on ventricular (heart) function, among patients without diabetes who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI; a procedure such as stent placement used to open narrowed coronary arteries) for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI; a certain pattern on an electrocardiogram following a heart attack), treatment with metformin did not result in improved ventricular function, according to a JAMA study released online to coincide ...
Cleveland Clinic study shows bariatric surgery provides long-term control of diabetes
2014-03-31
Cleveland: A study by Cleveland Clinic researchers shows bariatric surgery is a highly effective and durable treatment for type 2 diabetes in obese patients, enabling nearly all surgical patients to be free of insulin and many to be free of all diabetic medications three years after surgery.
The STAMPEDE (Surgical Therapy And Medications Potentially Eradicate Diabetes Efficiently) trial was simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine and presented today at the Annual Scientific Session of the American College of Cardiology in Washington, D.C.
The ...
Addicts who live in the moment may benefit most from certain kinds of treatment
2014-03-31
Drug-dependent people who least take the future into account may, paradoxically, be the ones to benefit the most from certain treatments.
The human instinct to choose instant gratification, such as a drug high, over a later benefit, such as good health — known as future or delay discounting — is strong in people with drug dependencies. An important component of addiction is failure to exert self-control in recognition of future consequences.
In a study in Clinical Psychological Science, a team of researchers has found an unexpected pattern that may provide hope for ...