(Press-News.org) Two UCLA professors who conducted the most thorough analysis to date of studies on school bullying have found that K-12 schools' efforts to curtail bullying are often disappointing.
The study revealed that schools are trying many different approaches to protect students, and while the more comprehensive programs have been the most effective, they require substantial commitment and school resources to be successful.
"Band-Aid solutions, such as holding one assembly a year that discourages bullying, do not work," said Jaana Juvonen, a UCLA professor of psychology and lead author of the review. "We are trying to figure out the right balance between comprehensive programs that are costly and require a lot of staff training versus programs that require fewer school resources."
The review, published in the journal Annual Review of Psychology, also debunks some common misconceptions about bullying. For example, while it was previously assumed that verbal aggression and exclusion were bullying tactics used more commonly by girls than by boys, the analysis revealed that boys use the tactics as much as girls do.
Perhaps less surprisingly, Juvonen said, gay and lesbian students and students who are overweight tend to get bullied significantly more than other students.
"Starting in elementary school, kids with characteristics that make them stand out are much more likely to get bullied," said Juvonen, who consults with several schools on anti-bullying programs. "They are prime targets for bullies because they are more likely to be friendless, and when they have nobody to defend them, the bullying often escalates."
Children with social connections — even just one friend — are at less risk of suffering severe symptoms after being bullied, Juvonen said. That insight indicates that schools could do a better job of preventing bullying by making sure students are not isolated, for example, by not eating lunch alone.
Anti-bullying programs are evaluated based on whether they are reducing the number of bullying incidents on school grounds, but Juvonen said it might be more telling to consider how much schools are helping the students who are most severely and most frequently bullied.
"It is important to distinguish between victims of prolonged bullying and those getting called names once or twice," Juvonen said. "Students who experience continual bullying are at risk for much more severe symptoms." Such students are most likely to blame themselves, feel depressed and feel that nothing can be done to stop the bullying.
Juvonen said school administrators have an especially difficult time addressing online bullying, or cyberbullying, and they tend to disagree about whether the issue should even be their responsibility.
"Students who have been cyberbullied at night often don't come to school the next day, or they come late or are not focused," she said. "There is a very strong association between what happens in cyberspace and what happens on the school grounds. Many of the same students who are bullied in school are also cyberbullied."
Some schools have been successful combatting bullying by training bystanders to respond to bullying. But Juvonen said the training needs to be a school-wide initiative that provides students with strategies against bullying and unites them in the cause.
Juvonen and co-author Sandra Graham, a UCLA professor of education, analyzed more than 140 studies — a mix of long-term and "snapshot" research — that were conducted in the U.S., Australia, Finland, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
Now, Juvonen and Graham are conducting an eight-year study of 6,000 California students ages 12 to 19. Focusing on schools that vary in ethnic diversity, they are studying friendships and the development of prejudice in addition to bullying. The current research is funded by the National Institutes of Health's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the National Science Foundation and the Spencer Foundation.
Previous studies on bullying by Juvonen and her colleagues have found that:
Bullies are considered the "cool" kids in school.
Nearly three in four teenagers say they were bullied online at least once during a 12-month period.
Nearly half of the sixth graders at two Los Angeles–area schools said they were bullied by classmates during a five-day period.
Students who get bullied often have headaches, colds and other illnesses, as well as psychological problems. Juvonen advises parents to talk with their children about bullying before it happens, to pay attention to changes in their children's behavior and to take their concerns about bullying seriously.
INFORMATION:
UCLA is California's largest university, with an enrollment of more than 40,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The UCLA College of Letters and Science and the university's 11 professional schools feature renowned faculty and offer 337 degree programs and majors. UCLA is a national and international leader in the breadth and quality of its academic, research, health care, cultural, continuing education and athletic programs. Seven alumni and six faculty have been awarded the Nobel Prize.
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
Schools have limited success in reducing bullying, new analysis finds
2014-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Oxytocin, the 'love' hormone, promotes group lying, according to Ben-Gurion U. researchers
2014-04-01
BEER-SHEVA, Israel…April 1, 2014 – According to a new study by researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and the University of Amsterdam, oxytocin caused participants to lie more to benefit their groups, and to do so more quickly and without expectation of reciprocal dishonesty from their group. Oxytocin is a hormone the body naturally produces to stimulate bonding.
The research was published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS).
"Our results suggest people are willing to bend ethical rules to help the people close to ...
Factor present in gestational and type 2 diabetes could provide new treatment options
2014-04-01
New research reveals that both pregnant women with diabetes and with type 2 diabetics have high levels of a fat metabolite that impairs pancreatic cells from secreting insulin. The findings, which are published in the April 1 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism, suggest that blocking the effects of this fat metabolite may help prevent and treat diabetes.
In nearly one-fifth of pregnancies, diabetes can arise (called gestational diabetes), and when this happens, it puts the woman at an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. To gain better ...
Obesity primes the colon for cancer, according to NIH study
2014-04-01
Obesity, rather than diet, causes changes in the colon that may lead to colorectal cancer, according to a study in mice by the National Institutes of Health. The finding bolsters the recommendation that calorie control and frequent exercise are not only key to a healthy lifestyle, but a strategy to lower the risk for colon cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States.
Paul Wade, Ph.D., and Thomas Eling, Ph.D., scientists at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), part of NIH, led a collaborative team that made ...
Common molecular defect offers treatment hope for group of rare disorders
2014-04-01
DURHAM, N.C. – Duke Medicine researchers studying tiny, antennae-like structures called cilia have found a potential way to ease some of the physical damage of numerous genetic disorders that result when these essential cellular components are defective.
Different genetic defects cause dysfunction of the cilia, which often act as sensory organs that receive signals from other cells. Individually, disorders involving cilia are rare, but collectively the more than 100 diseases in the category known as ciliopathies affect as many as one in 1,000 people. Ciliopathies are ...
Swimming pool urine combines with chlorine to pose health risks
2014-04-01
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A new study shows how uric acid in urine generates potentially hazardous "volatile disinfection byproducts" in swimming pools by interacting with chlorine, and researchers are advising swimmers to observe "improved hygiene habits."
Chlorination is used primarily to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from growing. The disinfection byproducts include cyanogen chloride (CNCl) and trichloramine (NCl3). Cyanogen chloride is a toxic compound that affects many organs, including the lungs, heart and central nervous system by inhalation. Trichloramine has ...
Got acne? There's an App for that!
2014-04-01
CHICAGO --- Acne sufferers around the world are using an iPhone app created at Northwestern University to learn how certain foods affect their skin conditions.
The app, called "diet & acne," can be downloaded from the iTunes app store for free. It uses data from a systematic analysis of peer-reviewed research studies to show people if there is or is not scientific evidence linking acne to foods such as chocolate, fat, sugar and whey protein.
"Users may be surprised to learn that there is no conclusive evidence from large randomized controlled trials that have linked ...
Plugged in but powered down
2014-04-01
It's not news that being a couch potato is bad for your health. Lack of physical activity is associated with a range of diseases from diabetes to heart attacks. It now turns out that young men who have experienced depression early in life may be especially vulnerable to becoming sedentary later in life. And particularly to spending large amounts of time online each day.
A study of 761 adults in Montreal who were identified at the age of 20 as suffering from the symptoms of depression (in 2007-08) were asked by researchers to keep track of how much leisure time they spent ...
Good vibrations: Using light-heated water to deliver drugs
2014-04-01
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, in collaboration with materials scientists, engineers and neurobiologists, have discovered a new mechanism for using light to activate drug-delivering nanoparticles and other targeted therapeutic substances inside the body.
This discovery represents a major innovation, said Adah Almutairi, PhD, associate professor and director of the joint UC San Diego-KACST Center of Excellence in Nanomedicine. Up to now, she said, only a handful of strategies using light-triggered ...
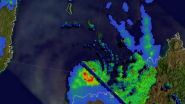
NASA caught Tropical Cyclone Hellen's rainfall near peak
2014-04-01
VIDEO:
This 3-D simulated flyby of Tropical Cyclone Hellen on March 30, showed some powerful storms in Hellen's eye wall were reaching heights of over 13 km/8 miles.
Click here for more information.
When Tropical Cyclone Hellen was near the "peak of her career" NASA's TRMM satellite picked up on her popularity in terms of tropical rainfall. Hellen was a very heavy rainmaker in her heyday with heavy rain rates. Hellen weakened to a remnant low pressure area by April 1, but has ...
Low sodium levels pre-transplant does not affect liver transplant recipient survival
2014-04-01
Researchers report that low levels of sodium, known as hyponatremia, prior to transplantation does not increase the risk of death following liver transplant. Full findings are published in Liver Transplantation, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society.
Medical evidence shows that low sodium concentration is common in patients with end stage liver disease (ESLD), with roughly half of those with cirrhosis having sodium levels below the normal range of 135-145 mmol/L. Moreover, previous research ...