(Press-News.org) The patented work, published in Nature today, provides a deeper understanding of our first line of defence, and what happens when it goes wrong. It will lead to new ways of diagnosing and treating inflammatory bowel disease, peptic ulcers and even TB. It could also lead to novel protective vaccines.
The discovery is the result of national and international collaboration between the universities of Melbourne, Monash, Queensland and Cork. It also depended on access to major facilities including the Australian Synchrotron and the Bio21 Institute.
One of the leads in the research, University of Melbourne Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Research) Professor James McCluskey said it builds on work conducted last year that was acknowledged with an Australian Museum Eureka Prize in 2013.
"Our intestines, lungs and mouths are lined with mysterious immune cells that make up to ten per cent of the T cells in our immune system. Last year we showed that these cells act as sentinels against invading bacteria and fungi. Now we've identified the precise biochemical key that wakes up these sentries and sends them into action," he said.
The immune cells, known as mucosal-associated invariant T cells (MAITS), initiate the immune system's action against foreign invaders when they are exposed to vitamin B2, which is made by bacteria and fungi.
"MAIT cells are a discovery so recent that they have not even made it into the textbooks," Professor McCluskey says. "Most doctors know nothing about them. Yet they constitute about one cell in ten of the body's T cells and half of all the T cells in the liver.
"This is an excellent example of how our collaborative research in Australia can bring groups with expertise in different areas together to make significant advances," Professor McCluskey said.
Dr Alexandra Corbett, a lead author on the study from the University of Melbourne said the team had unlocked a secret that will enable further investigation in the role that MAIT cells play in health and disease.
Professor Jamie Rossjohn, one of the senior authors and NHMRC Australia Fellow of Monash University,also noted the close collaborations that resulted in these findings.
"To get from the first observation to today's discovery required not just smart people but access to Melbourne's Bio21 Institute platforms, dozens of visits to the Australian Synchrotron, and a global research network including our Irish colleagues who provided access to mutant bacterial strains."
"All that coming together allowed us to beat our international competitors and secure the patent," he said.
Prof David Fairlie of the Institute for Molecular Bioscience at the University of Queensland said the findings may be a valuable clue to disease pathways and new drug therapies.
INFORMATION:
The work is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council and the new ARC Centre of Excellence in Advanced Molecular Imaging,focusing on how immune proteins interact and affect immune responses.
Immune cell defenders protect us from bacteria invasion
2014-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Women entrepreneurs have limited chances to lead their new businesses
2014-04-03
Women who start new businesses with men have limited opportunities to move into leadership roles, according to sociologists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; and when they co-found a business with their husbands, they have even fewer chances to be in charge.
The study, published in the April issue of the American Sociological Review, comes on the heels of a recent debate about businesses with all-male boards of directors and adds to a growing body of knowledge that documents women's limited access to leadership roles in the business world.
"This work ...
Women do not apply to 'male-sounding' job postings
2014-04-03
This news release is available in German. "We don't have many women in management roles because we get so few good applicants." Companies can be heard lamenting this state of affairs with increasing frequency. Just an excuse? Scientists from the TUM have discovered something that actually does deter women from applying for a job, even if they are qualified: the wording of the job ads.
The scientists showed some 260 test subjects fictional employment ads. These included, for example, a place in a training program for potential management positions. If the advertisement ...
Forward Looks report available 'Media in Europe: New Questions for Research and Policy'
2014-04-03
A new report from the European Science Foundation, 'Media in Europe: New Questions for Research and Policy', examines the field of media studies and proposes an agenda for research for the next decade
From newspapers and radio to internet, mobile telephony and digital communications, the media have in recent decades become ever more central to people's activities in personal, professional and social life. In this period of rapid social and technological change, it can be difficult to separate what we really know about the media from our assumptions and feelings about ...
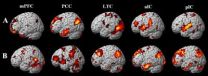
Resting-state functional connection during low back pain
2014-04-03
The default mode network is a key area in the resting state, involving the posterior cingulate cortex, precuneus, medial prefrontal and lateral temporal cortices, and is characterized by balanced positive and negative connections classified as the "hubs" of structural and functional connectivity in brain studies. Resting-state functional connectivity MRI is based on the observation that brain regions exhibit correlated slow fluctuations at rest, and has become a widely used tool for investigating spontaneous brain activity. Functional magnetic resonance imaging studies ...
Researcher: Chowing down on watermelon could lower blood pressure
2014-04-03
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Be sure to pick up a watermelon — or two — at your neighborhood farmers' market.
It could save your life.
A new study by Florida State University Associate Professor Arturo Figueroa, published in the American Journal of Hypertension, found that watermelon could significantly reduce blood pressure in overweight individuals both at rest and while under stress.
"The pressure on the aorta and on the heart decreased after consuming watermelon extract," Figueroa said.
The study started with a simple concept. More people die of heart attacks in cold ...
UCSB researchers create first regional Ocean Health Index
2014-04-03
With one of the world's longest coastlines, spanning 17 states, and very high marine and coastal biodiversity, Brazil owes much of its prosperity to the ocean. For that reason, Brazil was the site of the first Ocean Health Index regional assessment designed to evaluate the economic, social and ecological uses and benefits that people derive from the ocean. Brazil's overall score in the national study was 60 out of 100.
The findings from that study — conducted by researchers from UC Santa Barbara's National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS), the Department ...
Immune cell 'defenders' could beat invading bacteria
2014-04-03
An international team of scientists has identified the precise biochemical key that wakes up the body's immune cells and sends them into action against invading bacteria and fungi.
The patented work, published in Nature today, provides the starting point to understanding our first line of defence, and what happens when it goes wrong. It will lead to new ways of diagnosing and treating inflammatory bowel disease, peptic ulcers and even TB. It could also lead to new protective vaccines.
The discovery, the result of an international collaboration between Monash University ...
'Homo' is the only primate whose tooth size decreases as its brain size increases
2014-04-03
Andalusian researchers, led by the University of Granada, have discovered a curious characteristic of the members of the human lineage, classed as the genus Homo: they are the only primates where, throughout their 2.5-million year history, the size of their teeth has decreased alongside the increase in their brain size.
The key to this phenomenon, which scientists call "evolutionary paradox", could be in how Homo's diet has evolved. Digestion starts first in the mouth and, so, teeth are essential in breaking food down into smaller pieces. Therefore, the normal scenario ...
The feasibility of a crop should be investigated before it can be promoted for adoption by farmers
2014-04-03
NAIROBI, Kenya (2 April 2014) ----With rising food and energy costs, smallholder farmers are looking for alternative crops that can generate more income and provide a better livelihood; however, bringing in new crops without tried and tested evidence about its viability may be counter productive.
A study conducted in Kenya shows that crops should be promoted and adopted when farmers have knowledge about its cultivation and there is access to a reliable market.
In Kenya, Jathropha was promoted as a wonder crop that could improve farmer incomes and aid rural development, ...
When managers attack: Coaches who care about pundits' opinions worse at controlling anger
2014-04-03
The notoriously short fuses of some sports coaches could be explained by excessive concern with how they will be seen by others, according to new research.
A study by academics at the University of Leeds and Northumbria University found coaches who were more focused on their own high standards and less interested in the opinions of others were significantly better at controlling feelings of anger than those who were very focused on others' opinions of their performance.
Dr Andrew Hill, lecturer in sports and exercise science in the University of Leeds' Faculty of Biological ...