(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, April 3, 2014—Nearly 7% of Americans married between 2005-2012 met on social networking sites. How those couples compare to couples who met through other types of online meetings or the "old-fashioned" way in terms of age, race, frequency of Internet use, and other factors is explored in an article in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking website.
In "First Comes Social Networking, Then Comes Marriage? Characteristics of Americans Married 2005-2012 Who Met Through Social Networking Sites," Jeffrey Hall, PhD, University of Kansas, Lawrence, describes the characteristics that are more common among recently married individuals who met online via social networking sites (SNS).
"Facebook use grew dramatically during the 2005-2012 time period studied," says Brenda K. Wiederhold, PhD, MBA, BCB, BCN, Editor-in-Chief of Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, from the Interactive Media Institute, San Diego, CA. "It will be useful to continue to observe how these trends change as various groups of individuals become more frequent users of SNS," says Dr. Wiederhold.
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking is a peer-reviewed journal published monthly online with Open Access options and in print that explores the psychological and social issues surrounding the Internet and interactive technologies, plus cybertherapy and rehabilitation. Complete tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Games for Health Journal, Telemedicine and e-Health, and Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
Which couples who meet on social networking sites are most likely to marry?
2014-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sage grouse losing habitat to fire as endangered species decision looms
2014-04-03
As fires sweep more frequently across the American Great Basin, the US Bureau of Land Management (BLM) has been tasked with reseeding the burned landscapes to stabilize soils. BLM's interventions have not helped to restore habitat for the greater sage grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus) reported scientists from the US Geological Survey (USGS) and US Forest Service in the Ecological Society of America's journal Ecosphere last week, but outlier project sites with good grouse habitat may yield clues to successful management scenarios.
Their report arrives in the shadow of ...
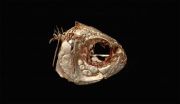
Examination of a cave-dwelling fish finds a possible genetic link to human disorders
2014-04-03
Researchers have identified a genetic association with facial asymmetry in an ancient cavefish, a natural trait that may solve mysteries surrounding facial asymmetries in humans – conditions such as cleft palate or hemifacial microsomia. This exciting discovery by Joshua Gross, a University of Cincinnati assistant professor for the Department of Biological Sciences; and doctoral students Amanda Krutzler and Brian Carlson, is published in the research journal, Genetics.
The researchers are studying the craniofacial features of the eyeless, cave-dwelling fish, Astyanax ...
Synergy of high protein intake and exercise in youth enhances bone structure and strength
2014-04-03
A study presented during the World Congress on Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases in Seville shows that high levels of protein intake (HProt) enhance the positive impact of high physical activity (HPA) on bone structure and strength in healthy pre-pubertal boys.
Researchers from the University of Geneva in Switzerland and Eindhoven University in the Netherlands tracked 176 healthy pre-pubertal boys (average age 7.4 years) to mid-adolescence (average age 15.2 years). Compared to moderate protein intake, HProt in combination with HPA was associated ...
Adults' tonsillectomy complications are higher than previously thought
2014-04-03
Twenty percent of adults who have tonsillectomies will have a complication, which is significantly higher than previously shown, according to a team of researchers. The team also found that these complications substantially increase health care expenditures.
"Since 1973, John Wenneberg and his colleagues at Dartmouth have been examining variation in the rates of tonsillectomy performed across regions, trying to explain why such wide variation is observed," said Dennis Scanlon, professor of health policy and administration, Penn State. "In other words, why are some patients ...
Report documents cardiopulmonary arrest in premature infant after cyclomydril eyedrops
2014-04-03
San Francisco, CA, April 2, 2014 – Eyedrops administered to infants as part of routine outpatient retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) screening can have life-threatening consequences. A case report published in the current issue of the Journal of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) describes cardiopulmonary arrest in a 27-week-old infant following administration of three sets of cyclopentolate 0.2%/phenylephrine 1% (Cyclomydril) eyedrops.
"Cardiopulmonary arrest can occur from just instillation of eyedrops in a premature infant seen ...
Drawing conclusions
2014-04-03
Is a picture worth only a thousand words? According to Dr. Carmit Katz of Tel Aviv University's Bob Shapell School of Social Work, illustrations by children can be a critical tool in forensic investigations of child abuse.
Dr. Katz's study, published in Child Abuse and Neglect, compared the results when child abuse victims were offered the opportunity to draw during questioning with victims not offered this opportunity. Her findings saw a significant difference, suggesting a therapeutic value and indicating that children empowered to draw pictures about their abuse provided ...
Radium-223 dichloride in prostate cancer: Major added benefit for certain patients
2014-04-03
Radium-223 dichloride (radium-223 for short, trade name: Xofigo) has been approved since November 2013 for men with advanced prostate cancer, in whom hormone blockade is no longer effective, and symptomatic bone metastases, but without visceral metastases. In an early benefit assessment pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG), the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined whether this new drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy specified by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA).
No ...
Nanoparticles cause cancer cells to self-destruct
2014-04-03
Using magnetically controlled nanoparticles to force tumour cells to 'self-destruct' sounds like science fiction, but could be a future part of cancer treatment, according to research from Lund University in Sweden.
Watch video:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vos0QW2Yclk&feature=youtu.be
"The clever thing about the technique is that we can target selected cells without harming surrounding tissue. There are many ways to kill cells, but this method is contained and remote-controlled", said Professor Erik Renström.
The point of the new technique is that it is much more ...
Tiny power generator runs on spit
2014-04-03
Saliva-powered micro-sized microbial fuel cells can produce minute amounts of energy sufficient to run on-chip applications, according to an international team of engineers.
Bruce E. Logan, Evan Pugh Professor and Kappe Professor of Environmental Engineering, Penn State, credited the idea to fellow researcher Justine E. Mink. "The idea was Justine's because she was thinking about sensors for such things as glucose monitoring for diabetics and she wondered if a mini microbial fuel cell could be used," Logan said. "There is a lot of organic stuff in saliva."
Microbial ...
Attracting wild bees to farms is a good insurance policy
2014-04-03
EAST LANSING, Mich. -- Investing in habitat that attracts and supports wild bees in farms is not only an effective approach to helping enhance crop pollination, but it can also pay for itself in four years or less, according to Michigan State University research.
The paper, published in the current issue of the Journal of Applied Ecology, gives farmers of pollination-dependent crops tangible results to convert marginal acreage to fields of wildflowers, said Rufus Isaacs, MSU entomologist and co-author of the paper.
"Other studies have demonstrated that creating flowering ...