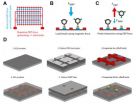
Tiny power generator runs on spit
2014-04-03
(Press-News.org) Saliva-powered micro-sized microbial fuel cells can produce minute amounts of energy sufficient to run on-chip applications, according to an international team of engineers.
Bruce E. Logan, Evan Pugh Professor and Kappe Professor of Environmental Engineering, Penn State, credited the idea to fellow researcher Justine E. Mink. "The idea was Justine's because she was thinking about sensors for such things as glucose monitoring for diabetics and she wondered if a mini microbial fuel cell could be used," Logan said. "There is a lot of organic stuff in saliva."
Microbial fuel cells create energy when bacteria break down organic material producing a charge that is transferred to the anode. Logan, who has studied microbial fuel cells for more than ten years, usually looks to wastewater as a source for both the organic material and the bacteria to create either electricity or hydrogen, but these tiny machines are a bit different.
"By producing nearly 1 microwatt in power, this saliva-powered, micro-sized MFC already generates enough power to be directly used as an energy harvester in microelectronic applications," the researchers report in a recent issue of Nature Publishing Group's Asia Materials.
The researchers believe that the emergence of ultra-low-power chip-level biomedical electronics, devices able to operate at sub-microwatt power outputs, is becoming a reality. One possible application would be a tiny ovulation predictor based on the conductivity of a woman's saliva, which changes five days before ovulation. The device would measure the conductivity of the saliva and then use the saliva for power to send the reading to a nearby cell phone.
Biomedical devices using micro-sized microbial fuel cells would be portable and have their energy source available anywhere. However, saliva does not have the type of bacteria necessary for the fuel cells, and manufacturers would need to inoculate the devices with bacteria from the natural environment.
In the past, the smallest fuel cells have been two-chambered, but this micro version uses a single chamber with a graphene- rather than platinum-coated carbon cloth anode and an air cathode. Air cathodes have not been used before because if oxygen can get to the bacteria, they can breath oxygen and do not produce electricity.
"We have previously avoided using air cathodes in these systems to avoid oxygen contamination with closely spaced electrodes," said Logan. "However, these micro cells operate at micron distances between the electrodes. We don't fully understand why, but bottom line, they worked."
The anode is actually composed of carbon nanomaterial graphene. Other microbial fuel cells used graphene oxide, but the researchers showed that pure multi-layered graphene can serve as a suitable anode material.
While the researchers tested this mini microbial fuel cell using acetate and human saliva, it can use any liquid with sufficient organic material.
INFORMATION:
Justine E. Mink, recent Ph.D. recipient, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, was first author of this paper. Also working on this project were Muhammad M. Hussain, assistant professor, and Ramy M. Qaisi, graduate student, KAUST.
KAUST supported this work.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Attracting wild bees to farms is a good insurance policy
2014-04-03
EAST LANSING, Mich. -- Investing in habitat that attracts and supports wild bees in farms is not only an effective approach to helping enhance crop pollination, but it can also pay for itself in four years or less, according to Michigan State University research.
The paper, published in the current issue of the Journal of Applied Ecology, gives farmers of pollination-dependent crops tangible results to convert marginal acreage to fields of wildflowers, said Rufus Isaacs, MSU entomologist and co-author of the paper.
"Other studies have demonstrated that creating flowering ...
Pulmonary hypertension deaths have increased over past decade according to CDC report in CHEST
2014-04-03
Deaths from pulmonary hypertension have increased over the past decade, according to a study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
In the study, published online in CHEST, researchers analyzed death rates from the National Vital Statistics System and data from the National Hospital Discharge Survey between 2001 and 2010 to analyze trends in hospitalizations and death rates related to pulmonary hypertension.
Pulmonary hypertension is characterized by increased blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, causing the right side of the heart to work ...
Tiny biomolecular tweezers studying force effect of cells
2014-04-03
A new type of biomolecular tweezers could help researchers study how mechanical forces affect the biochemical activity of cells and proteins. The devices — too small to see without a microscope — use opposing magnetic and electrophoretic forces to precisely stretch the cells and molecules, holding them in position so that the activity of receptors and other biochemical activity can be studied. Arrays of the tweezers could be combined to study multiple molecules and cells simultaneously, providing a high throughput capability for assessing the effects of mechanical forces ...
Enhancing the immune response through next generation polymeric vaccine adjuvants
2014-04-03
The great success of vaccines over the past two centuries as a preventive medicine has led to a significant reduction in morbidity and death caused by controllable infectious diseases. The effectiveness of vaccines is dependent on their ability to induce a protective immune response in recipients. Adjuvants, such as aluminum salts, have been integrated into vaccines for more than 70 years to augment the body's immune response to patho-gens. Adjuvants are especially necessary to boost the immune response for subunit vac-cines. However, conventional adjuvants are limited ...
Diffeomorphometry and geodesic positioning systems for human anatomy
2014-04-03
A team of researchers from the Center for Imaging Science at the Johns Hopkins University and the CMLA of the École Normale Supérieure Cachan have demonstrated new algorithmic technologies for the parametric representation of human shape and form. Coupled with advanced imaging technologies, this presents opportunities for tracking soft-tissue deformations associated with cardiovascular studies, radiation treatment planning in Oncology, and neurodegenerative brain illnesses. The software algorithms provide tools for basic science and pre-clinical investigations for synchronizing ...
Structural insights into the inner workings of a viral nanomachine
2014-04-03
Researchers at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute (VTCRI) are using new nanoscale imaging approaches to shed light on the dynamic activities of rotaviruses, important pathogens that cause life-threatening diarrhea in young children. Once a rotavirus enters a host cell, it sheds its outermost protein layer, leaving behind a double-layered particle (DLP). These DLPs are the form of the virus that produces messenger RNA molecules, which are critical for launching the infection.
Researchers, Deborah Kelly, Ph.D. and Sarah McDonald, Ph.D., both Assistant Professors ...
A pocket-size ultrasonic nebulizer employing a novel nozzle improves inhalers
2014-04-03
Inhalation is an increasingly important route for non-invasive drug delivery for both systemic and local applications. Control of particle size and output plays a critical role in the efficient and effective delivery of oft en expensive medications to the lung. Drugs designed to treat pulmonary diseases or for systemic absorption through the alveolar capillary bed require optimum particle sizes (1 to 6 μm) for effective delivery.
A team of researchers from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of California, Irvine has realized ...
An ethics framework should be used to decide health standards for extended, exploratory spaceflights
2014-04-03
WASHINGTON – NASA should use an ethics framework when deciding whether, and under what conditions, spaceflights that venture outside low Earth orbit or extend beyond 30 days are acceptable if they do not meet current health standards, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine, the health arm of the National Academy of Sciences. Exceptions to existing health standards should be granted by NASA on a mission-by-mission basis, and any exceptions should be rare and occur only in extenuating circumstances. The report provides an ethics framework based on six principles ...
Research studies highlight advantages and potential of computer-guided spinal surgery
2014-04-03
LOS ANGELES (April 3, 2014) – In a series of research studies, Cedars-Sinai spinal surgeons show that a new method of computer-guided spine surgery is beneficial for spinal reconstruction and for treating complex tumors and degenerative spine problems, resulting in fewer complications and better outcomes for patients.
The Cedars-Sinai surgeons highlight the advantages of a "spinal navigation" technique that uses high-speed computerized tomography (CT) imaging to navigate in and around the spinal column from different angles. They present their findings in six articles ...
Between accident and real harm in child injuries
2014-04-03
Child abuse is a leading cause of fatality in children 0-4 years of age. Roughly 1,500 children are fatally injured each year in association with child abuse and 150,000 are permanently disabled. Many serious injuries and fatalities could be prevented if it was possible to distinguish between injuries associated with abuse and those caused by accidents. Clinicians, child protective services and law enforcement personnel should be equipped with improved knowledge related to the types of injuries that are possible from common household accidents that are often falsely reported ...