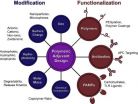
(Press-News.org) The great success of vaccines over the past two centuries as a preventive medicine has led to a significant reduction in morbidity and death caused by controllable infectious diseases. The effectiveness of vaccines is dependent on their ability to induce a protective immune response in recipients. Adjuvants, such as aluminum salts, have been integrated into vaccines for more than 70 years to augment the body's immune response to patho-gens. Adjuvants are especially necessary to boost the immune response for subunit vac-cines. However, conventional adjuvants are limited by their toxicity and limited cellular immune responses. Polymeric adjuvants in the form of nanoparticles, matrices or micelles have the ability to prompt strong adaptive immune responses without sacrificing biocompatibility.
This review article appearing in Technology and submitted by researchers from Iowa State University investigates the potential of polymeric adjuvants, both natural and synthetic. In addition to a comprehensive study of their use in vaccines, this article sum-marizes the benefits and challenges associated with the use of these polymer systems as adjuvants.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported funding from the U.S. Army (Grant #W81XWH-10-1-0806). Corresponding author for this study in TECHNOLOGY is Surya Mallapragada, suryakm@iastate.edu
For the paper, please visit http://www.worldscientific.com/doi/pdf/10.1142/S2339547814300017
About TECHNOLOGY
Fashioned as a high-impact, high-visibility, top-echelon publication, this new ground-breaking journal - TECHNOLOGY - will feature the development of cutting-edge new technologies in a broad array of emerging fields of science and engineering. The content will have an applied science and technological slant with a focus on both innovation and application to daily lives. It will cover diverse disciplines such as health and life science, energy and environment, advanced materials, technology-based manufacturing, information science and technology, and marine and transportations technologies.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research and professional communities. The company publishes about 500 books annually and more than 120 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organisations like the Nobel Foundation, US National Academies Press, as well as its subsidiary, the Imperial College Press, amongst others, to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.worldscientific.com.
Enhancing the immune response through next generation polymeric vaccine adjuvants
2014-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diffeomorphometry and geodesic positioning systems for human anatomy
2014-04-03
A team of researchers from the Center for Imaging Science at the Johns Hopkins University and the CMLA of the École Normale Supérieure Cachan have demonstrated new algorithmic technologies for the parametric representation of human shape and form. Coupled with advanced imaging technologies, this presents opportunities for tracking soft-tissue deformations associated with cardiovascular studies, radiation treatment planning in Oncology, and neurodegenerative brain illnesses. The software algorithms provide tools for basic science and pre-clinical investigations for synchronizing ...
Structural insights into the inner workings of a viral nanomachine
2014-04-03
Researchers at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute (VTCRI) are using new nanoscale imaging approaches to shed light on the dynamic activities of rotaviruses, important pathogens that cause life-threatening diarrhea in young children. Once a rotavirus enters a host cell, it sheds its outermost protein layer, leaving behind a double-layered particle (DLP). These DLPs are the form of the virus that produces messenger RNA molecules, which are critical for launching the infection.
Researchers, Deborah Kelly, Ph.D. and Sarah McDonald, Ph.D., both Assistant Professors ...
A pocket-size ultrasonic nebulizer employing a novel nozzle improves inhalers
2014-04-03
Inhalation is an increasingly important route for non-invasive drug delivery for both systemic and local applications. Control of particle size and output plays a critical role in the efficient and effective delivery of oft en expensive medications to the lung. Drugs designed to treat pulmonary diseases or for systemic absorption through the alveolar capillary bed require optimum particle sizes (1 to 6 μm) for effective delivery.
A team of researchers from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of California, Irvine has realized ...
An ethics framework should be used to decide health standards for extended, exploratory spaceflights
2014-04-03
WASHINGTON – NASA should use an ethics framework when deciding whether, and under what conditions, spaceflights that venture outside low Earth orbit or extend beyond 30 days are acceptable if they do not meet current health standards, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine, the health arm of the National Academy of Sciences. Exceptions to existing health standards should be granted by NASA on a mission-by-mission basis, and any exceptions should be rare and occur only in extenuating circumstances. The report provides an ethics framework based on six principles ...
Research studies highlight advantages and potential of computer-guided spinal surgery
2014-04-03
LOS ANGELES (April 3, 2014) – In a series of research studies, Cedars-Sinai spinal surgeons show that a new method of computer-guided spine surgery is beneficial for spinal reconstruction and for treating complex tumors and degenerative spine problems, resulting in fewer complications and better outcomes for patients.
The Cedars-Sinai surgeons highlight the advantages of a "spinal navigation" technique that uses high-speed computerized tomography (CT) imaging to navigate in and around the spinal column from different angles. They present their findings in six articles ...
Between accident and real harm in child injuries
2014-04-03
Child abuse is a leading cause of fatality in children 0-4 years of age. Roughly 1,500 children are fatally injured each year in association with child abuse and 150,000 are permanently disabled. Many serious injuries and fatalities could be prevented if it was possible to distinguish between injuries associated with abuse and those caused by accidents. Clinicians, child protective services and law enforcement personnel should be equipped with improved knowledge related to the types of injuries that are possible from common household accidents that are often falsely reported ...
Scientists emphasize metabolites' role in understanding disease
2014-04-03
TUSCALOOSA, Ala. — Overreliance on genetic-centered approaches in predicting, diagnosing and treating disease will lead to few future scientific breakthroughs, cautioned a University of Alabama researcher who co-authored an article in an early online issue of Genetics that advocates for a greater emphasis on the body's metabolites in understanding illnesses.
"To augment the value of genetic data, the scientific community needs to add additional information from things like metabolomics – the analysis of metabolites within an organism," said Dr. Laura Reed, a University ...
How electrodes charge and discharge
2014-04-03
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- The electrochemical reactions inside the porous electrodes of batteries and fuel cells have been described by theorists, but never measured directly. Now, a team at MIT has figured out a way to measure the fundamental charge transfer rate — finding some significant surprises.
The study found that the Butler-Volmer (BV) equation, usually used to describe reaction rates in electrodes, is inaccurate, especially at higher voltage levels. Instead, a different approach, called Marcus-Hush-Chidsey charge-transfer theory, provides more realistic results — revealing ...
An ultrathin collagen matrix biomaterial tool for 3D microtissue engineering
2014-04-03
A novel ultrathin collagen matrix assembly allows for the unprecedented maintenance of liver cell morphology and function in a microscale "organ-on-a-chip" device that is one example of 3D microtissue engineering.
A team of researchers from the Center for Engineering in Medicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital have demonstrated a new nanoscale matrix biomaterial assembly that can maintain liver cell morphology and function in microfluidic devices for longer times than has been previously been reported in microfluidic devices. This technology allows researchers to ...
Immune cell defenders protect us from bacteria invasion
2014-04-03
The patented work, published in Nature today, provides a deeper understanding of our first line of defence, and what happens when it goes wrong. It will lead to new ways of diagnosing and treating inflammatory bowel disease, peptic ulcers and even TB. It could also lead to novel protective vaccines.
The discovery is the result of national and international collaboration between the universities of Melbourne, Monash, Queensland and Cork. It also depended on access to major facilities including the Australian Synchrotron and the Bio21 Institute.
One of the leads in the ...