(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, April 3, 2014–In many recent incidents of premeditated mass shooting the perpetrators have been male and dressed in black, and may share other characteristics that could be used to identify potential shooters before they commit acts of mass violence. Risk factors related to the antihero, dark-knight persona adopted by these individuals are explored in an article in Violence and Gender, a new peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Violence and Gender website at http://www.liebertpub.com/vio.
In the article "Costuming, Misogyny, and Objectification as Risk Factors in Targeted Violence," Brian Van Brunt, EdD and W. Scott Lewis, The NCHERM Group, LLC (Malvern, PA), suggest reasons why persons who commit mass shootings are drawn to dark popular culture imagery, how these cultural factors may contribute to the violence, and what risk factors could be useful to law enforcement and behavioral investigation teams seeking to identify individuals who might be preparing for an attack.
"'Objectification' of victims and 'costuming' are specific offender behaviors that will give threat assessment teams throughout the world greater insights into the motivation of mass shooters and just how ceremonial their preparations are," says Mary Ellen O'Toole, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of Violence and Gender and Senior FBI Profiler/Criminal Investigative Analyst (ret.). "The value of this information in being able to identify these offenders beforehand based on their behavior so that we can prevent future acts of mass murder is very significant."
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Violence and Gender is the only peer-reviewed journal focusing on the understanding, prediction, and prevention of acts of violence. Through research papers, roundtable discussions, case studies, and other original content, the Journal critically examines biological, genetic, behavioral, psychological, racial, ethnic, and cultural factors as they relate to the gender of perpetrators of violence. Led by Editor-in-Chief Mary Ellen O'Toole, PhD, Forensic Behavioral Consultant and Senior FBI Profiler/Criminal Investigative Analyst (ret.), Violence and Gender explores the difficult issues that are vital to threat assessment and prevention of the epidemic of violence. Violence and Gender is published quarterly online with Open Access options and in print, and is the official journal of The Avielle Foundation.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking and Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website at http://www.liebertpub.com.
Dress and behavior of mass shooters as factors to predict and prevent future attacks
2014-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ouch! Computer system spots fake expressions of pain better than people
2014-04-03
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A joint study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, the University at Buffalo, and the University of Toronto has found that a computer–vision system can distinguish between real or faked expressions of pain more accurately than can humans.
This ability has obvious uses for uncovering pain malingering — fabricating or exaggerating the symptoms of pain for a variety of motives — but the system also could be used to detect deceptive actions in the realms of security, psychopathology, job screening, medicine and law.
The study, "Automatic ...
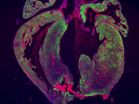
New study casts doubt on heart regeneration in mammals
2014-04-03
The mammalian heart has generally been considered to lack the ability to repair itself after injury, but a 2011 study in newborn mice challenged this view, providing evidence for complete regeneration after resection of 10% of the apex, the lowest part of the heart. In a study published by Cell Press in Stem Cell Reports on April 3, 2014, researchers attempted to replicate these recent findings but failed to uncover any evidence of complete heart regeneration in newborn mice that underwent apex resection.
"Our results question the usefulness of the apex resection model ...
Hummingbirds' 22-million-year-old history of remarkable change is far from complete
2014-04-03
The first comprehensive map of hummingbirds' 22-million-year-old family tree—reconstructed based on careful analysis of 284 of the world's 338 known species—tells a story of rapid and ongoing diversification. The decade-long study reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on April 3 also helps to explain how today's hummingbirds came to live where they do.
Part of the secret to the birds' remarkable success lies in the formation of nine principal groups or clades, hummingbirds' unique relationship to flowering plants, and the birds' continued spread into new ...
Lactase persistence alleles reveal ancestry of southern African Khoe pastoralists
2014-04-03
In a new study a team of researchers lead from Uppsala University show how lactase persistence variants tell the story about the ancestry of the Khoe people in southern Africa. The team concludes that pastoralist practices were brought to southern Africa by a small group of migrants from eastern Africa. The study is published in Current Biology today.
"This is really an exciting time for African genetics. Up until now, routes of human migration in Africa were inferred mostly based on linguistics and archaeology, now we can use genetics to test these hypotheses." says ...
Cancer and the Goldilocks effect
2014-04-03
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have found that too little or too much of an enzyme called SRPK1 promotes cancer by disrupting a regulatory event critical for many fundamental cellular processes, including proliferation.
The findings are published in the current online issue of Molecular Cell.
The family of SRPK kinases was first discovered by Xiang-Dong Fu, PhD, professor in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at UC San Diego in 1994. In 2012, Fu and colleagues uncovered that SPRK1 was a key signal transducer ...
Study helps unravel the tangled origin of ALS
2014-04-03
MADISON, Wis. — By studying nerve cells that originated in patients with a severe neurological disease, a University of Wisconsin-Madison researcher has pinpointed an error in protein formation that could be the root of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Also called Lou Gehrig's disease, ALS causes paralysis and death. According to the ALS Association, as many as 30,000 Americans are living with ALS.
After a genetic mutation was discovered in a small group of ALS patients, scientists transferred that gene to animals and began to search for drugs that might treat those ...
Patient stem cells help identify common problem in ALS
2014-04-03
Harvard stem cell scientists have discovered that a recently approved medication for epilepsy may possibly be a meaningful treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)—Lou Gehrig's disease, a uniformly fatal neurodegenerative disorder. The researchers are now collaborating with Massachusetts General Hospital to design an initial clinical trial testing the safety of the treatment in ALS patients.
The investigators all caution that a great deal needs to be done to assure the safety and efficacy of the treatment in ALS patients, before physicians should start offering ...
Tumor suppressor gene TP53 mutated in 90 percent of most common childhood bone tumor
2014-04-03
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – April 3, 2014) – The St. Jude Children's Research Hospital—Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project found mutations in the tumor suppressor gene TP53 in 90 percent of osteosarcomas, suggesting the alteration plays a key role early in development of the bone cancer. The research was published today online ahead of print in the journal Cell Reports.
The discovery that TP53 is altered in nearly every osteosarcoma also helps to explain a long-standing paradox in osteosarcoma treatment, which is why at standard doses radiation therapy is largely ...
ER doctors commonly miss more strokes among women, minorities and younger patients
2014-04-03
Analyzing federal health care data, a team of researchers led by a Johns Hopkins specialist concluded that doctors overlook or discount the early signs of potentially disabling strokes in tens of thousands of American each year, a large number of them visitors to emergency rooms complaining of dizziness or headaches.
The findings from the medical records review, reported online April 3 in the journal Diagnosis, show that women, minorities and people under the age of 45 who have these symptoms of stroke were significantly more likely to be misdiagnosed in the week prior ...
Jamming a protein signal forces cancer cells to devour themselves
2014-04-03
HOUSTON -- Under stress from chemotherapy or radiation, some cancer cells dodge death by consuming a bit of themselves, allowing them to essentially sleep through treatment and later awaken as tougher, resistant disease.
Interfering with a single cancer-promoting protein and its receptor can turn this resistance mechanism into lethal, runaway self-cannibalization, researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report in the journal Cell Reports.
"Prolactin is a potent growth factor for many types of cancers, including ovarian cancer," said senior author ...