Antioxidants can protect against omega 6 damage -- or promote it
2014-04-04
(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO — Given omega 6 fatty acid's reputation for promoting cancer — at least in animal studies — researchers are examining the role that antioxidants play in blocking the harmful effects of this culprit, found in many cooking oils. After all, antioxidants are supposed to prevent DNA damage. But employing antioxidants could backfire, say researchers at Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center.
In their study, being reported at the AACR Annual Meeting 2015, researchers found that vitamin E actually increased specific damage linked to omega 6 fatty acids. The vitamin promoted the formation of an "adduct," a structure that links a chemical to DNA, and which may cause mutations.
On the other hand, in the setting of omega 6, the antioxidant green tea polyphenol reduced formation of another commonly found "adduct" from omega-6 fatty acid — suggesting it may have beneficial health effects.
The third antioxidant tested, alpha-lipoic acid — found in spinach and broccoli and proven to have anti-cancer properties — had no effect on either of the two adducts studied.
The study was designed to understand why omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote liver cancer, while their cousin, omega 3, helps prevent cancer.
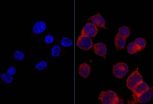
Researchers examined formation of DNA-damaging adducts in liver cells treated with omega 6. One of those adducts, ϒ-OHPdG, is well known, but the research team discovered a second one — DHHedA.
"This study revealed that DHHedA is a novel type of DNA damage, found in the tissues of rodents and humans, that is caused by omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acid," says the study's lead author, Fung-Lung Chung, PhD, a professor of oncology at Georgetown Lombardi and professor of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University Medical Center.
In rats engineered to develop liver cancer, green tea polyphenols reduced formation of ϒ-OHPdG adducts, and vitamin E increased production of DHHedA adducts.
Researchers also discovered that although alpha-lipoic acid had no effect on either adduct, rats who ate the antioxidant had a significantly longer lifespan, compared with rats treated with the other antioxidants. "The precise reason why this happened is not yet known," says Chung.
"Our findings are beginning to shed light on why omega 6 fatty acids are believed to have negative health effects," Chung says, "but we have a long way to go before we can make definitive health claims on these antioxidants."
He added, "Not all antioxidants are created equal. They all have different properties, and they play different roles in various tissues. What we find in liver cancer may not hold true for other cancers."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute (ROI-CA-134892).
About Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer CenterGeorgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of Georgetown University Medical Center and MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, seeks to improve the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cancer through innovative basic and clinical research, patient care, community education and outreach, and the training of cancer specialists of the future. Georgetown Lombardi is one of only 41 comprehensive cancer centers in the nation, as designated by the National Cancer Institute (grant #P30 CA051008), and the only one in the Washington, DC area. For more information, go to http://lombardi.georgetown.edu.
About Georgetown University Medical Center
Georgetown University Medical Center is an internationally recognized academic medical center with a three-part mission of research, teaching and patient care (through MedStar Health). GUMC's mission is carried out with a strong emphasis on public service and a dedication to the Catholic, Jesuit principle of cura personalis – or "care of the whole person." The Medical Center includes the School of Medicine and the School of Nursing & Health Studies, both nationally ranked; Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, designated as a comprehensive cancer center by the National Cancer Institute; and the Biomedical Graduate Research Organization (BGRO), which accounts for the majority of externally funded research at GUMC including a Clinical and Translational Science Award from the National Institutes of Health. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Light-activated neurons from stem cells restore function to paralyzed muscles
2014-04-04
A new way to artificially control muscles using light, with the potential to restore function to muscles paralysed by conditions such as motor neuron disease and spinal cord injury, has been developed by scientists at UCL and King's College London.
The technique involves transplanting specially-designed motor neurons created from stem cells into injured nerve branches. These motor neurons are designed to react to pulses of blue light, allowing scientists to fine-tune muscle control by adjusting the intensity, duration and frequency of the light pulses.
In the study, ...
UN climate report: Pricing of CO2 emissions critical
2014-04-04
Despite climate change, most polluters still pay little or nothing when they release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
'A cost USD 0.15 per kilo CO2 would be enough to solve the whole climate change problem,' says Thomas Sterner, professor of environmental economics at the University of Gothenburg. Sterner is the only Swedish researcher to serve as a coordinating lead author of a new report that the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change will present next week.
The third part of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's fifth assessment report, Working Group ...
Flipping the switch on scleroderma
2014-04-04
Scleroderma is a rare and often fatal disease, causing the thickening of tissue, that currently lacks a cure and any effective treatments. A group of researchers, including a Michigan State University professor, is looking to change that.
"Our findings provide a new approach to developing better treatment options where few have existed," said Richard Neubig, chairperson of the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology in MSU's College of Osteopathic Medicine.
Neubig, along with several of his colleagues from the University of Michigan, have identified the core signaling ...
NASA sees Tropical Depression 05W's bulk west of center
2014-04-04
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Depression 05W on April 4 at 07:09 UTC/3:09 a.m. EDT. The VIIRS instrument captured a visible picture of the storm, revealing most of the clouds and thunderstorms were west of the center.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC noted that animated multispectral satellite imagery today, April 3, showed that the low-level circulation center is well-defined and that there is fragmented convective banding of thunderstorms wrapping from the north into the southwest, so most of the strongest convection and thunderstorms ...
Researchers probe the next generation of 2-D materials
2014-04-04
As the properties and applications of graphene continue to be explored in laboratories all over the world, a growing number of researchers are looking beyond the one-atom-thick layer of carbon for alternative materials that exhibit similarly captivating properties.
One of these materials is molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), which is part of a wider group of materials known as transition metal dichalcogenides, and has been put forward by a group of researchers in the US as a potential building block for the next generation of low-cost electrical devices.
Due to its impressive ...
Discovery of a mechanism that makes tumor cells sugar addicted
2014-04-04
For almost a hundred years ago is known that cancer cells feel a special appetite for a type of sugar called glucose. The tumor uses this molecule is like the gasoline which depends a sports car to burn faster and grows and multiplies rapidly. It is a little cash process from the energy point of view but allows a superaccelerated cancer cell division. It is what is known as the Warburg effect, which was described in 1927.
Until now little was known about how healthy cells that have a balanced energy consumption depend on this "fast food" calorie in the tumor cell. Today, ...
Vascular changes caused by deep brain stimulation using brain MRI
2014-04-04
Deep brain stimulation has been widely used to treat patients with movement disorders and increasing attention has been paid to its use in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. However, the influence of subthalamic nucleus or pallidal deep brain stimulation on cerebral vasculature is poorly understood. Even though the metabolic changes caused by deep brain stimulation are being studied using positron emission tomography, the structural changes in cerebral areas like the intracerebral vasculature have not yet been evaluated. Dr. Byeong Sam Choi and colleagues ...
Clinical value of ginsenoside Rb1 against neuronal damage following cerebral ischemia
2014-04-04
Activated microglia-mediated inflammation promotes neuronal damage under cerebral hypoxic-ischemic conditions, so it is likely that inhibiting hypoxia-induced activation of microglia will alleviate neuronal damage. To test this hypothesis, Dr. Lining Ke and co-workers from Southern Medical University and Fujian Medical University in China co-cultured ginsenoside Rb1, an active component of ginseng, and cortical neurons. Their findings indicate that ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates damage to cerebral cortex neurons by downregulation of nitric oxide, superoxide, and tumor necrosis ...
Depression increases heart failure risk by 40 percent
2014-04-04
Stavanger, Norway – 4 April 2014: Moderate to severe depression increases the risk of heart failure by 40%, a study of nearly 63 000 Norwegians has shown. The findings were presented for the first time today at EuroHeartCare 2014.
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). This year's meeting is organised jointly with the Norwegian Society of Cardiovascular Nurses and is held 4-5 April in Stavanger, Norway.
Ms Lise Tuset Gustad, first author of the ...
Tracking sperm whales' ecology through stomach contents
2014-04-04
AMHERST, Mass. – In the largest regional study of its type to date, marine ecologist Michelle Staudinger and colleagues offer better understanding of the feeding ecologies of two very rare sperm whale species in waters off the southeast U.S. coast, adding baseline data they say are important as climate change, fishing and pollution alters the animals' environment and food sources.
"Understanding what resources support populations of these incredibly rare animals is important to conservation," Staudinger, adjunct assistant professor in environmental conservation at the ...