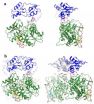
(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- University of Michigan researchers have solved the structure of a protein that is integral to processes responsible for maintaining a healthy heart and nervous system.
The protein structure in question is cystathionine beta-synthase, known as CBS. CBS uses vitamin B6 to make hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gaseous signaling molecule that helps maintain a healthy heart and nervous system. H2S also induces a state of suspended animation or hibernation in animals by decreasing body temperature and lowering metabolic rate.
The work to decode the structure was led by Ruma Banerjee, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Biological Chemistry at the U-M Medical Schoool, Janet Smith, Ph.D., a research professor at the U-M Life Sciences Institute, and their colleagues. Their findings are published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"The structure of full-length CBS, which has eluded the science community for more than a decade, provides a wealth of new information about gas generation by CBS, which is especially important in the brain," says Banerjee, the study's senior author and the Vincent Massey Collegiate Professor of Biological Chemistry and associate chair of biological chemistry . "It also provides a framework for understanding homocystinuria-causing mutations."
Mutations in the gene for CBS cause homocystinuria, an inherited disorder that affects the central nervous system, ocular, skeletal, and cardiovascular systems.
The structure of the full-length CBS, seen here for the first time, provides a molecular explanation for homocystinuria due to CBS defects.
The activity of CBS is increased by SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine), a dietary supplement that is used for its anti-depressant and anti-inflammatory activities. SAMe also increases production of H2S by binding to CBS.
"Molecular insights into the architecture of the CBS domain to which SAMe binds open doors to rational drug design for fine-tuning H2S production for pharmaceutical purposes," says colleague Markos Koutmos, Ph.D., a research investigator in Smith's research group .
"We captured the CBS enzyme at two points in its complex chemical reaction by trapping two highly reactive chemical intermediates in the active site of the enzyme," says researcher Omer Kabil, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Banerjee's lab. The structures of these trapped species reveal details of how vitamin B6 helps CBS perform the complex chemical reactions leading to H2S production.
"The important chemical details we see in CBS can be applied to understanding the other human enzymes that depend on vitamin B6, of which there are more than 50," says Smith, who in addition to her LSI position is also the Martha L. Ludwig Professor of Protein Structure & Function in the Department of Biological Chemistry of the Medical School.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
Structure of a protein related to heart and nervous system health revealed
May lead to smarter drug design, better understanding of a genetic disorder of the cardiovascular system
2010-11-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New dry powder antibiotic targets tuberculosis, reduces treatment time
2010-11-17
Arlington, Va. — New research being presented at the 2010 International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) Pharmaceutical Sciences World Congress (PSWC) in association with the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) Annual Meeting and Exposition will feature an inhalable dry powder antibiotic that when used alone or with current treatments may significantly reduce treatment for tuberculosis (TB) and multi-drug resistant TB.
There are an estimated 9.4 million new cases of TB worldwide, according to the most recent statistics from the World Health Organization. ...
Dressing indicates infections
2010-11-17
Whether a small cut with a fruit knife, a surgical wound or a major injury caused by a fall – the body's defense and repair system leaps into action and tries to close the wound as quickly as possible. Small injuries usually heal within a few days, but a gaping wound will take longer to heal, and an infection can take hold even after several days. Dressings protect the site of the injury but to check the wound they have to be removed. This can be painful for the patient and moreover it risks giving germs the chance to enter and cause infection. Scientists at the Fraunhofer ...
Back off, Rudolph: Protecting this year's Christmas tree crop
2010-11-17
Hair clippings, cayenne pepper and raw eggs – these are just a few of the odd ingredients recommended to keep those pesky deer away from your backyard garden. But what about farmers who have hundreds of acres of Christmas trees to protect? North Carolina State University extension specialists have now found an effective, inexpensive alternative to available commercial products to keep the deer at bay.
The NC State researchers, led by Jeff Owen, a Christmas-tree production specialist, are exploring the use of inexpensive, inedible food byproducts – such as dried blood ...
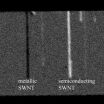
Imaging tool may aid nanoelectronics by screening tiny tubes
2010-11-17
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers have demonstrated a new imaging tool for rapidly screening structures called single-wall carbon nanotubes, possibly hastening their use in creating a new class of computers and electronics that are faster and consume less power than today's.
The semiconducting nanostructures might be used to revolutionize electronics by replacing conventional silicon components and circuits. However, one obstacle in their application is that metallic versions form unavoidably during the manufacturing process, contaminating the semiconducting nanotubes.
Now ...
Engineers test effects of fire on steel structures
2010-11-17
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers at Purdue University are studying the effects of fire on steel structures, such as buildings and bridges, using a one-of-a-kind heating system and a specialized laboratory for testing large beams and other components.
Building fires may reach temperatures of 1,000 degrees Celsius, or more than 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit, said Amit Varma, a Purdue associate professor of civil engineering who is leading the work.g1
"At that temperature, exposed steel would take about 25 minutes to lose about 60 percent of its strength and stiffness," he ...
Organ network uses Carnegie Mellon algorithm to match live kidney donors with recipients
2010-11-17
PITTSBURGH—A computer algorithm developed at Carnegie Mellon University matched living kidney donors with medically compatible transplant candidates late last month as the national Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN), operated by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS), began a national pilot program to increase the number of kidney paired-donation (KPD) transplants.
The initial run of the computer matching process included just 43 kidney transplant candidates and 45 potential living donors, but a national KPD pool eventually could include as many ...
International discussions on FRAX smooth the way for implementation in clinical practice
2010-11-17
Three days of critical international discussion and debate, led by a panel of experts from the International Society of Clinical Densitometry (ISCD) and the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), have served to clarify a number of important questions pertaining to the interpretation and use of FRAX® in clinical practice.
The WHO Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX®), with models for some 26 countries, is an important new online tool that is being used by a steadily increasing number of physicians around the world. FRAX® is country-specific and calculates a patient's ...
Heart surgeries can trigger strokes, seizures and other neurological complications
2010-11-17
Strokes, seizures and other neurological complications related to heart surgery account for "considerable morbidity and mortality," Loyola University Health System neurologists report in the November issue of the journal Hospital Practice.
Other complications include delirium, central nervous system infections, pituitary gland problems, spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries, residual effects of anesthesia and medication toxicity.
Complications can involve any part of the central and peripheral nervous systems. "Neurologic complications are always a risk with cardiac ...
Depression linked to HIV risk among South African young people, study shows
2010-11-17
University of Alberta research has discovered a strong link between depression and risky sexual behaviours such as improper condom use, transactional sex and relationship violence among young people in South Africa.
The research shows that depression is common among young South Africans, and could be making a significant contribution towards the HIV epidemic.
As well, the researchers believe that depression could be contributing to risky sexual behaviours around the world, and that preventing or treating it may reduce the global burden of sexually transmitted diseases, ...
Listening for ocean spills and their ecological effects
2010-11-17
November 16, 2010 -- Scientists who study acoustics (the "science of sound") have over the years developed a variety of techniques to probe the hidden depths of oceans. This week, many of these acoustic researchers will come together to discuss how these technologies were used to monitor April's Deepwater Horizon oil spill, to present new data on the gusher's ecological impacts, and to highlight new techniques under development that could improve our ability to detect oil in ocean water.
This special session will take place on November 17, 2010 at the 2nd Pan-American/Iberian ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
[Press-News.org] Structure of a protein related to heart and nervous system health revealedMay lead to smarter drug design, better understanding of a genetic disorder of the cardiovascular system