(Press-News.org) Receptors for the messenger molecule serotonin can be modified in such a way that they can be activated by light. Together with colleagues, neuroscientists from the Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) report on this finding in the journal "Neuron". An imbalance in serotonin levels seems to cause anxiety and depression. The researchers have provided a new model system for investigating the mechanism underlying these dysfunctions in cell cultures as well as living organisms.
G protein coupled receptors play an important role in medicine and health
One receptor, which is important for the regulation of serotonin levels in the brain, is the 5-HT1A receptor. It belongs to a protein family called G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). These receptors can activate different signalling pathways in cells to support or suppress various signalling events. "About 30 per cent of the current drugs target specifically GPCRs", says Prof Dr Stefan Herlitze from the Department of General Zoology and Neurobiology at the RUB. Due to the lack of tools to control intracellular signalling pathways with high temporal and spatial accuracy, it was so far difficult to analyse these pathways precisely.
Coupling of visual pigments to serotonin receptors
Applying optogenetic methods the scientists in Bochum used cone opsins from the mouse and human eye to control specifically serotonin signalling pathways either with blue or red light. Prof Dr Stefan Herlitze has been working with optogenetic techniques since 2005 and is one of the pioneers in the field. The light-activated serotonin receptors can be switched on within milliseconds, are extremely light sensitive in comparison to other optogenetic tools and can be repetitively activated. "We hope that with the help of these optogenetic tools, we will be able to gain a better understanding about how anxiety and depression originate", states RUB neuroscientist Dr Olivia Masseck.
Successful behavioural tests
The scientists also demonstrated that they were able to modulate mouse emotional behaviour using the light-activated receptors. When they switched on the serotonergic signals by light in a certain brain area, the mice became less anxious.
INFORMATION:
Bibliographic record
O.A. Masseck, K. Spoida, D. Dalkara, T. Maejima, J.M. Rubelwoski, L. Wallhorn,
E.S. Deneris, S. Herlitze (2014): Vertebrate cone opsins enable sustained and highly
sensitive rapid control of Gi/o signaling in anxiety circuitry. Neuron, DOI:
10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.041
Further Information
Dr Olivia Masseck, Department of General Zoology and Neurobiology, Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology at the Ruhr-Universität, 44780 Bochum, Germany, phone: +49/234/32-
27246, email: masseck@neurobiologie.rub.de
Click for more
Video: Summary of the article
Editor: Dr Julia Weiler
Switching off anxiety with light
RUB scientists couple cone opsins with serotonin receptors
2014-04-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The tiniest greenhouse gas emitters
2014-04-07
Climate feedbacks from decomposition by soil microbes are one of the biggest uncertainties facing climate modelers. A new study from the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) and the University of Vienna shows that these feedbacks may be less dire than previously thought.
The dynamics among soil microbes allow them to work more efficiently and flexibly as they break down organic matter – spewing less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than previously thought, according to a new study published in the journal Ecology Letters.
"Previous climate ...
Exploring the genetics of 'I'll do it tomorrow'
2014-04-07
Procrastination and impulsivity are genetically linked, suggesting that the two traits stem from similar evolutionary origins, according to research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The research indicates that the traits are related to our ability to successfully pursue and juggle goals.
"Everyone procrastinates at least sometimes, but we wanted to explore why some people procrastinate more than others and why procrastinators seem more likely to make rash actions and act without thinking," explains psychological ...
Green tea boosts your brain
2014-04-07
Green tea is said to have many putative positive effects on health. Now, researchers at the University of Basel are reporting first evidence that green tea extract enhances the cognitive functions, in particular the working memory. The Swiss findings suggest promising clinical implications for the treatment of cognitive impairments in psychiatric disorders such as dementia. The academic journal Psychopharmacology has published their results.
In the past the main ingredients of green tea have been thoroughly studied in cancer research. Recently, scientists have also been ...
New method for prostate cancer detection can save millions of men painful examination
2014-04-07
Each year prostate tissue samples are taken from over a million men around the world – in most cases using 12 large biopsy needles – to check whether they have prostate cancer. This medical procedure, which was recently described by an American urology professor as 'barbaric'**, shows that 70% of the subjects do not have cancer. The examination is unnecessarily painful and involves risk for these patients, and it is also costly to carry out. A patient-friendly examination, which drastically reduces the need for biopsies, and may even eliminate them altogether, has been ...
Rilpivirine combination product in pretreated HIV-1 patients: added benefit not proven
2014-04-07
The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) reassessed the antiviral drug combination rilpivirine/emtricitabine/tenofovir. In early 2012, the combination was approved for the treatment of adults infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) who have not received previous antiretroviral treatment. For men, the Institute then found proof, and for women, indications of a considerable added benefit of the fixed combination in comparison with the appropriate comparator therapy.
In the end of 2013, the approval was expanded to people ...
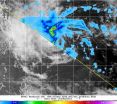
Tropical Cyclone Peipah passes Palau, Philippines prepare
2014-04-07
Tropical Cyclone Peipah passed the island of Palau on April 5 moving through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean as it heads for a landfall in the Philippines. Peipah was formerly known as Tropical Cyclone 05W and was renamed when it reached tropical storm-force. Since then, however, wind shear has weakened the storm to a tropical depression.
On April 5 at 2100 UTC/5 p.m. EDT, Tropical Storm 05W, renamed Peipah (and known locally in the Philippines as Domeng) was located about 262 nautical miles east-southeast of Koror. It was centered near 5.5 north and 137.8 east and moving ...
Cleft palate discovery in dogs to aid in understanding human birth defect
2014-04-07
UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine researchers have identified the genetic mutation responsible for a form of cleft palate in the dog breed Nova Scotia Duck Tolling Retrievers.
They hope that the discovery, which provides the first dog model for the craniofacial defect, will lead to a better understanding of cleft palate in humans. Although cleft palate is one of the most common birth defects in children, affecting approximately one in 1,500 live human births in the United States, it is not completely understood.
The findings appear this week online in the journal ...
Remedial courses fail bachelor's degree seekers, but boost those in associate's programs
2014-04-07
CHESTNUT HILL, MA (April 7, 2014) – Taking remedial courses at the four-year college level may hold students back from earning their bachelor's degrees, but at the community college level remedial education can help earn an associate's degree, according to researchers from Boston College's Lynch School of Education.
The role of remedial education has been under scrutiny for years, viewed as an essential tool in efforts to raise rates of degree completion. At the same time, critics question whether the courses are appropriate for institutions of higher education.
The ...
Movies synchronize brains
2014-04-07
When we watch a movie, our brains react to it immediately in a way similar to brains of other people. Researchers at Aalto University in Finland have succeeded in developing a method fast enough to observe immediate changes in the function of the brain even when watching a movie.
By employing movies it was possible to investigate the function of the human brain in experimental conditions that are close to natural. Traditionally, in neuroscience research, simple stimuli, such as checkerboard patterns or single images, have been used.
Viewing a movie creates multilevel ...
Caffeine against Alzheimer's disease
2014-04-07
As part of a German-French research project, a team led by Dr. Christa E. Müller from the University of Bonn and Dr. David Blum from the University of Lille was able to demonstrate for the first time that caffeine has a positive effect on tau deposits in Alzheimer's disease. The two-years project was supported with 30,000 Euro from the non-profit Alzheimer Forschung Initiative e.V. (AFI) and with 50,000 Euro from the French Partner organization LECMA. The initial results were published in the online edition of the journal "Neurobiology of Aging."
Tau deposits, along ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] Switching off anxiety with lightRUB scientists couple cone opsins with serotonin receptors