(Press-News.org) One of graphene's most sought-after properties is its high conductivity. Argentinian and Brazilian physicists have now successfully calculated the conditions of the transport, or conductance mechanisms, in graphene nanoribbons. The results, recently published in a paper in EPJ B, yield a clearer theoretical understanding of conductivity in graphene samples of finite size, which have applications in externally controlled electronic devices.
When the conductivity is high, the electrons, carriers of electrical current, are minimally hampered during transport through graphene. One aspect of conductivity is the electron transport gap, which is the minimal energy required for electric current to pass through the material. The electron transport gap is an important factor for applications in electronic devices, because when the transport gap is controllable, it can be used as a switch in transistors – the main components of any electronic device.
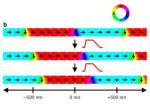
To study the electron transport gap, scientists prefer to use graphene nanoribbons, which can have variable crystallographic structures at their edges. In this EPJ B paper, the authors found that the transport gap is larger when the ribbon is narrower in width and that it is independent of the crystallographic orientation of the ribbon's edges.
The team found that the transport gap is inversely proportional to the ribbon's width and is independent of the crystallographic orientation of the ribbon's edges. Also, the conductance varies with the applied external voltage. These findings confirm previous theoretical and experimental results.
In addition, the authors focused on direct current conductivity, which is expected to jump through well-defined sharp steps, and referred to as quantisation. However, the authors' theoretical models present a somewhat different picture: the steps are not equally spaced and are not clearly separate but more blurred. By comparison, the conductance quantisation in graphene nanoribbons was previously observed experimentally in several works.
Unfortunately, none of the experiments can yet resolve the form of the steps. Further, the precision of existing measurements cannot yet clearly discriminate between different predictions for quantisation. More precise theoretical models are now required for a better understanding of the experimental behaviour of nanoribbons.
INFORMATION:
Reference: C. G. Beneventano, I. V. Fialkovsky, E. M. Santangelo and D. V. Vassilevich (2014), Charge density and conductivity of disordered Berry-Mondragon graphene nanoribbons, European Physical Journal B, DOI 10.1140/epjb/e2014-40990-x
For more information visit: http://www.epj.org
The full-text article is available to journalists on request.
Graphene nanoribbons as electronic switches
A new theoretical study shows the conductivity conditions under which graphene nanoribbons can become switches in externally controlled electronic devices
2014-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists use Google Glass to map the future of medical testing (video)
2014-04-08
WASHINGTON, April 8, 2014 — A team of researchers at UCLA has transformed Google Glass into powerful, wearable medical testing laboratory. Aydogan Ozcan and his team developed an application that reads dozens of different types of diagnostic tests for malaria, prostate cancer and HIV, to name a few. Glass uploads the results to secure servers and provides anonymous data to epidemiologists. In the American Chemical Society's (ACS') newest Breakthrough Science video, Ozcan demonstrates how the app works, and explains the broad impact it could have on medicine. The video is ...
UC geographers develop a system to track the dynamics of drought
2014-04-08
University of Cincinnati researchers are at work tracking drought patterns across the United States. Qiusheng Wu, a doctoral student and research assistant for the UC Department of Geography, and Hongxing Liu, a UC professor and head of the Department of Geography, will present details this week at the annual meeting of the Association of American Geographers (AAG) in Tampa, Fla.
To trace the dynamics around agricultural drought, the UC researchers implemented an Event-based Spatial-Temporal Data Model (ESTDM) to detect, track and monitor conditions. The framework organizes ...
Back to basics: Redesigning systems of care for older adults with Alzheimer's disease
2014-04-08
INDIANAPOLIS -- The number of older adults with dementia in the United States is forecast to more than double over the next 40 years. Caring for these individuals will have a significant impact on caregivers as well as the health care system and its workforce.
In a paper published in the April issue of the peer-reviewed journal Health Affairs, Regenstrief Institute investigator Christopher M. Callahan, M.D., founding director of the Indiana University Center for Aging Research, reviews two new dementia care models that seek to decrease stress for caregivers, reduce health ...
Kitchens are a source of multi-drug resistant bacteria
2014-04-08
CHICAGO (April 8, 2014) – After handling raw poultry, hands of food preparers and cutting boards remain a source of transmission for multi-drug resistant bacteria, such as E. coli that produce extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs). The study of household and hospital kitchens was published in the May issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
"The spread of multi-drug resistant bacteria has been associated with the hospital setting, but these findings suggest that transmission of drug-resistant ...
Expert guidance highlights practices to reduce prevalence of catheter-associated UTIs
2014-04-08
CHICAGO (April 8, 2014) – New expert guidance highlights strategies for implementing and prioritizing efforts to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) in hospitals. The practice recommendations, published in the May issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, are the first in a series to be published over several months sharing evidence-based strategies to help healthcare professionals effectively control and prevent the spread of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
A Compendium of Strategies to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections ...
Domain walls in nanowires cleverly set in motion
2014-04-08
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have achieved a major breakthrough in the development of methods of information processing in nanomagnets. Using a new trick, they have been able to induce synchronous motion of the domain walls in a ferromagnetic nanowire. This involved applying a pulsed magnetic field that was perpendicular to the plane of the domain walls. "This is a radically new solution," explained Professor Mathias Kläui of the Institute of Physics of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz. "It enables us to move domain walls synchronously over ...
Montreal researchers explain how our immune system kills abnormal blood cells
2014-04-08
A team of researchers at the IRCM, led by André Veillette, MD, explains how our immune system kills abnormal blood cells. Their discovery, recently published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, could eventually lead to new treatment avenues for leukemia, lymphoma and certain types of infectious viral diseases.
"Our team is studying how natural killer cells can eliminate abnormal hematopoietic (blood) cells," explains Dr. Veillette, Director of the Molecular Oncology research unit at the IRCM. "NK (natural killer) cells are crucial to the immune system and play a ...
How coughs and sneezes float farther than you think
2014-04-08
The next time you feel a sneeze coming on, raise your elbow to cover up that multiphase turbulent buoyant cloud you're about to expel.
That's right: A novel study by MIT researchers shows that coughs and sneezes have associated gas clouds that keep their potentially infectious droplets aloft over much greater distances than previously realized.
"When you cough or sneeze, you see the droplets, or feel them if someone sneezes on you," says John Bush, a professor of applied mathematics at MIT, and co-author of a new paper on the subject. "But you don't see the cloud, ...
Gothenburg scientist in Nature: Climate models underestimate costs to future generations
2014-04-08
The seven scientists behind the article, due to be published 10 April, conclude that the reports by the UN climate panel serve an important function in setting the agenda for climate research. Yet the most important role of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is to inform the global political discussion on how the harm caused by climate change should be handled.
Thomas Sterner, expert on policy instruments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, is a Coordinating Lead Author of one key chapter on policy instruments in the Working Group III of the Fifth Assessment ...
Are women in Iran who use Facebook less likely to wear a veil?
2014-04-08
New Rochelle, NY, April 8, 2014—Use of social media such as Facebook can influence attitudes and behaviors among people of all countries and cultures. Among women in Iran, the duration and amount of daily Facebook activity is associated with their desire to wear a traditional head-covering and their willingness to display pictures of themselves without a veil, according to an article in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Graphene nanoribbons as electronic switchesA new theoretical study shows the conductivity conditions under which graphene nanoribbons can become switches in externally controlled electronic devices