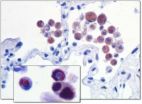
(Press-News.org) A unique population of microbes in the female breast may lay the groundwork for understanding how this bacterial community contributes to health and disease, according to a new study out of Western University (London, Canada). The study titled "Microbiota of human breast tissue," is now published online, in advance of the May issue of Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
The human body is home to a large and diverse population of bacteria with properties that are both harmful and beneficial to our health. Studies are revealing the presence of bacteria in unexpected sites.
This new research has uncovered bacteria in breast tissue associated with cancer. Forms of bacteria known as 'Proteobacteria' were the most abundant, potentially as they are able to metabolize the fatty tissue, said the paper's first author, Camilla Urbaniak, a PhD student in the Department of Microbiology & Immunology. Her studies, under the supervision of Lawson Health Research Institute Scientist and Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry Professor Gregor Reid, involved breast tissue from 81 women in Canada and Ireland. Ten of the women undergoing breast reduction acted as controls, with 71 having benign or cancerous tumors. Bacteria were found in and beside the tumours.
"Although we have not proven that bacteria cause cancer, or that certain types of bacteria actually may reduce the risk of cancer, the findings open a completely new avenue for this important disease," said Reid. "Imagine if women have a microbiota in the breast that puts them at higher risk of cancer? Or, if various drugs such as antibiotics or birth control pills alter the types of bacteria and their risk of cancer?"
INFORMATION:
Urbaniak is the recipient of a scholarship from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and also the Translational Breast Cancer Studentship from the London Regional Cancer Program. The University College Cork School of Medicine and the Irish Health Research Board funded their component. END
Western University study unlocking secrets of breast tissue
2014-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Expanding particles to engineer defects
2014-04-08
Materials scientists have long known that introducing defects into three-dimensional materials can improve their mechanical and electronic properties. Now a new Northwestern study finds how defects affect two-dimensional crystalline structures, and the results hold information for designing new materials.
In packed, two-dimensional crystalline systems, such as in photonic two-dimensional crystals, the particles are organized in hexagonal lattices. One particle is in the center of the hexagon with six neighboring particles around it. A defective lattice is when the center ...
More insights from tissue samples
2014-04-08
This news release is available in German.
They discovered that the so-called HOPE method allows tissue samples to be treated such that they do not only meet the requirements of clinical histology, but can still be characterised later on by modern methods of proteomics, a technique analysing all proteins at once. This is successful, since the structure of the tissue is "fixed" in a way that the protein molecules remain accessible for systematic analysis. This technique therefore meets current requirements in terms of a more personalised medicine and thus opens up ...
Few Americans know where elected officials and candidates stand on government support for research
2014-04-08
ALEXANDRIA, Va.—April 8, 2014—Two-thirds of Americans (66%) say it's important for candidates running for office to assign a high priority to funding medical research, according to America Speaks, Volume 14, a compilation of key questions from public opinion polls commissioned by Research!America. Polling shows that Americans place a high value on U.S. leadership in medical innovation, yet only 12% say they are very well informed about the positions of their senators and representative when it comes to their support of medical and scientific research. http://www.researchamerica.org/poll_summary. ...
Thinking about a majority-minority shift leads to more conservative views
2014-04-08
Facing the prospect of racial minority groups becoming the overall majority in the United States leads White Americans to lean more toward the conservative end of the political spectrum, according to research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
The findings suggest that increased diversity in the United States could actually lead to a wider partisan divide, with more White Americans expressing support for conservative policies.
Psychological scientists Maureen Craig and Jennifer Richeson of Northwestern University ...
Logo color affects consumer emotion toward brands, MU study finds
2014-04-08
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Many studies have shown that a company's logo is one of the most important aspects of marketing and advertising a brand, or features that distinctly identifies a company's product or service from its competitors. Now, a researcher at the University of Missouri has found that the specific colors used in a company's logo have a significant impact on how that logo, and the brand as a whole, is viewed by consumers.
Jessica Ridgway, a doctoral student in the MU Department of Textile and Apparel Management, surveyed 184 adults using generic logos of different ...
Synthetic gene circuits pump up cell signals
2014-04-08
Synthetic genetic circuitry created by researchers at Rice University is helping them see, for the first time, how to regulate cell mechanisms that degrade the misfolded proteins implicated in Parkinson's, Huntington's and other diseases.
The Rice lab of chemical and biomolecular engineer Laura Segatori has designed a sophisticated circuit that signals increases in the degradation of proteins by the cell's ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS).
The research appears online today in Nature Communications.
The UPS is essential to a variety of fundamental cellular processes, ...
Unexpected results in cancer drug trial
2014-04-08
Research from the University of Southampton has shown a drug, used in combination with chemotherapy to treat advanced colorectal cancer, is not effective in some settings, and indeed may result in more rapid cancer progression.
The New EPOC study, published in The Lancet Oncology and funded by Cancer Research UK, evaluated whether the drug cetuximab and chemotherapy together worked better than chemotherapy alone as a treatment in addition to surgery for people with bowel cancer that had spread to the liver but could be surgically removed. In the trial patients either ...
Scalable CVD process for making 2-D molybdenum diselenide
2014-04-08
Nanoengineering researchers at Rice University and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore have unveiled a potentially scalable method for making one-atom-thick layers of molybdenum diselenide -- a highly sought semiconductor that is similar to graphene but has better properties for making certain electronic devices like switchable transistors and light-emitting diodes.
The method for making two-dimensional molybdenum diselenide uses a technique known as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and is described online in a new paper in the American Chemical Society journal ...
Study: Black carbon is ancient by the time it reaches seafloor
2014-04-08
A fraction of the carbon that finds its way into Earth's oceans -- the black soot and charcoal residue of fires -- stays there for thousands for years, and a new first-of-its-kind analysis shows how some black carbon breaks away and hitches a ride to the ocean floor on passing particles.
The study by scientists from Rice University, the University of California, Irvine, and the University of South Carolina offers the first detailed analysis of how black carbon gets into deep ocean sediments, as well as an accounting of the types and amounts of black carbon found in those ...
Graphene nanoribbons as electronic switches
2014-04-08
One of graphene's most sought-after properties is its high conductivity. Argentinian and Brazilian physicists have now successfully calculated the conditions of the transport, or conductance mechanisms, in graphene nanoribbons. The results, recently published in a paper in EPJ B, yield a clearer theoretical understanding of conductivity in graphene samples of finite size, which have applications in externally controlled electronic devices.
When the conductivity is high, the electrons, carriers of electrical current, are minimally hampered during transport through graphene. ...