(Press-News.org) Work at the University of Colorado Cancer Center led to phase II trial of efatutazone with erlotinib in patients with refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Results are reported today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2014. While efatutazone did not improve the efficacy of erlotinib in this trial, researchers hope lessons from the trial will allow them to make better future use of the drug or other drugs in its class.
"In oncology and especially in lung cancer, everything is personalized. We're exploring different molecular markers that identify which drugs are for the right patient After this phase II trial, we're working to find the right biomarker that could help us discover who is most likely to respond to efatutazone. This trial was done in an unselected population. But if we had the right population with the right marker, we hope that we could find a meaningful effect," says Ana Oton, MD, investigator at the CU Cancer Center, Associate Professor of Medical Oncology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, and the study's first author.
Efatutazone belongs to a class of drugs known as thiazolidinediones, members of which are currently in use for the treatment of type II diabetes. Drugs in this class influence the expression of cell proteins by binding to the nuclear receptor PPARy. In diabetes, the drugs increase the production of proteins that drive metabolism. In cancer, the drug showed anti-cancer activity in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer. A phase I trial the drug alone showed anti-cancer activity in patients with solid malignancies.
The current, multi-center study compared efatutazone with erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in 90 patients previously treated for non-small cell lung cancer. Unfortunately, Oton explains, "In vitro it looked really promising, but in vivo it was not so good."
The majority of the difference between success in the lab and lack of success in patients was due to the side effect of fluid retention.
"Fluid retention in lower extremities is a side effect that can be easily managed," Oton says, "however, if this fluid retention is in the pleural space in patients that have already metastatic lung cancer, it can be very detrimental."
"We're not denying this combination could be useful, but with the knowledge we have we shouldn't do more studies in vivo at this time. We need to determine what patient population will be best served and second, discover how to manage this side-effect" Oton says.
INFORMATION: END
Phase II trial of efatutazone shows challenge of matching treatment to population
2014-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Glucosamine promotes longevity by mimicking a low-carb diet
2014-04-08
Glucosamine has been freely available in drugstores for many decades. It is widely used to treat arthritis and to prevent joint degeneration. Moreover, glucosamine is known to delay cancer growth. In addition, glucosamine reduces metabolism of nutritive sugars, as was already shown some 50 years ago.
In 2007, Michael Ristow showed that too much nutritive sugar shortens the lifespan of roundworms, a widely studied model organism in ageing research. Conversely, impairing carbohydrate metabolism in these worms was capable of extending lifespan [reference 1]. Unfortunately, ...
Future computers that are 'normally off'
2014-04-08
WASHINGTON D.C., April 8, 2014 -- If a research team in Japan gets its wish, "normally off" computers may one day soon be replacing present computers in a move that would both eliminate volatile memory, which requires power to maintain stored data, and reduce the gigantic energy losses associated with it.
Most parts of present computers are made with volatile devices such as transistors and dynamic random access memory (DRAM), which loses information when powered off. So computers are designed on the premise that power is "normally on."
Back in 2000, the concept of ...
Is the power grid too big?
2014-04-08
WASHINGTON D.C., April 8, 2014 -- Some 90 years ago, British polymath J.B.S. Haldane proposed that for every animal there is an optimal size -- one which allows it to make best use of its environment and the physical laws that govern its activities, whether hiding, hunting, hoofing or hibernating. Today, three researchers are asking whether there is a "right" size for another type of huge beast: the U.S. power grid.
David Newman, a physicist at the University of Alaska, believes that smaller grids would reduce the likelihood of severe outages, such as the 2003 Northeast ...
Rice U. study: Creativity and innovation need to talk more
2014-04-08
HOUSTON – (April 8, 2014) – Creativity and innovation are not sufficiently integrated in either the business world or academic research, according to a new study by Rice University, the University of Edinburgh and Brunel University.
The findings are the result of the authors' review of the rapidly growing body of research into creativity and innovation in the workplace, with particular attention to the period from 2002 to 2013.
"There are many of us who study employee creativity and many of us who study innovation and idea implementation, but we don't talk to each ...
The surprising truth about obsessive-compulsive thinking
2014-04-08
Montreal, April 8, 2014 — People who check whether their hands are clean or imagine their house might be on fire are not alone. New research from Concordia University and 15 other universities worldwide shows that 94 per cent of people experience unwanted, intrusive thoughts, images and/or impulses.
The international study, which was co-authored by Concordia psychology professor Adam Radomsky and published in the Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, examined people on six continents.
Radomsky and his colleagues found that the thoughts, images and ...
Where credit is due: How acknowledging expertise can help conservation efforts
2014-04-08
Scientists know that tapping into local expertise is key to conservation efforts aimed at protecting biodiversity – but researchers rarely give credit to these local experts. Now some scientists are saying that's a problem, both for the local experts and for the science itself.
To address the problem, a group of scientists is calling for conservation researchers to do a better job of publicly acknowledging the role of local experts and other non-scientists in conservation biology.
"For example, in the rainforests of the Yucatán, scientists couldn't even begin to do ...
Blocking DNA repair mechanisms could improve radiation therapy for deadly brain cancer
2014-04-08
DALLAS – April 8, 2014 – UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have demonstrated in both cancer cell lines and in mice that blocking critical DNA repair mechanisms could improve the effectiveness of radiation therapy for highly fatal brain tumors called glioblastomas.
Radiation therapy causes double-strand breaks in DNA that must be repaired for tumors to keep growing. Scientists have long theorized that if they could find a way to block repairs from being made, they could prevent tumors from growing or at least slow down the growth, thereby extending patients' survival. ...
What songbirds tell us about how we learn
2014-04-08
This news release is available in French. When you throw a wild pitch or sing a flat note, it could be that your basal ganglia made you do it. This area in the middle of the brain is involved in motor control and learning. And one reason for that errant toss or off-key note may be that your brain prompted you to vary your behavior to help you learn, from trial-and-error, to perform better.
But how does the brain do this, how does it cause you to vary your behavior?
Along with researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, Indian Institute of Science ...
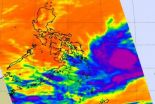
NASA satellite sees Tropical Depression Peipah approaching Philippines
2014-04-08
As Tropical Depression Peipah continues moving toward the central Philippines, NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and took an infrared look at the cloud top temperatures for clues about its strength.
On April 8 at 05:11 UTC/1:11 a.m. EDT/11 p.m. Manila local time, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument known as AIRS gathered infrared data on Tropical Depression Peipah. AIRS is one of the instruments that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. The AIRS data showed thunderstorms with very cold cloud-top temperatures surrounded the center of the low-level circulation ...
Intranasal ketamine confers rapid antidepressant effect in depression
2014-04-08
A research team from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai published the first controlled evidence showing that an intranasal ketamine spray conferred an unusually rapid antidepressant effect –within 24 hours—and was well tolerated in patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder. This is the first study to show benefits with an intranasal formulation of ketamine. Results from the study were published online in the peer-reviewed journal Biological Psychiatry on April 2, 2014.
Of 18 patients completing two treatment days with ketamine or saline, eight ...