(Press-News.org) It's a guessing game parents like to ponder: What will my child look like when she grows up? A computer could now answer the question in less than a minute.
University of Washington researchers have developed software that automatically generates images of a young child's face as it ages through a lifetime. The technique is the first fully automated approach for aging babies to adults that works with variable lighting, expressions and poses.
"Aging photos of very young children from a single photo is considered the most difficult of all scenarios, so we wanted to focus specifically on this very challenging case," said Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, a UW assistant professor of computer science and engineering. "We took photos of children in completely unrestrained conditions and found that our method works remarkably well."
The research team has posted a paper on the new technique and will present its findings at the June IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition conference in Columbus, Ohio.
The shape and appearance of a baby's face – and variety of expressions – often change drastically by adulthood, making it hard to model and predict that change. This technique leverages the average of thousands of faces of the same age and gender, then calculates the visual changes between groups as they age to apply those changes to a new person's face.
More specifically, the software determines the average pixel arrangement from thousands of random Internet photos of faces in different age and gender brackets. An algorithm then finds correspondences between the averages from each bracket and calculates the average change in facial shape and appearance between ages. These changes are then applied to a new child's photo to predict how she or he will appear for any subsequent age up to 80.
The researchers tested their rendered images against those of 82 actual people photographed over a span of years. In an experiment asking random users to identify the correct aged photo for each example, they found that users picked the automatically rendered photos about as often as the real-life ones.
"Our extensive user studies demonstrated age progression results that are so convincing that people can't distinguish them from reality," said co-author Steven Seitz, a UW professor of computer science and engineering. "When shown images of an age-progressed child photo and a photo of the same person as an adult, people are unable to reliably identify which one is the real photo."
Real-life photos of children are difficult to age-progress, partly due to variable lighting, shadows, funny expressions and even milk moustaches. To compensate for these effects, the algorithm first automatically corrects for tilted faces, turned heads and inconsistent lighting, then applies the computed shape and appearance changes to the new child's face.
Perhaps the most common application of age progression work is for rendering older versions of missing children. These renderings usually are created manually by an artist who uses photos of the child as well as family members, and editing software to account for common changes to a child's face as it ages, including vertical stretching, wrinkles and a longer nose.
But this process takes time, and it's significantly harder to produce an accurate image for children younger than age 5, when facial features more closely resemble that of a baby.
The automatic age-progression software can run on a standard computer and takes about 30 seconds to generate results for one face. While this method considered gender and age, the research team that also includes UW doctoral student Supasorn Suwajanakorn hopes to incorporate other identifiers such as ethnicity, and cosmetic factors such as hair whitening and wrinkles to build a robust enough method for representing every human face.
"I'm really interested in trying to find some representation of everyone in the world by leveraging the massive amounts of captured face photos," Kemelmacher-Shlizerman said. "The aging process is one of many dimensions to consider."
INFORMATION:
Posted with photos, video: http://www.washington.edu/news/2014/04/09/see-what-a-child-will-look-like-using-automated-age-progression-software/
This research was funded by Google and Intel Corp.
For more information, contact Kemelmacher-Shlizerman at kemelmi@cs.washington.edu or 206-616-0621.
Project website: http://grail.cs.washington.edu/aging/
Related paper: http://grail.cs.washington.edu/aging/Aging_CVPR14.pdf
Supplementary materials (photos): http://grail.cs.washington.edu/aging/Aging_CVPR14_supp.pdf
Video: http://youtu.be/bXsIE-3PBQo
See what a child will look like using automated age-progression software
2014-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sunken logs create new worlds for seafloor animals
2014-04-09
MOSS LANDING, CA — When it comes to food, most of the deep sea is a desert. Many seafloor animals feed on marine snow—the organic remnants of algae and animals that live in the sunlit surface waters, far above. However, marine snow only falls as a light dusting and doesn't have much nutritional value. Thus, any other sources of food that reach the deep sea provide a temporary feast. Even bits of dead wood, waterlogged enough to sink, can support thriving communities of specialized animals. A new paper by biologists at the National Evolutionary Synthesis Center and the Monterey ...
Scientists reconstruct ancient impact that dwarfs dinosaur-extinction blast
2014-04-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- Picture this: A massive asteroid almost as wide as Rhode Island and about three to five times larger than the rock thought to have wiped out the dinosaurs slams into Earth. The collision punches a crater into the planet's crust that's nearly 500 kilometers (about 300 miles) across: greater than the distance from Washington, D.C. to New York City, and up to two and a half times larger in diameter than the hole formed by the dinosaur-killing asteroid. Seismic waves bigger than any recorded earthquakes shake the planet for about half an hour at any one ...
Counting the invisible by sound -- a new approach to estimate seabird populations
2014-04-09
AUDIO:
This is a typical one minute recording of an active Cory's Shearwater colony on the island of Corvo in the North Atlantic Ocean, June 2011.
Click here for more information.
Seabirds nest in places that are inaccessible for most humans - vertical cliffs and remote islands surrounded by raging waves. Worse still, many seabirds lay their eggs in burrows or cavities where they are protected from inclement weather and invisible for researchers. Hidden under rocks or in burrows ...
Rabbits kept indoors could be vitamin D deficient
2014-04-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Rabbits that remain indoors may suffer from a lack of vitamin D, researchers report in a new study. In rabbits kept as pets or used in laboratory studies, the deficiency could lead to dental problems, undermine their cardiovascular health, weaken their immune systems and skew scientific findings.
The study found that regular exposure to artificial ultraviolet B light for two weeks doubled rabbits' serum vitamin D levels – an increase not seen in animals raised in artificial light lacking UVB radiation. Future studies will seek to determine optimal levels ...
Recycling astronaut urine for energy and drinking water
2014-04-09
On the less glamorous side of space exploration, there's the more practical problem of waste — in particular, what to do with astronaut pee. But rather than ejecting it into space, scientists are developing a new technique that can turn this waste burden into a boon by converting it into fuel and much-needed drinking water. Their report, which could also inspire new ways to treat municipal wastewater, appears in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Eduardo Nicolau, Carlos R. Cabrera and colleagues point out that human waste on long-term journeys into ...
Can animals really help people in hospitals, aged care?
2014-04-09
While many people have an opinion on whether animals can help to improve wellbeing and care for patients in hospitals, does anyone really know whether there are benefits both for the patients and the animals themselves?
Not according to a team of researchers from the University of Adelaide, which has conducted a worldwide review of all studies looking at the impact of "animal interventions" in healthcare settings for children.
The researchers, from the University's School of Psychology and School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, have found that despite theories emerging ...
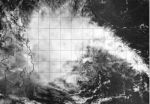
NASA satellite sees Tropical Depression Peipah crawling toward Philippines
2014-04-09
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over the remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah on April 9 as the storm slowly approached the Philippines from the east. According to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center, Peipah is now not expected to make landfall in eastern Visayas until April 12.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard Suomi NPP captured a visible, high-resolution image of the storm as it continued moving through the Philippine Sea. The storm appeared disorganized in the image, and the center was difficult to pinpoint on the visible ...
Promising agents burst through 'superbug' defenses to fight antibiotic resistance
2014-04-09
In the fight against "superbugs," scientists have discovered a class of agents that can make some of the most notorious strains vulnerable to the same antibiotics that they once handily shrugged off. The report on the promising agents called metallopolymers appears in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Chuanbing Tang and colleagues note that the antibiotic-resistant bacteria known as MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is responsible for a significant fraction of the infections that patients acquire in hospitals. According to the Centers for ...
Pharma firms turn attention to hearing loss
2014-04-09
Hearing loss affects 36 million Americans to some degree, often leaving them feeling isolated, but it has received little attention from the pharmaceutical industry — until now. Small firms have brought a handful of potential therapies to the development pipeline, and pharmaceutical heavyweights are taking notice, according to an article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society.
The story states that the most common cause of hearing loss is loud noise, either from a single event like the bang of a firecracker or from ...
Europeans and biomedical research
2014-04-09
This news release is available in French. The French National Institute of Health and Medical Research (Inserm) is currently the leading biomedical research organisation in Europe, and plays a key role in developing European research. To mark its 50th anniversary, Inserm wanted to assess the perceptions of Europeans regarding biomedical research.
To create this European panorama, Ipsos carried out an Internet survey of over 4,000 Europeans (with 1,001 French, 1,004 German, 1,001 Italians and 1,005 British respondents) from 10 to 23 January 2014. Representative samples ...