(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Department of Applied Physics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, in Xi'an, China, are engaged in revealing the mysteries of solidification process and the development of new materials using self-designed experimental instrument which can simulate the space environment such as containerless state. Solidification mechanism is of great importance to better understand the relationship between solidification process and microstructure evolution, so that we can follow them to design and prepare new materials which can meet the application requirements.
Dr. Yan and coworkers recently used the glass-fluxing method to realize the containerless processing and investigate the solidification mechanism of ternary Co-Cu-Pb immiscible alloys. This study was published in SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2014; 57 (3): 393-399.
Immiscible alloys possess good properties such as lubrication in bearing materials. It is a promising option for applications in reducing the friction of mechanical transmission part. It is also important for designers to have some basic knowledge of how Co-Cu-Pb alloy solidifies under different conditions, because its mechanical performance is usually controlled by solidification mechanism and microstructural characteristics. However, so far there has been little research on its rapid solidification mechanism under the extremely nonequilibrium condition.
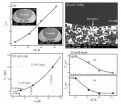
In this work, Co-35%Cu-32.5%Pb immiscible alloy was undercooled by 125 K. Because of the evaporation of Pb element and metestable phase separation, such alloy melt is difficult to obtain high undercoolings. Here, they used a special denucleating agent, a high-vacuum environment and a periodic melting processing. In addition, the experimental parameters, such as cooling rate, superheating, and holding time, were controlled in order to get a wider undercooling range for comparison.
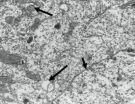
Metastable phase separation happens in the undercooled Co-35%Cu-32.5%Pb alloy melt and the macrosegregation pattern is characterized by a top Co-rich zone and a bottom Cu-rich zone. The average solute contents of the two separated zones decrease with the increase of undercooling, except for the solute Pb in Cu-rich zone. With the enhancement of undercooling, a morphological transition from dendrites into equaxied grains occurs to the primary α(Co) phase in Co-rich zone. The solute redistribution of Cu in primary α(Co) phase is found to depend upon both the undercooling and composition of Co-rich zone. Stokes migration is proved to be the main dynamic mechanism of droplet movement during liquid phase separation.
Two other relevant papers about the phase separation and containerless solidification of ternary Co-Cu-Pb alloys have been published in J. Alloys Comp. and Appl. Phys. A. "The present work reports interesting experimental results of phase separation in metastable monotectic ternary Co-Cu-Pb alloys." said one journal reviewer. "It is an interesting study. The authors develop a phenomenological concept how phase separation takes place in ternary Co-Cu-Pb alloy system." said another reviewer.
INFORMATION:
Reference:
N. Yan, W. L. Wang, Z. C. Xia, B. Wei, "Solute redistribution profiles during rapid solidification of undercooled ternary Co-Cu-Pb alloy", Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2014; 57 (3): 393-399.
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11433-013-5389-6
N. Yan, W. L. Wang, S.B. Luo, L. Hu, B. Wei, "Correlated Process of Phase Separation and Microstructure Evolution of Ternary Co-Cu-Pb Alloy" Applied Physics A, 113 (2013) 763-770.
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00339-013-7586-6
N. Yan, W. L. Wang, B. Wei, "Complex Phase Separation of Ternary Co-Cu-Pb Alloy Under Containerless Processing Condition", Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 558 (2013) 109-116.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092583881300056X
Science China Press Co., Ltd. (SCP) is a scientific journal publishing company of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). For 50 years, SCP takes its mission to present to the world the best achievements by Chinese scientists on various fields of natural sciences researches.
http://www.scichina.com/
Solute redistribution profiles during rapid solidification of undercooled ternary Co-Cu-Pb alloy
2014-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New report provides solution to NEET challenge in UK and abroad
2014-04-10
A NEW strategy to help young people find jobs that pay fair wages, accompanied by high quality training and better career opportunities, has been developed by a University of Huddersfield professor. Outlined in a specially-commissioned research report, it is beginning to catch the attention of policy-makers throughout the UK.
After conducting years of funded research into the challenges that face young people dubbed NEET – meaning that they are not in employment, education or training – Professor Robin Simmons has devised the concept of a Youth Resolution designed to ...
Researchers show fruit flies have latent bioluminescence
2014-04-10
WORCESTER, Mass. – New research from scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School shows that fruit flies are secretly harboring the biochemistry needed to glow in the dark —otherwise known as bioluminescence.
The key to activating this latent ability is a novel synthetic analog of D-luciferin developed at UMMS. The findings, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that the inherent biochemistry needed for bioluminescence is more common than previously thought. Synthetic luciferins can unmask latent enzymatic ...
Coral reefs of the Mozambique Channel a leading candidate for saving marine diversity
2014-04-10
Marine scientists keen on finding patterns of coral decline and persistence in gradually warming oceans have a complex challenge: how to save reefs containing the most diversity with limited resources. In the Western Indian Ocean, researchers from the Wildlife Conservation Society, the University of Warwick, the ARC Centre for Excellence of Coral Reef Studies, Simon Fraser University, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and other groups have found that the corals of the Mozambique Channel should be a priority for protection as climate change continues to threaten ...
Reef fish arrived in 2 waves
2014-04-10
The world's reefs are hotbeds of biological diversity, including over 4,500 species of fish. A new study shows that the ancestors of these fish colonized reefs in two distinct waves, before and after the mass extinction event about 66 million years ago that wiped out the dinosaurs.
Reef fish represent one of the largest and most diverse assemblages of vertebrates, according to Samantha Price, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Evolution and Ecology at UC Davis. Price is first author on a paper describing the work, published April 2 in the journal Proceedings ...
CU researchers unraveling what's behind the sniffles, hoping for a treatment
2014-04-10
Scientists at the University of Colorado School of Medicine have shed light on one of the most common of ailments – the runny nose.
Your respiratory tract is under constant attack and the nose is the first line of defense. Often, especially as the weather warms, the assault comes from allergens, which cause the body to fight off a perceived threat. Infections, too, are a problem.
But millions of people get a runny nose and have difficulty breathing without an allergic attack or infection. What many people call the sniffles, scientists refer to as "non-allergic rhinitis."
Although ...
China looks to science and technology to fuel its economy
2014-04-10
Maintaining stability in the face of rapid change and growth, and proactively partaking in cooperative global ties in science and technology fields will be key in helping China become an innovation-based economy, according to Denis Simon, vice provost for International Strategic Initiatives at Arizona State University.
One of the world's leading experts on science, technology and innovation in China, Simon recently hosted an ASU conference that focused on the evolving role of science and technology in China's international relations.
Supplemented with strategic investments ...
Researchers looking to create new bone tissue generation technique
2014-04-10
UT Arlington and Texas Health Arlington Memorial Hospital are investigating whether bone grown from the body's own stem cells can replace traditional types of bone grafting.
The process, which has been successful in previous lab experiments, uses biodegradable polymer scaffolding material and bone morphogenetic protein, or BMP, which was inserted into the abdomen of mice to attract stem cells that in turn produced bone. BMPs are proteins known to promote bone growth. The research is detailed in a new paper, "Tissue Engineering Bone Using Autologous Progenitor Cells in ...
La Brea Tar Pit fossil research shows climate change drove evolution of Ice Age predators
2014-04-10
LOS ANGELES — Concerns about climate change and its impact on the world around us are growing daily. New scientific studies at the La Brea Tar Pits are probing the link between climate warming and the evolution of Ice Age predators, attempting to predict how animals will respond to climate change today.
The La Brea Tar Pits are famous for the amazing array of Ice Age fossils found there, such as ground sloths, mammoths, and predators like saber-toothed cats and powerful dire wolves. But the climate during the end of the Ice Age (50,000-11,000 years ago) was unstable, ...
Acupuncture normalizes brain structure and damaged neurons following heroin relapse
2014-04-10
Heroin abuse can damage many brain areas, including the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus of the midbrain, the ventral tegmental area, and nucleus accumbens. Persistent use of heroin induced irreversible damage to the nervous system. To verify the relationship between acupuncture, neurotrophic factor expression and brain cell structural changes, a research team from Anhui University of Chinese Medicine in China established a rat model of heroin relapse using intramuscular injection of increasing amounts of heroin. During the detoxification period, rat models received acupuncture ...
Brainy courage of the rainbowfish
2014-04-10
The boldest black-lined rainbowfish are those that are born in the wild. Also more fearless are those that analyze information both sides of their brains. This is the conclusion of Australian researchers Culum Brown and Anne-Laurence Bibost from Macquarie University, in a study published in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
The preference to analyze and react to information with either the left or right hemisphere of the brain is called cerebral lateralization, and is widespread among vertebrates. Lateralization is seen in the preference of humans ...