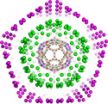
(Press-News.org) Symmetry is ubiquitous in the natural world. It occurs in gemstones and snowflakes and even in biology, an area typically associated with complexity and diversity. There are striking examples: the shapes of virus particles, such as those causing the common cold, are highly symmetrical and look like tiny footballs.
A research programme led by Reidun Twarock at the University of York, UK has developed new mathematical tools to better understand the implications of this high degree of symmetry in these systems. The group pioneered a mathematical theory that reveals unprecedented insights into how different components of a virus, the protein container encapsulating the viral genome and the packaged genome within, mutually constrain each other's structures [Acta Cryst. (2013). A69, 140–150 doi:10.1107/S0108767312047150].
A paper recently published in Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations and Advances [Acta Cryst. (2014). A70, 162–167 doi: 10.1107/S2053273313034220] in collaboration with Pierre-Philippe Dechant from the University of Durham, UK shows that these mathematical tools apply more widely in the natural world and interestingly also account for the structures of Russian-doll-like arrangements of carbon cages known as carbon onions. It was known previously that individual shells could be modeled using symmetry techniques, but the fact that the entire structure is collectively constrained by a single symmetry principle is a surprising new result.
Such insights are crucial for understanding how different components contribute collectively to function. In the case of viruses this work has resulted in a new understanding of the interplay of the viral genome and protein capsid in virus formation, which in turn has opened up novel opportunities for anti-viral intervention that are actively being explored. Similarly, we expect that the work on carbon onions will provide a basis for a better understanding of the structural constraints on their overall organisation and formation, which in the future can be exploited in nanotechnology applications.
INFORMATION: END
Virus structure inspires novel understanding of onion-like carbon nanoparticles
2014-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New towns going up in developing nations pose major risk to the poor
2014-04-10
DENVER (April 10, 2014) – Satellite city projects across the developing world are putting an increasing number of poor people at risk to natural hazards and climate change, according to a new study from the University of Colorado Denver.
Throughout Asia, Africa and Latin America `new towns' are rapidly being built on the outskirts of major cities with the goal of relieving population pressures, according to study author Andrew Rumbach, PhD, assistant professor of planning and design at CU Denver's College of Architecture and Planning.
The towns often sit in high flood ...
Four-eyed daddy longlegs fossil fills in evolutionary tree
2014-04-10
Living harvestmen—a group of arachnids more commonly known as daddy longlegs—have a single pair of eyes that help them navigate habitats in every continent except Antarctica. But a newly described 305-million-year-old fossil found in eastern France shows that wasn't always the case. New research recently published in the journal Current Biology and led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History and the University of Manchester indicates that primitive harvestmen had two pairs of eyes, adding significant details to the evolutionary story of this diverse and ...
New research on gigabit wireless communications
2014-04-10
Research on gigabit wireless communications has been presented by researchers from the University of Bristol at the world's leading wireless communications and networking conference, IEEE WCNC 2014, in Turkey earlier this week [Monday 6 to Wednesday 9 April].
The two research papers, led by Andrew Nix, Professor of Wireless Communication Systems and Dr Simon Armour, Senior Lecturer in Software Radio, from the University's Communication Systems and Networks research group in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, could have significant implications for ...
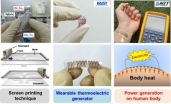
Thermoelectric generator on glass fabric for wearable electronic devices
2014-04-10
Wearable computers or devices have been hailed as the next generation of mobile electronic gadgets, from smart watches to smart glasses to smart pacemakers. For electronics to be worn by a user, they must be light, flexible, and equipped with a power source, which could be a portable, long-lasting battery or no battery at all but a generator. How to supply power in a stable and reliable manner is one of the most critical issues to commercialize wearable devices.
A team of KAIST researchers headed by Byung Jin Cho, a professor of electrical engineering, proposed a solution ...
Common sense health for young adult cancer survivors
2014-04-10
Many factors influence the life expectancy of childhood cancer survivors: not getting enough exercise, being underweight, and being worried about their future health or their health insurance. These are the findings of research led by Cheryl Cox of the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in the US, published in Springer's Journal of Cancer Survivorship. The study found that, on average, childhood cancer survivors passed away before they were 40 years old.
Health-related behavior, self-perceived health status, and health concerns often influence mortality in the general ...
Iconic boreal bird species declining in the Adirondacks, study says
2014-04-10
A new study from the Wildlife Conservation Society finds that several iconic Adirondack birds are in trouble, with declines driven by the size of their wetland habitats, how connected these wetlands are to one another, and how near they are to human infrastructure.
The Adirondack Park represents the southern range extent for several species of boreal forest birds in eastern North America. Like any species at the edge of its range, they face challenges in this environment. The habitats of these boreal specialists – cool, wet, sphagnum-draped bogs and swampy woods – are ...
Uncovering a new angle on mental distance
2014-04-10
Why does the second hour of a journey seem shorter than the first? According to research from University of Toronto Scarborough (UTSC) and the Rotman School of Management, the answer lies in how we're physically oriented in space.
In a series of six studies, Sam Maglio, an assistant professor in UTSC's Department of Management, demonstrated that a person's orientation — the direction they are headed — changed how they thought of an object or event.
The research is forthcoming in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Feeling ...
Sunlight generates hydrogen in new porous silicon
2014-04-10
Porous silicon manufactured in a bottom up procedure using solar energy can be used to generate hydrogen from water, according to a team of Penn State mechanical engineers, who also see applications for batteries, biosensors and optical electronics as outlets for this new material.
The surface area of this porous silicon is high," said Donghai Wang, assistant professor of mechanical engineering. "It is widely used and has a lot of applications."
The standard method for manufacturing porous silicon is a subtraction method, similar to making a sculpture.
"Silicon is ...
Extending terrorism insurance program could lower federal costs, study finds
2014-04-10
Federal spending after future terrorist attacks on the United States may be higher if the nation's terrorism risk insurance program is allowed to expire, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
The analysis finds that in a terrorist attack with losses up to $50 billion, the federal government would spend more helping to cover losses than if it had continued to support a national terrorism risk insurance program.
In the wake of the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11, 2001, terrorism risk insurance quickly became either unavailable or very expensive. Congress reacted by ...
Health of ecosystems on US golf courses better than predicted
2014-04-10
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Currently, there are more than 18,300 golf courses in the U.S. covering over 2.7 million acres. The ecological impacts of golf courses are not always straightforward with popular opinion suggesting that environmentally, golf courses have a negative impact on ecosystems. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that golf courses can offer a viable habitat for stream salamanders, and enhanced management practices may be beneficial to ecosystems within golf courses.
"If you look at the literature on golf courses, historically they get ...