(Press-News.org) A study in The Journal of General Physiology provides new insights about singlet oxygen and sets the stage for better understanding of this highly reactive and challenging substance.
Singlet oxygen is an electronically excited state of oxygen that is less stable than normal oxygen. Its high reactivity has enabled its use in photodynamic therapy, in which light is used in combination with a photosensitizing drug to generate large amounts of singlet oxygen to kill cancer cells or various pathogens.
Light-generated singlet oxygen also plays a role in a range of biological processes. It is produced during photosynthesis in plants, for example, and its production in skin cells has been linked to aging and cancer development. Moreover, small amounts of singlet oxygen produced during metabolic reactions can act as a local signaling factor that oxidizes and modifies target molecules, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood.
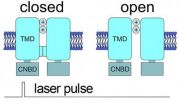
Lei Zhou and colleagues from Virginia Commonwealth University unveil a new technique to show how singlet oxygen modifies HCN channels— "pacemaker channels" that contribute to memory, heart rate, pain sensation, and other functions. By applying millisecond laser light pulses to HCN channels tagged with a fluorescent photosensitizer, Zhou and colleagues were able to elicit the production of small amounts of singlet oxygen in a precise location and monitor its effects on the channels in open and closed states. Their results indicate that some of its effects on HCN channels are state specific and involve specific modifications near the activation gate.
The findings not only help explain how singlet oxygen functions, they introduce a method that can be used for further exploration of this important signaling factor.
INFORMATION:
Gao, W., et al. 2014. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201311112
About The Journal of General Physiology
Founded in 1918, The Journal of General Physiology (JGP) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editor. JGP content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit http://www.jgp.org.
Research reported in the press release was supported by Virginia Commonwealth University and the American Heart Association.
A stable model for an unstable target
Researchers use a new technique to explore how light-activated singlet oxygen modifies target molecules
2014-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Better solar cells, better LED light and vast optical possibilities
2014-04-14
Changes at the atom level in nanowires offer vast possibilities for improvement of solar cells and LED light. NTNU-researchers have discovered that by tuning a small strain on single nanowires they can become more effective in LEDs and solar cells.
NTNU researchers Dheeraj Dasa and Helge Weman have, in cooperation with IBM, discovered that gallium arsenide can be tuned with a small strain to function efficiently as a single light-emitting diode or a photodetector. This is facilitated by the special hexagonal crystal structure, referred to as wurtzite, which the NTNU ...
Pioneering findings on the dual role of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis
2014-04-14
Scientists at Umeå University in Sweden have found that carbon dioxide, in its ionic form bicarbonate, has a regulating function in the splitting of water in photosynthesis. This means that carbon dioxide has an additional role to being reduced to sugar. The pioneering work is published in the latest issue of the scientific journal PNAS.
It is well known that inorganic carbon in the form of carbon dioxide, CO2, is reduced in a light driven process known as photosynthesis to organic compounds in the chloroplasts. Less well known is that inorganic carbon also affects the ...
The result of slow degradation
2014-04-14
This news release is available in German. Although persistent environmental pollutants have been and continue to be released worldwide, the Arctic and Antarctic regions are significantly more contaminated than elsewhere. The marine animals living there have some of the highest levels of persistent organic pollutant (POP) contamination of any creatures. The Inuit people of the Arctic, who rely on a diet of fish, seals and whales, have also been shown to have higher POP concentrations than people living in our latitudes.
Today, the production and use of nearly two dozen ...
Nutrient-rich forests absorb more carbon
2014-04-14
The ability of forests to sequester carbon from the atmosphere depends on nutrients available in the forest soils, shows new research from an international team of researchers including the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA).
The study showed that forests growing in fertile soils with ample nutrients are able to sequester about 30% of the carbon that they take up during photosynthesis. In contrast, forests growing in nutrient-poor soils may retain only 6% of that carbon. The rest is returned to the atmosphere as respiration.
"This paper produces ...
Scientists open door to better solar cells, superconductors and hard-drives
2014-04-14
Using DESY's bright research light sources, scientists have opened a new door to better solar cells, novel superconductors and smaller hard-drives. The research reported in the scientific journal Nature Communications this week enhances the understanding of the interface of two materials, where completely new properties can arise. With their work, the team of Prof. Andrivo Rusydi from the National University of Singapore and Prof. Michael Rübhausen from the Hamburg Center for Free-Electron Laser Science (CFEL) have solved a long standing mystery in the physics of condensed ...
Combs of light accelerate communication
2014-04-14
This news release is available in German.
Miniaturized optical frequency comb sources allow for transmission of data streams of several terabits per second over hundreds of kilometers – this has now been demonstrated by researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the Swiss École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in a experiment presented in the journal Nature Photonics. The results may contribute to accelerating data transmission in large computing centers and worldwide communication networks. (DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2014.57.)
The amount of ...
Proteomics International biomarker study closer to a CDx test for diabetic kidney disease
2014-04-14
April 2014, Perth, Australia. Drug discovery company Proteomics International has completed an important milestone towards the development of a companion diagnostic (CDx) test with the validation of several of its protein biomarkers.
The research team authenticated the panel of biomarkers after taking 508 highly curated disease and control samples. Seven biomarkers were validated at high stringency using the company's proprietary mass spectrometry approach.
The mass spectrometry data was then cross-validated using immunoassays in collaboration with the KTH Royal Institute ...
Beneficial organisms react differently to parasite drug
2014-04-14
The substance ivermectin has been used for more than thirty years all over the world to combat parasites like roundworms, lice and mites in humans, livestock and pets. The active ingredient belongs to the chemical group of avermectins, which generally disrupt cell transport and thus attack pests. When ivermectin is excreted in the faeces of treated animals, at overly high doses it also harms dung-degrading beneficial insects like dung beetles and dung flies. This impairs the functioning of the ecosystem. In extreme cases the dung is not decomposed and the pasture is destroyed.
Sensitivity ...
Does germ plasm accelerate evolution?
2014-04-14
Scientists at The University of Nottingham have published research in the leading academic journal Science that challenges a long held belief about the way certain species of vertebrates evolved.
Dr Matt Loose and Dr Andrew Johnson who are experts in genetics and cell development in the School of Life Sciences carried out the research, funded by the Medical Research Council (MRC). It suggests that genes evolve more rapidly in species containing germ plasm. The results came about as they put to the test a novel theory that early developmental events dramatically alter ...
Novel technique developed by NUS scientists opens door to better solar cells
2014-04-14
A team of scientists, led by Assistant Professor Andrivo Rusydi from the Department of Physics at the National University of Singapore's (NUS) Faculty of Science, has successfully developed a technique to study the interface between materials, shedding light on the new properties that arise when two materials are put together.
With a better understanding of how materials interface, scientists can tweak the properties of different materials more easily, and this opens doors to the development of better solar cells, novel superconductors and smaller hard drives.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
[Press-News.org] A stable model for an unstable targetResearchers use a new technique to explore how light-activated singlet oxygen modifies target molecules