(Press-News.org) Somewhere in the cosmos an ordinary galaxy spins, seemingly at slumber. Then all of a sudden, WHAM! A flash of light explodes from the galaxy's center. A star orbiting too close to the event horizon of the galaxy's central supermassive black hole is torn apart by the force of gravity, heating up its gas and sending out a beacon to the far reaches of the universe.
In a universe with tens of billions of galaxies, how would we see it? What would such a beacon look like? How would we distinguish it from other bright, monumental intergalactic events, like supernovas?
"Black holes by themselves do not emit light," said Tamara Bogdanovic, Assistant Professor of Physics at the Georgia Institute of Technology. "Our best chance to discover them in distant galaxies is if they interact with stars and gas that are around them."
In recent decades, with improved telescopes and observational techniques designed to repeatedly survey the vast numbers of galaxies on the sky, scientists noticed that some galaxies that previously looked inactive would suddenly light up at their very center.
"This flare of light was found to have a characteristic behavior as a function of time," Bogdanovic explained. "It starts very bright and its luminosity then decreases in time in a particular way. Astronomers have identified those as galaxies where a central black hole just disrupted and 'ate' a star. It's like a black hole putting up a sign that says: 'Here I am.'"
Bogdanovic relies on National Science Foundation-funded supercomputers like Stampede at the Texas Advanced Computing Center and Kraken at the National Institute for Computational Sciences. Using these systems, she and her collaborators recently simulated the dynamics of these super powerful forces and charted their behavior using numerical models. Stampede and Kraken are part of the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE), a single virtual system that scientists use to interactively share computing resources, data and expertise.
Using a mix of theoretical and computational approaches, Bogdanovic tries to predict the observational signatures of events like the black-hole-devouring-star scenario described above, also known as a "tidal disruption"— or two supermassive black holes merging, another of her interests. Such events would have a distinct signature to someone analyzing data from a ground-based or a space-based observatory.
Tidal disruptions are rare cosmic occurrences.
Astrophysicists have calculated that a Milky Way-like galaxy stages the disruption of a star only once in about 10,000 years. The luminous flare of light, on the other hand, can fade away in only a few years. This difference in timescale highlights the observational challenge in pinpointing such events in the sky and underlines the importance of astronomical surveys that monitor vast numbers of galaxies at the same time.
So far, only a few dozen of these characteristic flare signatures have been observed and deemed "candidates" for tidal disruptions. But with data from PanSTARRS, Galex, the Palomar Transient Factory and other upcoming astronomical surveys becoming available to scientists, Bogdanovic believes this scarcity will change dramatically.
"As opposed to a few dozen that have been found over the past 10 years, now imagine hundreds per year — that's a huge difference!" she said. "It means that we will be able to build a varied sample of stars of different types being disrupted by supermassive black holes."
With hundreds of such events to explore, astrophysicists' understanding of black holes and the stars around them would advance by leaps and bounds, helping determine some key aspects of galactic physics.
"A diversity in the type of disrupted stars tells us something about the makeup of the star clusters in the centers of galaxies," Bodganovic said. "It may give us an idea about how many main sequence stars, how many red giants, or white dwarf stars are there on average."
It also tells us something about the population and properties of supermassive black holes that are doing the disrupting.
"We use these observations as a window of opportunity to learn important things about the black holes and their host galaxies," she continued. "Once the tidal disruption flare dims below some threshold luminosity that can be seen in observations, the window closes for that particular galaxy."
In a recent paper submitted to the Astrophysical Journal, Bogdanovic, working with Roseanne Cheng (Center for Relativistic Astrophysics at Georgia Tech) and Pau Amaro-Seoane (Albert Einstein Institute in Potsdam, Germany), considered the tidal disruption of a red giant star by a supermassive black hole using computer modeling.
The paper comes on the heels of the discovery of a tidal disruption event in which a black hole disrupted a helium-rich stellar core, thought to be a remnant of a red giant star, named PS1-10jh, 2.7 billion light years from Earth.
The sequence of events they described aims to explain some unusual aspects of the observational signatures associated with this event, such as the absence of the hydrogen emission lines from the spectrum of PS1-10jh.
As a follow-up to this theoretical study, the team has been running simulations on Georgia Tech's Keeneland supercomputer, in addition to as Stampede and Kraken. The simulations reconstruct the chain of events by which a stellar core, similar to the remnant of a tidally disrupted red giant star, might evolve under the gravitational tides of a massive black hole.
"Calculating the messy interplay between hydrodynamics and gravity is feasible on a human timescale only with a supercomputer," Cheng said. "Because we have control over this virtual experiment and can repeat it, fast forward, or rewind as needed, we can examine the tidal disruption process from many perspectives. This in turn allows us to determine and quantify the most important physical processes at play."
The research shows how computer simulations complement and constrain theory and observation.
"There are many situations in astrophysics where we cannot get insight into a sequence of events that played out without simulations," Bogdanovic said. "We cannot stand next to the black hole and look at how it accretes gas. So we use simulations to learn about these distant and extreme environments."
One of Bogdanovic's goals is to use the knowledge gained from simulations to decode the signatures of observed tidal disruption events.
"The most recent data on tidal disruption events is already outpacing theoretical understanding and calling for the development of a new generation of models," she explained. "The new, better quality data indicates that there is a great diversity among the tidal disruption candidates. This is contrary to our perception, based on earlier epochs of observation, that they are a relatively uniform class of events. We are yet to understand what causes these differences in observational appearance and computer simulations are guaranteed to be an important part of this journey."
INFORMATION:
Cosmic slurp
Georgia Tech researchers use NSF XSEDE supercomputers to understand and predict how black holes swallow stars
2014-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify children with emotional behavior difficulties
2014-04-14
Research on children orphaned by HIV/AIDS in South Africa may provide insight on how to identify and help children with emotional behavior issues in other areas of the world, which may have limited access to healthcare and further research that could lead to successful interventions.
A report on the global AIDS epidemic published by the United Nations mentions that due to the HIV/AIDS pandemic, which has left 12 million children orphaned in Sub-Saharan African, children are at an increased risk for mental health problems.
"There has been a big push to understand what ...
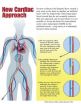
Henry Ford Hospital hits new heart valve surgery milestone
2014-04-14
DETROIT – Doctors at Henry Ford Hospital reached a medical milestone April 3, performing the 25th successful transcatheter valve replacement using a novel way to access the heart.
Henry Ford is the only hospital in the United States performing the unique procedure called transcaval valve replacement, which accesses the heart by temporarily connecting major blood vessels.
Northern Michigan resident Viola Waller, 80, underwent Henry Ford's first transcaval procedure on July 3, 2013 when traditional valve replacement was not medically viable.
"Nobody could help me here," ...
Dog ownership benefits families of children with autism, MU researcher finds
2014-04-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. –Many families face the decision of whether to get a dog. For families of children with autism, the decision can be even more challenging. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has studied dog ownership decisions in families of children with autism and found, regardless of whether they owned dogs, the parents reported the benefits of dog ownership included companionship, stress relief and opportunities for their children to learn responsibility.
"Children with autism spectrum disorders often struggle with interacting with others, which can make it difficult ...
Rare bone diseases and their dental, oral and craniofacial manifestations
2014-04-14
Alexandria, Va., USA – The International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) have published a paper titled "Rare Bone Diseases and Their Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Manifestations." The complete review by researchers Sunday O. Akintoye, Andrea B. Burke, Alison M. Boyce, Michael Collins, Brian L. Foster, Rachel I. Gafni, Janice S. Lee, Mary Scott Ramnitz, Martha J. Somerman and J. Timothy Wright is published in the OnlineFirst portion of the IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research (JDR).
Hereditary diseases affecting the skeleton are heterogeneous ...
Researchers describe 4 new species of 'killer sponges' from the deep sea
2014-04-14
MOSS LANDING, CA — Killer sponges sound like creatures from a B-grade horror movie. In fact, they thrive in the lightless depths of the deep sea. Scientists first discovered that some sponges are carnivorous about 20 years ago. Since then only seven carnivorous species have been found in all of the northeastern Pacific. A new paper authored by MBARI marine biologist Lonny Lundsten and two Canadian researchers describes four new species of carnivorous sponges living on the deep seafloor, from the Pacific Northwest to Baja California.
A far cry from your basic kitchen sponge, ...
Babies prefer fairness -- but only if it benefits them -- in choosing a playmate
2014-04-14
A couple of years ago a University of Washington researcher who studies how children develop social behaviors like kindness and generosity noticed something odd. The 15-month-old infants in her experiments seemed to be playing favorites among the researchers on her team, being more inclined to share toys or play with some researchers than others.
"It's not like one experimenter was nicer or friendlier to the babies – we control for factors like that," said Jessica Sommerville, a UW associate professor of psychology. She took a closer look at the data and realized that ...
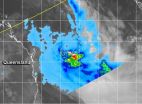
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Ita over the Coral Sea
2014-04-14
Tropical Cyclone Ita made landfall in northeastern Queensland, Australia on April 11 as a powerful Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale, moved south and re-emerged in the Coral Sea on April 14 where NASA's TRMM and NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP Satellites captured imagery of the weakened storm.
The VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a visible look at Ita's elongating structure on April 14 at 4:12 UTC/12:12. The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of ...
Website information on colon cancer too complex, fails to address key concerns
2014-04-14
DALLAS – April 14, 2014 – Popular web information on colorectal cancer is too difficult for most lay people to read and doesn't address the appropriate risks to and concerns of patients, a study by UT Southwestern Medical Center gastroenterologists suggests.
In a review of a dozen popular websites, most of the online patient education materials for colorectal cancer screening were written beyond the recommended sixth-grade reading level, while content on the sites failed to address key risks, as well as the barriers to and benefits of screening, according to the study's ...
Beam on target!
2014-04-14
Late on April 1, the crown jewel of the Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility ("Jefferson Lab") sparkled its way into a new era. Following an upgrade of the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility, the CEBAF accelerator delivered the highest-energy electron beams it has ever produced into a target in an experimental hall, recording the first data of the 12 GeV era. The machine sent electrons around the racetrack three times (known as "3-pass" beam), resulting in 6.11 GeV electrons at 2 nanoAmps average current for more than an hour.
"This ...
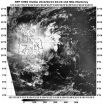
NASA sees remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah over Southern Philippines
2014-04-14
Tropical Depression Peipah has been very stubborn and has moved over the southern and central Philippines bringing clouds, showers and gusty winds. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured an image that showed Peipah's clouds covering the Visayas and Mindanao regions of the country.
The VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a visible look at the remnant clouds associated with former Tropical Depression Peipah on April 14 at 4:24 UTC/12:24 a.m. EDT. The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument collects visible and infrared ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
[Press-News.org] Cosmic slurpGeorgia Tech researchers use NSF XSEDE supercomputers to understand and predict how black holes swallow stars