(Press-News.org) By solving a long standing scientific mystery, the common saying "you just hit a nerve" might need to be updated to "you just hit a Merkel cell," jokes Jianguo Gu, PhD, a pain researcher at the University of Cincinnati (UC).
That's because Gu and his research colleagues have proved that Merkel cells— which contact many sensory nerve endings in the skin—are the initial sites for sensing touch.
"Scientists have spent over a century trying to understand the function of this specialized skin cell and now we are the first to know … we've proved the Merkel cell to be a primary point of tactile detection," Gu, principal investigator and a professor in UC's department of anesthesiology, says of their research study published in the April 15 edition of Cell, a leading scientific journal.
Of all the five senses, touch, Gu says, has been the least understood by science—especially in relation to the Merkel cell, discovered by Friedrich Sigmund Merkel in 1875.
"It's been a great debate because for over two centuries nobody really knew what function this cell had," Gu says, adding that while some scientists—including him—suspected that the Merkel cell was related to touch because of the high abundance of these cells in the ridges of fingertips, the lips and other touch sensitive spots throughout the body; others dismissed the cell as not related to sensing touch at all.
To prove their hypothesis that Merkel cells were indeed the very foundation of touch, Gu's team—which included UC postgraduate fellow Ryo Ikeda, PhD—studied Merkel cells in rat whisker hair follicles , because the hair follicles are functionally similar to human fingertips and have high abundance of Merkel cells. What they found was that the cells immediately fired up in response to gentle touch of whiskers.
"There was a marked response in Merkel cells; the recording trace 'spiked'. With non-Merkel cells you don't get anything," says Ikeda.
What they also found, and of equal importance, both say, was that gentle touch makes Merkel cells to fire "action potentials" and this mechano-electrical transduction was through a receptor/ion channel called the Piezo2.
"The implications here are profound," Gu says, pointing to the clinical applications of treating and preventing disease states that affect touch such as diabetes and fibromyalgia and pathological conditions such as peripheral neuropathy. Abnormal touch sensation, he says, can also be a side effect of many medical treatments such as with chemotherapy.
The discovery also has relevance to those who are blind and rely on touch to navigate a sighted world.
"This is a paradigm shift in the entire field," Gu says, pointing to touch as also indispensable for environmental exploration, tactile discrimination and other tasks in life such as modern social interaction.
"Think of the cellphone. You can hardly fit into social life without good touch sensation."
INFORMATION:
Funding for this research was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
UC research illuminates 'touchy' subject
2014-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Predicting bioavailable cadmium levels in soils
2014-04-15
New Zealand's pastoral landscapes are some of the loveliest in the world, but they also contain a hidden threat. Many of the country's pasture soils have become enriched in cadmium. Grasses take up this toxic heavy metal, which is then eaten by the cattle and sheep that graze them. The problem is not unique to New Zealand; cadmium-enriched soils being reported worldwide.
The concern is that if cadmium concentrations rise to unsafe levels in meat and dairy products, human health and New Zealand's agricultural economy could be jeopardized. That so far hasn't happened.
But, ...
Remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah still raining on Philippines
2014-04-15
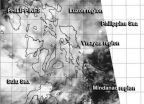
Several regions in the south and central Philippines have flood advisories as the remnants of now dissipated Tropical Depression Peipah continue to linger over the country. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite got a look at the remnant clouds from its orbit in space on April 15.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a look at Peipah's remnant clouds on April 15 at 5:44 a.m. EDT. VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. The VIIRS ...
Study examines Vitamin D deficiency and cognition relationship
2014-04-15
WINSTON-SALEM – April 15, 2014 – Vitamin D deficiency and cognitive impairment are common in older adults, but there isn't a lot of conclusive research into whether there's a relationship between the two.
A new study from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center published online ahead of print this month in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society enhances the existing literature on the subject.
"This study provides increasing evidence that suggests there is an association between low vitamin D levels and cognitive decline over time," said lead author Valerie Wilson, ...
NASA's TRMM Satellite adds up Tropical Cyclone Ita's Australian soaking
2014-04-15
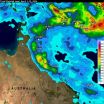
After coming ashore on April 11, Tropical Cyclone Ita dropped heavy rainfall over the weekend that caused flooding in many areas of northeastern Australia's state of Queensland. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM gathered data on rainfall that was used to create a rainfall map at NASA.
TRMM is a satellite managed by both NASA and JAXA, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Hal Pierce created a TRMM-based near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). The TMPA precipitation ...
The key to easy asthma diagnosis is in the blood
2014-04-15
MADISON, Wis. — Using just a single drop of blood, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers has developed a faster, cheaper and more accurate tool for diagnosing even mild cases of asthma.
This handheld technology — which takes advantage of a previously unknown correlation between asthmatic patients and the most abundant type of white blood cells in the body — means doctors could diagnose asthma even if their patients are not experiencing symptoms during their visit to the clinic.
The team described its findings in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
Girls' mental health suffers when romances unfold differently than they imagined
2014-04-15
WASHINGTON, DC, April 15, 2014 — A new study reveals that for adolescent girls, having a romantic relationship play out differently than they imagined it would has negative implications for their mental health.
"I found that girls' risk of severe depression, thoughts of suicide, and suicide attempt increase the more their relationships diverge from what they imagined," said the study's author Brian Soller, an assistant professor of sociology and a senior fellow of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico.
"Conversely, ...
Genetic pre-disposition toward exercise and mental development may be linked
2014-04-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. – University of Missouri researchers have previously shown that a genetic pre-disposition to be more or less motivated to exercise exists. In a new study, Frank Booth, a professor in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, has found a potential link between the genetic pre-disposition for high levels of exercise motivation and the speed at which mental maturation occurs.
For his study, Booth selectively bred rats that exhibited traits of either extreme activity or extreme laziness. Booth then put the rats in cages with running wheels and measured how much ...
How mothers help children explore right and wrong
2014-04-15
Montreal, April 15, 2014 — There's no question that mothers want their children to grow up to be good people — but less is known about how they actually help their offspring sort out different types of moral issues.
According to a new study published in Developmental Psychology and led by Holly Recchia, assistant professor in Concordia's Department of Education and the Centre for Research in Human Development, many mums talk to their kids in ways that help them understand moral missteps.
The study — co-written by Cecilia Wainryb, Stacia Bourne and Monisha Pasupathi ...
Biologists develop nanosensors to visualize movements and distribution of plant hormone
2014-04-15
Biologists at UC San Diego have succeeded in visualizing the movement within plants of a key hormone responsible for growth and resistance to drought. The achievement will allow researchers to conduct further studies to determine how the hormone helps plants respond to drought and other environmental stresses driven by the continuing increase in the atmosphere's carbon dioxide, or CO2, concentration.
A paper describing their achievement appears in the April 15 issue of the scientific journal eLife and is accessible at: http://elife.elifesciences.org/lookup/doi/10.7554/elife.01739 ...
Pharmacist-led interventions show high success rates for post-stroke care
2014-04-15
A new study from the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry is looking at nurse- and pharmacist-led interventions to improve the standard of care for patients who have suffered minor stroke or transient ischemic attack, also known as "mini stoke."
"What we were finding was that six months or 12 months after their stroke, a lot of patients still had uncontrolled blood pressure and uncontrolled cholesterol," said Finlay McAlister (MD '90), lead author of the study. "[This factor] puts the patients at an increased risk of recurrent events, including strokes, heart attacks, amputation ...