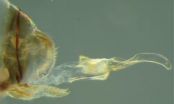
(Press-News.org) Researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on April 17 have discovered little-known cave insects with rather novel sex lives. The Brazilian insects, which represent four distinct but related species in the genus Neotrogla, are the first example of an animal with sex-reversed genitalia.
"Although sex-role reversal has been identified in several different animals, Neotrogla is the only example in which the intromittent organ is also reversed," says Kazunori Yoshizawa from Hokkaido University in Japan.
During copulation, which lasts an impressive 40 to 70 hours, female insects insert an elaborate, penis-like organ into males' much-reduced, vagina-like opening. The researchers speculate that the insects' sex organs and sex-role reversal may have been driven over evolutionary time by the resource-poor cave environment in which the bugs live. Males of the genus provide females with nutritious seminal gifts in addition to sperm, making it advantageous for females to mate at a higher rate.
At first, Rodrigo Ferreira from the Federal University of Lavras in Brazil was focused on a description of species in the cave environment where Neotrogla lives. He sent specimens off to insect specialist Charles Lienhard in Geneva, who recognized them as a new genus. Lienhard also discovered the females' very impressive penis-like organs.
Yoshizawa joined the team to take a closer look. To learn more, the researchers observed the mating behavior of all four species to find that the penis-like structure, termed the gynosome, is inserted into males and used to receive generous capsules of nourishment and sperm. Once inside a male, the membranous part of the female gynosome inflates and numerous spines internally anchor the two insects together.
In one instance, when the researchers attempted to pull a male and female apart, the male's abdomen was ripped from the thorax without breaking the genital coupling. In other words, it appears that females can hold males very tightly indeed.
The findings pave the way for interesting studies in these insects to learn what makes them so special. Neotrogla offers new opportunities to test ideas about sexual selection, conflict between the sexes, and the evolution of novelty, the researchers say.
"It will be important to unveil why, among many sex-role-reversed animals, only Neotrogla evolved the elaborated female penis," says Yoshitaka Kamimura from Keio University in Japan. For that, the researchers will look into studies of behavior, physiology, and more. First on the list, they say, is to establish a healthy population of the insects in the lab.
INFORMATION:
Current Biology, Yoshizawa et al.: "Female penis, male vagina, and their correlated evolution in a cave insect.
In sex-reversed cave insects, females have the penises
2014-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows lasting effects of drought in rainy eastern US
2014-04-17
This spring, more than 40 percent of the western U.S. is in a drought that the USDA deems "severe" or "exceptional." The same was true in 2013. In 2012, drought even spread to the humid east.
It's easy to assume that a 3-year drought is an inconsequential blip on the radar for ecosystems that develop over centuries to millennia. But new research just released in Ecological Monographs shows how short-lived but severe climatic events can trigger cascades of ecosystem change that last for centuries.
Some of the most compelling evidence of how ecosystems respond to drought ...
New technique detects microscopic diabetes-related eye damage
2014-04-17
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- Indiana University researchers have detected new early-warning signs of the potential loss of sight associated with diabetes. This discovery could have far-reaching implications for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy, potentially impacting the care of over 25 million Americans.
"We had not expected to see such striking changes to the retinas at such early stages," said Ann Elsner, professor and associate dean in the IU School of Optometry and lead author of the study. "We set out to study the early signs, in volunteer research subjects ...
Rapid and accurate mRNA detection in plant tissues
2014-04-17
Gene expression is the process whereby the genetic information of DNA is used to manufacture functional products, such as proteins, which have numerous different functions in living organisms. Messenger RNA (mRNA) serves as an important intermediary during gene expression, by relating the genetic information of DNA to the molecular mechanisms involved in manufacturing proteins.
By examining the different types and amounts of mRNA molecules present in an organism at a given time, researchers can determine which specific genes are being expressed. This, in turn, offers ...
IU cognitive scientists use 'I spy' to show spoken language helps direct children's eyes
2014-04-17
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- In a new study, Indiana University cognitive scientists Catarina Vales and Linda Smith demonstrate that children spot objects more quickly when prompted by words than if they are only prompted by images.
Language, the study suggests, is transformative: More so than images, spoken language taps into children's cognitive system, enhancing their ability to learn and to navigate cluttered environments. As such the study, published last week in the journal Developmental Science, opens up new avenues for research into the way language might shape the course ...
Radiation therapy for cervical cancer increases risk for colorectal cancer
2014-04-17
Researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston are the first to recommend that young women treated with radiation for cervical cancer should begin colorectal cancer screening earlier than traditionally recommended.
The UTMB researchers, finding a high incidence of secondary colorectal cancers among cervical cancer survivors treated with radiation, offer new recommendations that the younger women in this group begin colorectal cancer screening about eight years after their initial cervical cancer diagnosis instead of waiting until age 50. The study ...
Stanford biologists help solve fungal mysteries
2014-04-17
Pine forests are chock full of wild animals and plant life, but there's an invisible machine underground. Huge populations of fungi are churning away in the soil, decomposing organic matter and releasing carbon into the atmosphere.
Despite the vital role these fungi play in ecological systems, their identities have only now been revealed. A Stanford-led team of scientists has generated a genetic map of more than 10,000 species of fungi across North America. The work was published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Fungi are much more important ...
Genetic study tackles mystery of slow plant domestications
2014-04-17
"The Modern View of Domestication," a special feature of The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) published April 29, raises a number of startling questions about a transition in our deep history that most of us take for granted. At the end of the last Ice Age, people in many spots around the globe shifted from hunting animals and gathering fruits and tubers to cultivating livestock and plants.
It seems so straightforward and yet the more scientists learn, the more complex the story becomes. Recently, geneticists and archeologists working on domestication ...
The story of animal domestication retold
2014-04-17
Many of our ideas about domestication derive from Charles Darwin, whose ideas in turn were strongly influenced by British animal-breeding practices during the 19th century, a period when landowners vigorously pursued systematic livestock improvement.
It is from Darwin that we inherit the ideas that domestication involved isolation of captive animals from wild species and total human control over breeding and animal care.
But animal management in this industrial setting has been applied too broadly in time and space, said Fiona Marshall, PhD, professor of anthropology ...
Study finds adverse respiratory outcomes for older people with COPD taking benzodiazepines
2014-04-17
TORONTO, April 17, 2014—A group of drugs commonly prescribed for insomnia, anxiety and breathing issues "significantly increase the risk" that older people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, need to visit a doctor or Emergency Department for respiratory reasons, new research has found.
Benzodiazepines, such as Ativan or Xanax, may actually contribute to respiratory problems, such as depressing breathing ability and pneumonia, in these patients, said Dr. Nicholas Vozoris, a respirologist at St. Michael's Hospital.
Dr. Vozoris said the findings are significant, ...
Wine, Research and Crowdfunding: Italian Winemaker Roberto Cipresso Hits on Indiegogo
2014-04-17
One week has gone since the first crowdfunding campaign by a multi-awarded winemaker was launched, and the results are promising for Roberto Cipresso. Fifth in the TOP 10 "Popular Now - Food" on Indiegogo and above all with more than the 6% of the final budget already raised.
After all it is not easy not to be fascinated by the possibility to take part to the remaking of an ancient wine, supporting the research of the forty-six years old winemaker borne in Bassano del Grappa (Italy). Looking at Roberto Cipresso while at his stand at Vinitaly 2014 tells to a bunch of ...