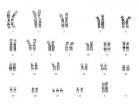
(Press-News.org) Occurring in about one per eight hundred births, Down syndrome - or trisomy 21 - is the most frequent genetic cause of intellectual disability. It results from a chromosomal abnormality where cells of affected individuals contain a third copy of chromosome 21 (1% of the human genome). A study conducted by Stylianos Antonarakis and his team in the Department of Genetic Medicine and Development at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) Faculty of Medicine, published in Nature, shed light on how the extra chromosome 21 upsets the equilibrium of the entire genome, causing a wide variety of pathologies.
Despite much research, the exact mechanisms causing the various symptoms associated with Down syndrome remain a mystery. According to a hypothesis called «gene dosage disequilibrium», the presence of a third chromosome 21 could influence the expression of all the other genes in the genome. That is, this extra genetic material could disrupt the process through which information carried in the genes is decoded, therefore modifying the cellular function.
Based on this hypothesis, several research groups have tried, so far without success, to identify changes in gene expression within trisomic cells and link them with symptoms seen in patients. However, as the level of most gene expression varies from one person to another, it is extremely difficult to discriminate between changes exclusively linked to trisomy 21 and those due to natural variation between individuals.
Comparing Identical Twins
At UNIGE, Stylianos Antonarakis's team has the unique opportunity to examine the genomes of two identical twins with the exact same genetic makeup, except for an extra chromosome 21 present in one of them. Indeed, the chromosome 21 distribution error can take place during an early cellular division, after the original fertilized egg splits in two.
To compare gene expression levels between the twins, UNIGE researchers used recent, high-throughput sequencing technologies and other biotechnological tools developed within the Department of Genetic Medicine and Development, or in collaboration with scientists in Strasbourg, Barcelona, Amsterdam, and Seattle. They were thus able to eliminate interindividual variations and identify the changes in gene expression exclusively due to trisomy 21.
Small chromosome, big consequences
The researchers noticed that the expression of genes located on all the other chromosomes (outside of chromosome 21) were disturbed in trisomic cells. «We were very surprised by this result», explains Audrey Letourneau, who co-authored this study. «It does seem that this extra little chromosome has a huge influence on the entire genome».
Generally speaking, chromosomes are divided into domains that contain genes with rather similar levels of RNA production. RNA is the molecule which transmits the information contained in DNA, before this information is translated into proteins with precise functions. In the twin with Down syndrome, the domains are sometimes over-expressed, and sometimes under-expressed when compared with the healthy twin.
By comparing their results with data previously published by other research groups, UNIGE researchers noticed that this specific chromosomes organization correlates with DNA position in the cell nucleus. Therefore, domains over-expressed in the twin with Down syndrome correspond to portions of DNA known to primarily interact with the nucleus periphery.
This study therefore shows for the first time that the DNA position in the nucleus or the biochemical characteristics of DNA-proteins interactions in the trisomic cells is modified, leading to changes in the gene expression profile. Federico Santoni, who co-authored this study, notes that, «These changes do not only affect chromosome 21, but the entire genome. The presence of about 1% of extra genetic material in the trisomic cells hence modifies the function of the whole genome, and disrupts the general equilibrium of gene expression.» «We could make an analogy with climate change», adds Professor Antonarakis. «Even if the temperature rises by only one or two degrees, it will rain a lot less in the tropics, and a lot more in temperate zones. Global climate equilibrium can thus be disrupted by a tiny element.»
This study opens the door to a new way of understanding the molecular mechanisms that explain the symptoms of Down syndrome. The UNIGE team will now continue its research to understand molecular mechanisms at stake, and link this disrupted gene expression with the phenotypes associated with Down syndrome. The end goal of this research is to find ways to revert the dysregulation of cellular gene expression back to normal, with the objective to correct the cellular abnormalities in this disease. Progress in this field could also be applied to other diseases with genome imbalance.
INFORMATION:
This study, which lasted several years, received financial support from the Swiss National Science Foundation (FNS) and the European Research Council (ERC).
Trisomy 21: How an extra little chromosome throws the entire genome off balance
2014-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Re-emergence of Ebola focuses need for global surveillance strategies
2014-04-17
NEW YORK – April 17, 2014 – EcoHealth Alliance, a nonprofit organization that focuses on conservation and global public health issues, published a comprehensive review today examining the current state of knowledge of the deadly Ebola and Marburg virus. The review calls for improved global surveillance strategies to combat the emergence of infectious diseases such as the recent outbreak of Ebola in West Africa that has claimed the lives of 122 people in the countries of Guinea and Liberia. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the deadly Ebola virus can cause ...
Long-term effects of battle-related 'blast plus impact' concussive TBI in US military
2014-04-17
New Rochelle, NY, April 17, 2014—U.S. military personnel who served in Iraq and Afghanistan and suffered "blast plus impact" concussive traumatic brain injury (TBI) were compared to military personnel without TBI who were evacuated for other medical reasons. Differences in measures of overall disability, cognitive function, post-traumatic stress, and depression 6-12 months after injury are reported in an article in Journal of Neurotrauma, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Neurotrauma website ...
Fish consumption advisories fail to cover all types of contaminants
2014-04-17
A new modeling study suggests that fish consumption advisories for expecting mothers are ineffective in reducing infant exposure to long-lived contaminants like persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
The study, performed by a team of researchers including University of Toronto Scarborough PhD student Matt Binnington and Professor Frank Wania, looks at how different levels of environmental contamination, a mother's compliance with advisories, and the behavior of chemicals in the body influenced exposure in her children.
Their model estimates that women who stop eating ...
Proper stem cell function requires hydrogen sulfide
2014-04-17
Stem cells in bone marrow need to produce hydrogen sulfide in order to properly multiply and form bone tissue, according to a new study from the Center for Craniofacial Molecular Biology at the Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC.
Professor Songtao Shi, principal investigator on the project, said the presence of hydrogen sulfide produced by the cells governs the flow of calcium ions. The essential ions activate a chain of cellular signals that results in osteogenesis, or the creation of new bone tissue, and keeps the breakdown of old bone tissue at a proper level.
Conversely, ...
Orchid named after UC Riverside researcher
2014-04-17
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — One day about eight years ago, Katia Silvera, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Riverside, and her father were on a field trip in a mountainous area in central Panama when they stumbled upon an orchid they had never seen before.
Unable to identify it, they contacted German Carnevali, a world authority on orchids. The orchid turned out to be an unnamed species. So Carnevali recently named it after the Silveras: Lophiaris silverarum.
"Lophiaris" is the genus name, comprising about 40 species in the world. Carnevali, the director ...
New MRSA superbug emerges in Brazil
2014-04-17
An international research team led by Cesar A. Arias, M.D., Ph.D., at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) has identified a new superbug that caused a bloodstream infection in a Brazilian patient. The report appeared in the April 17 issue of The New England Journal of Medicine.
The new superbug is part of a class of highly-resistant bacteria known as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA, which is a major cause of hospital and community-associated infections. The superbug has also acquired high levels of resistance to vancomycin, ...
Study IDs new cause of brain bleeding immediately after stroke
2014-04-17
Irvine, Calif., April 17, 2014 — By discovering a new mechanism that allows blood to enter the brain immediately after a stroke, researchers at UC Irvine and the Salk Institute have opened the door to new therapies that may limit or prevent stroke-induced brain damage.
A complex and devastating neurological condition, stroke is the fourth-leading cause of death and primary reason for disability in the U.S. The blood-brain barrier is severely damaged in a stroke and lets blood-borne material into the brain, causing the permanent deficits in movement and cognition seen ...
20 years of data shows treatment technique improvement for advanced abdominal cancer
2014-04-17
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – April 17, 2014 – Meaningful long-term survival is possible for selected patients suffering from advanced cancer of the abdomen when treated with cytoreductive surgery with Hyperthermic IntraPeritoneal Chemotherapy, or HIPEC, according to a first-of-its-size analysis by physicians at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
Wake Forest Baptist has the largest reported, single-center experience with cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC, said lead author Edward A. Levine, M.D., and analysis of 20 years' worth of patient data shows that outcomes have clearly improved ...
Surprising material could play role in saving energy
2014-04-17
One strategy for addressing the world's energy crisis is to stop wasting so much energy when producing and using it, which can happen in coal-fired power plants or transportation. Nearly two-thirds of energy input is lost as waste heat.
Now Northwestern University scientists have discovered a surprising material that is the best in the world at converting waste heat to useful electricity. This outstanding property could be exploited in solid-state thermoelectric devices in a variety of industries, with potentially enormous energy savings.
An interdisciplinary team led ...
How vision makes sure that little fish do not get carried away
2014-04-17
This news release is available in German. Our eyes not only enable us to recognise objects; they also provide us with a continuous stream of information about our own movements. Whether we run, turn around, fall or sit still in a car – the world glides by us and leaves a characteristic motion trace on our retinas. Seemingly without effort, our brain calculates self-motion from this "optic flow". This way, we can maintain a stable position and a steady gaze during our own movements. Together with biologists from the University of Freiburg, scientists from the Max Planck ...