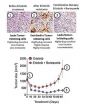
(Press-News.org) Most drugs used to treat lung, breast and pancreatic cancers also promote drug-resistance and ultimately spur tumor growth. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have discovered a molecule, or biomarker, called CD61 on the surface of drug-resistant tumors that appears responsible for inducing tumor metastasis by enhancing the stem cell-like properties of cancer cells.
The findings, published in the April 20, 2014 online issue of Nature Cell Biology, may point to new therapeutic opportunities for reversing drug resistance in a range of cancers, including those in the lung, pancreas and breast.
"There are a number of drugs that patients respond to during their initial cancer treatment, but relapse occurs when cancer cells become drug-resistant," said David Cheresh, PhD, Distinguished Professor of Pathology and UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center associate director for Innovation and Industry Alliances. "We looked at the cells before and after they became resistant and asked, 'What has changed in the cells?'"
Cheresh and colleagues investigated how tumor cells become resistant to drugs like erlotinib or lapatinib, known as receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and commonly used in standard cancer therapies. They found that as drug resistance occurs, tumor cells acquire stem cell-like properties that give them the capacity to survive throughout the body and essentially ignore the drugs.
Specifically, the scientists delineated the molecular pathway that facilitates both cancer stemness and drug resistance, and were able to identify existing drugs that exploit this pathway. These drugs not only reverse stem cell-like properties of tumors, but also appear to re-sensitize tumors to drugs that the cancer cells had developed resistance to.
"The good news is that we've uncovered a previously undefined pathway that the tumor cells use to transform into cancer stem cells and that enable tumors to become resistant to commonly used cancer drugs," said Cheresh.
Based on these findings, Hatim Husain, MD, an assistant professor who treats lung and brain cancer patients at Moores Cancer Center, has designed a clinical trial to attack this pathway in patients whose tumors are drug-resistant. The trial will be open to patients with lung cancer who have experienced cancer progression and drug resistance to erlotinib. It is expected to begin in the next year.
"Resistance builds to targeted therapies against cancer, and we have furthered our understanding of the mechanisms by which that happens," said Husain. "Based on these research findings we now better understand how to exploit the 'Achilles heel' of these drug-resistant tumors. Treatments will evolve into combinational therapies where one may keep the disease under control and delay resistance mechanisms from occurring for extended periods of time."
Although the trial is expected to begin with patients who have already experienced drug resistance, Husain hopes to extend the study to reach patients in earlier stages to prevent initial resistance.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Laetitia Seguin, Aleksandra Franovic, M. Fernanda Camargo, Jacqueline
Lesperance, Kathryn C. Elliott, Mayra Yebra, Ainhoa Mielgo, Jay S. Desgrosellier, Sudarshan Anand and Sara M. Weis, UCSD Department of Pathology and UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center; Shumei Kato, UCSD Division of Hematology/Oncology; Andrew Lowy, UCSD Department of Surgery, Division of Surgical Oncology; Tina Cascone, Lixia Diao, Jing Wang, Ignacio I. Wistuba and John V. Heymach, University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center; and Scott M. Lippman, UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center.
Funding for this research came, in part, from National Institutes of Health grants CA45726, CA168692, HL57900, R37-50286 and CA155620, National Cancer Institute grant T32CA121938, the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer ARC and La Fondation Philippe.
Cancer stem cells linked to drug resistance
Discovery of previously undefined molecular pathway is step toward novel clinical trial
2014-04-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study of gut microbes, antibiotics: Clues to improving immunity in premature infants
2014-04-20
Mothers give a newborn baby a gift of germs—germs that help to kick-start the infant's immune system. But antibiotics, used to fend off infection, may paradoxically interrupt a newborn's own immune responses, leaving already-vulnerable premature babies more susceptible to dangerous pathogens.
A new animal study by neonatology researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) sheds light on immunology in newborns by revealing how gut microbes play a crucial role in fostering the rapid production of infection-fighting white blood cells, called granulocytes.
"At ...
Dana-Farber researchers uncover link between Down syndrome and leukemia
2014-04-20
BOSTON –Although doctors have long known that people with Down syndrome have a heightened risk of developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) during childhood, they haven't been able to explain why. Now, a team of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators has uncovered a connection between the two conditions.
In a study posted online today by the journal Nature Genetics, the researchers track the genetic chain of events that links a chromosomal abnormality in Down syndrome to the cellular havoc that occurs in ALL. Their findings are relevant not only to people with ...
Stanford scientists identify source of most cases of invasive bladder cancer
2014-04-20
STANFORD, Calif. — A single type of cell in the lining of the bladder is responsible for most cases of invasive bladder cancer, according to researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Their study, conducted in mice, is the first to pinpoint the normal cell type that can give rise to invasive bladder cancers. It's also the first to show that most bladder cancers and their associated precancerous lesions arise from just one cell, and explains why many human bladder cancers recur after therapy.
"We've learned that, at an intermediate stage during cancer ...
Study casts doubt on climate benefit of biofuels from corn residue
2014-04-20
Lincoln, Neb., April 20, 2014 -- Using corn crop residue to make ethanol and other biofuels reduces soil carbon and can generate more greenhouse gases than gasoline, according to a study published today in the journal Nature Climate Change.
The findings by a University of Nebraska-Lincoln team of researchers cast doubt on whether corn residue can be used to meet federal mandates to ramp up ethanol production and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Corn stover -- the stalks, leaves and cobs in cornfields after harvest -- has been considered a ready resource for cellulosic ...
Score Promotions Opens Florida Office to Better Serve Promotional Product Needs of U.S. Clients
2014-04-20
The Fort Lauderdale, Florida office represents a more concerted push into the U.S. market following the success of the Toronto office and continued growth worldwide", said Tom Greenberg, President.
With the opening of a new office in Florida, promotional product company Score Promotions will be able to offer a number of services and logistical upgrades to its U.S. clients. The expansion comes as the Company celebrates 15 years in business, during which time it has become one of the leading promotional products suppliers in Canada.
Score Promotions continually seeks ...
Scores.fm Gives Sports Fans a Voice
2014-04-20
One thing most sports fans have in common is that they have an opinion about the game and they are willing to share that opinion with anyone who will listen. The problem is finding those like-minded listeners who will appreciate, and even discuss, that opinion. Now a young sports media company is stepping up to provide that audience for anyone who wishes to share their thoughts with the masses.
Scores.fm is an online sports magazine and sports radio station that has gained international recognition. Operated by Scores Media Group, the publishing and broadcasting venture ...
Shea Homes San Diego to Unveil the Most Innovative Architecture at Civita on April 26
2014-04-20
Lucent is introducing dramatic new concepts in vertical architecture, with 36 of 54 homes offering all living space on a single level, surrounded on three sides by walls of windows and balconies. The other 18 homes are two-story penthouses, which feature an upstairs family room and an outdoor deck and fireplace.
Lucent consists of multiple five-story buildings, with either six or 12 homes per building. Ranging from 1,457 to 1,878 square feet, homes at Lucent offer two bedrooms, two to two-and-a-half baths, and a two-car garage located on the ground floor. An interior ...
Teletherm Releases Update to Online Infrared Training Course
2014-04-20
The new update from Teletherm Infrared Systems for their Thermology Certified Online Training Course provides extensively narrated presentations for three major sections in this comprehensive package of twenty modules. The full program offers a convenient way for users and novices, alike, to learn all relevant topics associated with the procedures, science, technology, health evaluations, and applications for thermal imaging. Designed specifically for the biomedical, clinical research and health care fields, subscribers are provided unlimited access to the course site. ...
Underground Herbal Spirit Wins 2014 Booze Brackets
2014-04-20
The several week event, sponsored by BourbonBlog.com, puts liquor brands head-to-head in a 64-brand NCAA basketball tournament style bracket. The fans of each brand vote and brands receiving the most votes move on to the next round.
"We entered both Underground Herbal Spirits and Five Wives Vodka," explained Steve Conlin, managing partner of Ogden's Own. "Both brands made it to the Final Four and had to face each other with Underground moving on to the final."
"While Utah may have the lowest per capita of drinkers, when it comes to passion for local brands, Utah is ...
Attune to Your Soul Energy in the 21 Day Soul Attunement, June 2-22, 2014
2014-04-20
Alicia Isaacs Howes, Soul Connection Expert and Founder of Your Soul Story, is teaching her third-annual 21 Day Soul Attunement programme from June 2 - 22, 2014.
The programme features three weeks and ten hours of daily energetic support, in which Alicia will work with participants to release recurring, negative patterns or mindsets, physical or emotional pains and illusions about their health, relationships and finances.
Brenda Strong, a previous participant in the 21 Day Soul Attunement, says:
"Before the Soul Attunement I felt stuck. It felt like I had been ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
The Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to Charles Manski for incorporating uncertainty into economic research and its application to public policy analysis
Walter Koroshetz joins Dana Foundation as senior advisor
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
Women more likely to choose wine from female winemakers
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
[Press-News.org] Cancer stem cells linked to drug resistanceDiscovery of previously undefined molecular pathway is step toward novel clinical trial