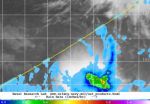
(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Jack may have hurricane-force winds today, April 21, but strong vertical wind shear is expected to weaken the storm. NASA's TRMM satellite passed overhead and saw that the bulk of the storm's rainfall was being pushed south of the center from the wind shear.
Tropical Cyclone Jack formed on Sunday, April 20, near 13.4 south and 91.1 east, and began moving to the south at 6 knots/6.9 mph/11.1 kph. Jack strengthened quickly and hours after its birth, the storm already had maximum sustained winds near 55 knots/63.2 mph/101.9 kph.
On April 21 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Cyclone Jack was moving through the Southern Indian Ocean at hurricane-force with maximum sustained winds near 75 knots/86.3 mph/138.9 kph. Jack was far from land and centered near 16.5 south latitude and 92.9 east longitude. That's about 346 nautical miles/398.0 miles/640.8 km southwest of Cocos Island. Jack was moving to the east-southeast at 10 knots/11.5 mph/18.5 kph.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated multispectral satellite imagery showed Jack continued in the buildup of thunderstorms despite strong vertical wind shear affecting them, and elongating the tropical cyclone to the southeast.
On April 21 at 04:02 UTC/12:02 a.m. EDT the microwave imager aboard NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite was used to find an eye-like feature. By 12:15 UTC/8:15 a.m. EDT TRMM data no longer showed that eye-like feature. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center coupled TRMM data with infrared data from Europe's METEO-7 satellite to show Jack's clouds. That imagery showed how the rainfall was pushed to the south and southeast of the center by vertical wind shear.
Because of the increasing wind shear and the cooler sea surface temperatures in the direction Jack is moving, the storm is expected to weaken and dissipate in three days' time.
INFORMATION: Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees wind shear affecting newborn Tropical Cyclone Jack
2014-04-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taking the pulse of mountain formation in the Andes
2014-04-21
Scientists have long been trying to understand how the Andes and other broad, high-elevation mountain ranges were formed. New research by Carmala Garzione, a professor of earth and environmental sciences at the University of Rochester, and colleagues sheds light on the mystery.
In a paper published in the latest Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Garzione explains that the Altiplano plateau in the central Andes—and most likely the entire mountain range—was formed through a series of rapid growth spurts.
"This study provides increasing evidence that the plateau formed ...
Edible flowers may inhibit chronic diseases
2014-04-21
A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), found that common edible flowers in China are rich in phenolics and have excellent antioxidant capacity. Edible flowers, which have been used in the culinary arts in China for centuries, are receiving renewed interest. Flowers can be used as an essential ingredient in a recipe, provide seasoning to a dish, or simply be used as a garnish. Some of these flowers contain phenolics that have been correlated with anti-inflammatory activity and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease ...
MSU physicists push new Parkinson's treatment toward clinical trials
2014-04-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- The most effective way to tackle debilitating diseases is to punch them at the start and keep them from growing.
Research at Michigan State University, published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, shows that a small "molecular tweezer" keeps proteins from clumping, or aggregating, the first step of neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease.
The results are pushing the promising molecule toward clinical trials and actually becoming a new drug, said Lisa Lapidus, MSU associate professor ...
The anti-inflammatory factory
2014-04-21
Russian scientists, in collaboration with their colleagues from Pittsburgh University, find how lipid mediators are produced. The relevant paper was publish in Nature Chemistry. Lipid mediators are molecules playing an important role in inflammation process. A study devoted to some of them has earned a Nobel prize in 1982.
Mitochondria are known as "cellular power plants", the organelles where oxidation of various substances leads to formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule universally used for storage and transportation of energy inside cells. But this is ...
IU study: Death of public figures provides important opportunities for health education
2014-04-21
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- An Indiana University study of reactions to the 2011 death of Apple co-founder Steve Jobs suggests health communicators have a critical window of opportunity after a public figure dies to disseminate information about disease prevention and detection.
The study, involving a survey of 1,400 adult men and women, found that immediately after Jobs' death, more than a third of survey participants sought information about how he died or about cancer in general, and 7 percent sought information about pancreatic cancer, the disease that took Jobs' life.
Lead ...
Allina Health study shows information sharing between health systems reduces tests
2014-04-21
MINNEAPOLIS – (April 21, 2014) – An Allina Health study published in the current issue of the journal Applied Clinical Informatics showed that a significant number of diagnostic tests and procedures can be avoided if clinicians exchange health information with other health systems.
Allina Health uses Care Everywhere which is a health information exchange tool embedded in the Allina Health electronic health record called Excellian® that is powered by Epic (Epic Systems Corporation, Verona, Wis.) With patient consent, Allina Health providers can use this tool to exchange ...
Regulating legal marijuana could be guided by lessons from alcohol and tobacco, study says
2014-04-21
As U.S. policymakers consider ways to ease prohibitions on marijuana, the public health approaches used to regulate alcohol and tobacco over the past century may provide valuable lessons, according to new RAND Corporation research.
Recent ballot initiatives that legalized marijuana in Colorado and Washington for recreational uses are unprecedented. The move raises important questions about how to best allow the production, sales and the use of marijuana while also working to reduce any related social ills.
A new study published online by the American Journal of Public ...
More questions than answers as mystery of domestication deepens
2014-04-21
We all think we have a rough idea of what happened 12,000 years ago when people at several different spots around the globe brought plants under cultivation and domesticated animals for transport, food or fiber. But how much do we really know?
Recent research suggests less than we think. For example, why did people domesticate a mere dozen or so of the roughly 200,000 species of wild flowering plants? And why only about five of the 148 species of large wild mammalian herbivores or omnivores? And while we're at it, why haven't more species of either plants or animals been ...
NNI researchers discover novel function of protein linked to Alzheimer's disease
2014-04-21
Singapore, 19 April 2014 – A research team led by the National Neuroscience Institute (NNI) has uncovered a novel function of the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP), one of the main pathogenic culprits of Alzheimer's disease. This discovery may help researchers understand how the protein goes awry in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients, and potentially paves the way for the development of innovative therapeutics to improve the brain function of dementia patients.
The findings were published in the prestigious scientific research journal Nature Communications last ...
Financial incentives help economically-disadvantaged pregnant smokers quit and improve fetal growth
2014-04-21
Smoking during pregnancy – particularly among economically-disadvantaged women – leads to a host of poor pregnancy outcomes, including miscarriage, preterm birth, SIDS, and additional adverse effects later in life. Without a formal treatment intervention, women in this population continue to smoke, and their babies suffer. Vermont Center on Behavior and Health Director Stephen Higgins, Ph.D., and colleagues, have developed an effective behavioral economic approach that offers women financial incentives for quitting.
The groups' most recent findings, published online ...