(Press-News.org) Recent projects in two Minnesota cities demonstrate how communities can protect themselves from worsening storms. These projects continue a ten year program in New England and the Midwest providing practical and affordable plans tailored to local conditions.
"Our goal is to help communities begin the steps to protect themselves," said program co-leader Latham Stack, of Syntectic International, Portland, OR. "It's important because storms have already worsened. We help communities move beyond feeling paralyzed from the lack of local information and the sense that the problem is overwhelming."
Recent news stories and White House actions cite the need to adapt to changing conditions. Minneapolis and Victoria, MN, through the Minnehaha Creek Watershed District, took this to heart and asked to be project sites. At these and previous sites in New England, program results consistently show that portions of existing drainage systems are already undersized. At the same time, significant portions of these systems should be adequate for even pessimistic mid-21st century projections.
"Uncertainty in climate projections is not a show-stopper," said Michael Simpson, program co-leader and Chair of Environmental Studies at Antioch University, Keene, NH. "For over a century, engineers have designed drainage systems using models and data that are more uncertain than is generally acknowledged. Preventing loss of life and flood damage was more important than waiting for perfect knowledge that never came anyway. In spite of the uncertainty, these systems perform remarkably well."
According to the Government Financial Officers Association, planning for the future is especially critical when projections are uncertain. By starting to adapt now, communities can spread costs over a number of years. This is easier to afford, especially because significant portions of systems should not require upgrading.
"The decision of how large to build a drainage system has always been a gamble, even ignoring the uncertainty in methods", said Stack. "Designing systems for a certain sized storm is a gamble that the damage from storms exceeding design will cost less than building a system with larger capacity."
For many communities, extreme storms are already exceeding designs more frequently than intended. This is reflected in rising flood insurance costs. Public works departments, emergency responders, and financial resources are stressed beyond capacity. Communities are not always able to recover.
"So the question becomes, how do we respond, as individuals, as communities, and as a nation?" asks Simpson. "Do we use common sense and take responsible steps now, or do we ignore what's in plain sight? We're saying that communities need to act now."
INFORMATION:
A conference on local solutions for climate change, May 19-21 in Manchester, NH, sponsored by Antioch University, is open to anyone interested.
Minnesota projects offer hope and practical help to communities facing more extreme storms
The NOAA-funded projects are models for other communities nationally and internationally
2014-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
False-positive mammogram anxiety has limited impact on women's well-being
2014-04-22
(Lebanon, NH, 4/22/14). Dartmouth researchers have found that the anxiety experienced with a false-positive mammogram is temporary and does not negatively impact a woman's overall well-being. Their findings are reported in "Consequences of False-Positive Screening Mammograms," which was published online in the April 21, 2014 JAMA Internal Medicine
Anywhere from 40 to 60 percent of women who undergo routine screening mammography during a ten-year period will experience a false-positive mammogram. Such mammograms require additional testing, sometimes involving a biopsy, ...
Cannabis chemistry: How scientists test pot for potency and safety (video)
2014-04-22
WASHINGTON, April 22, 2014 — Marijuana is in the headlines as more and more states legalize it for medicinal use or decriminalize it entirely. In the American Chemical Society's (ACS') newest Reactions video, we explain the chemistry behind marijuana's high, and investigate what scientists are doing to ensure that legalized weed won't send users on a bad trip. The video is available at http://youtu.be/4ukdUDCE56c
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The American ...
Researchers identify a mechanism linking bariatric surgery to health benefits
2014-04-22
Bariatric surgery has positive effects not only on weight loss but also on diabetes and heart disease. Researchers at the Sahlgrenska Academy and University of Cincinnati have shown that the health benefits are not caused by a reduction in the stomach size but by increased levels of bile acids in the blood. These findings, reported in Nature, indicate that bile acids could be a new target for treating obesity and diabetes.
Previous research from the Sahlgrenska Academy has demonstrated that obesity surgery is the only effective treatment for obesity and obesity-related ...
NeuroPhage discovers GAIM-changing molecules to combat Alzheimer's and related diseases
2014-04-22
Cambridge, MA, April 22, 2014 – Researchers from NeuroPhage Pharmaceuticals, Inc. have engineered a series of molecules with the potential to treat most neurodegenerative diseases that are characterized by misfolded proteins, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases. These molecules are based on what the Company calls a general amyloid interaction motif, or GAIM, which recognizes a characteristic common to many toxic, misfolded proteins, not just one type of misfolded protein. This approach provides NeuroPhage with an array of therapeutic targets, so that ...
Sleep disorder linked to brain disease
2014-04-22
Researchers at the University of Toronto say a sleep disorder that causes people to act out their dreams is the best current predictor of brain diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
"Rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) is not just a precursor but also a critical warning sign of neurodegeneration that can lead to brain disease," says associate professor and lead author Dr. John Peever. In fact, as many as 80 to 90 per cent of people with RBD will develop a brain disease."
As the name suggests, the disturbance occurs during the rapid-eye-movement (REM) ...
Mysteries of a nearby planetary system's dynamics now are solved
2014-04-22
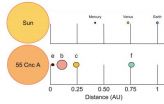
Mysteries of one of the most fascinating nearby planetary systems now have been solved, report authors of a scientific paper to be published by the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society in its early online edition on 22 April 2014. The study, which presents the first viable model for the planetary system orbiting one the first stars discovered to have planets -- the star named 55 Cancri -- was led by Penn State University graduate student Benjamin Nelson in collaboration with faculty at the Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds at Penn State and ...
Protein expression gets the heart pumping
2014-04-22
HOUSTON – (April 22, 2014) – Most people think the development of the heart only happens in the womb, however the days and weeks following birth are full of cellular changes that play a role in the structure and function of the heart. Using mouse models, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have now been able to categorize the alternative splicing (the process in which genes code proteins, determining their role) that takes place during these changes and what mechanisms they affect.
The findings, which appear in Nature Communications, also helped to identify a ...
First brain images of African infants enable research into cognitive effects of nutrition
2014-04-22
Brain activity of babies in developing countries could be monitored from birth to reveal the first signs of cognitive dysfunction, using a new technique piloted by a London-based university collaboration.
The cognitive function of infants can be visualised and tracked more quickly, more accurately and more cheaply using the method, called functional near infra-red spectroscopy (fNIRS), compared to the behavioural assessments Western regions have relied upon for decades.
Professor Clare Elwell, Professor of Medical Physics at University College London (UCL), said: "Brain ...
Scientists discover a new way to enhance nerve growth following injury
2014-04-22
New research published today out of the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain Institute (HBI) uncovers a mechanism to promote growth in damaged nerve cells as a means to restore connections after injury. Dr. Doug Zochodne and his team have discovered a key molecule that directly regulates nerve cell growth in the damaged nervous system. His study was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, with lead authors Drs. Kim Christie and Anand Krishnan.
"We made the surprising discovery that a protein called Retinoblastoma (Rb) is present in adult neurons," ...
Trio @ Sam Leong Road Preview 2nd Preview 2nd Quarter 2014
2014-04-22
Trio @ Sam Leong is a 4 story commercial development that consists of retail shops, entertainment outlets and restaurants. Developed by Singapore listed developer Tee Land, this development is strategically located behind Mustafa and is expected to draw traffic with its city fringe location.
The nearest MRT is Farrer Park MRT station within a 5 minute walk. A Central Business District (CBD), Orchard Road, Marina Bay Sands is only 10 minutes via train or drive.
Trio @ Sam Leong road has a good unit mix of retails shops and restaurants targeted to individual business ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
[Press-News.org] Minnesota projects offer hope and practical help to communities facing more extreme stormsThe NOAA-funded projects are models for other communities nationally and internationally