(Press-News.org) Spectral properties optimization is an important issue for developing schemes to resolve flow fields that are characterized by a wide range of length scales such as turbulent flows and aero acoustic phenomena. The work finished by Dr SUN Zhensheng and his ground provided a novel approach to optimize the dissipation and dispersion properties of a family of tri-diagonal compact schemes. The corresponding paper entitled "A high-resolution, hybrid compact-WENO scheme with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation" was published in Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014 Vol. 57(5).
For the detailed and high-fidelity simulation of compressible flows with a broadband of length scales, the numerical scheme should have spectral-like properties to resolve these small scales. Spectral properties optimization is an effective way to construct schemes with good spectral properties. Concerning the optimization of the spectral properties of a scheme, it is generally accepted the dispersion error should be minimized due to some chosen criteria. However, there are no general guidelines on how the dissipation should be optimized. In the previous work for the optimization of the spectral properties of a scheme, the cost functions are the blending of the dissipation and dispersion errors. As a result, the change of the dissipation properties will deteriorate the already optimized dispersion. Therefore, it would be beneficial if we can control the dissipation and dispersion properties of a scheme separately.
To design such kinds of schemes, a sufficient condition for a family of tri-diagonal compact schemes to have independent dispersion and dissipation is firstly derived. Then, a specific a fourth order compact scheme with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation (MDCD) properties is constructed and analyzed. The dispersion properties of the corresponding scheme are optimized by minimizing an elaborately designed integrated error function while the dissipation is controlled by variation of one free parameter. Finally, the optimized compact scheme is blended with the wide-used weighted essentially non-oscillatory (WENO) scheme to handle the discontinuities for the practical use. Moreover, the approximation dispersion relation (ADR) approach is employed to study the spectral properties of the hybrid scheme to yield the true wave propagation behavior of the nonlinear scheme. The dispersion and dissipation curves of the proposed scheme are shown in the following figure.
The main novelty of the present research is the idea of designing a family of tri-diagonal compact schemes with independent dissipation and dispersion properties. The most important feature of such kinds of scheme is the adjustment of the dissipation will not affect the already optimized dispersion properties. Several benchmark test cases which contains both a broadband of length scales and discontinuities have been carried out to validate the flexible, robustness and less time-consuming of the proposed scheme.
This research was partially supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and a National University Research Grant from Xi'an Research Institute of High-tech. The idea of controlling dissipation and dispersion separately is a breakthrough for the designing of the spectral-like schemes. The researchers suggested this approach to be absorbed in the in-house code for the direct numerical simulation (DNS) and large eddy simulation (LES) of compressible turbulence. The proposed scheme will be effective in extending the well-resolved wave numbers range and more small scale turbulent structures can be captured.
INFORMATION:
See the article: Sun Z S, Hu Y, Luo L, et al. A high-resolution, hybrid compact-WENO scheme with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014 Vol. 57(5): 971-982.
http://phys.scichina.com:8083/sciGe/EN/abstract/abstract508376.shtml
Science China Press Co., Ltd. (SCP) is a scientific journal publishing company of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). For 60 years, SCP takes its mission to present to the world the best achievements by Chinese scientists on various fields of natural sciences researches.
http://www.scichina.com/
A family of compact schemes with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation was developed
2014-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Tween' television programming promotes some stereotypical conceptions of gender roles
2014-04-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The term "tween" denotes a child who is between the ages of 8 and 12 and is used to describe a preadolescent who is "in between" being a child and a teen. This demographic watches more television than any other age group and is considered to be a very lucrative market. Tween television programming consists of two genres: "teen scene" (geared toward girls) and "action-adventure" (geared toward boys). Researchers at the University of Missouri found that these programs could lead tweens to limit their views of their potential roles in society just as they begin ...
How often are unauthorized immigrant workers trafficked and abused?
2014-04-22
Los Angeles, CA (April 22, 2014) Labor trafficking – or recruiting a person for labor through force, fraud, or coercion for involuntary servitude, debt bondage, or even slavery – has been a difficult problem to track among undocumented migrant workers. With unique access to a "hidden population" from one of America's largest Spanish-speaking immigrant destinations, a recent study finds that more than 30% of undocumented migrant laborers in this area are victims of labor trafficking and 55% are victims of other labor abuses.
In this study, published in the May issue of ...
New tool helps doctors better predict, prevent deadly respiratory failure
2014-04-22
A new prediction tool can help doctors better identify patients who are at highest risk for respiratory failure after surgery and therefore prevent the often deadly condition, suggest data from a large multi-center study published in the May issue of Anesthesiology.
Affecting nearly 200,000 Americans a year, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a sudden failure of the lungs caused by a number of issues ranging from smoke inhalation to pneumonia or blood infection. High-risk patients can develop ARDS after surgery. ARDS is difficult to treat once it develops and ...
Minnesota projects offer hope and practical help to communities facing more extreme storms
2014-04-22
Recent projects in two Minnesota cities demonstrate how communities can protect themselves from worsening storms. These projects continue a ten year program in New England and the Midwest providing practical and affordable plans tailored to local conditions.
"Our goal is to help communities begin the steps to protect themselves," said program co-leader Latham Stack, of Syntectic International, Portland, OR. "It's important because storms have already worsened. We help communities move beyond feeling paralyzed from the lack of local information and the sense that the problem ...
False-positive mammogram anxiety has limited impact on women's well-being
2014-04-22
(Lebanon, NH, 4/22/14). Dartmouth researchers have found that the anxiety experienced with a false-positive mammogram is temporary and does not negatively impact a woman's overall well-being. Their findings are reported in "Consequences of False-Positive Screening Mammograms," which was published online in the April 21, 2014 JAMA Internal Medicine
Anywhere from 40 to 60 percent of women who undergo routine screening mammography during a ten-year period will experience a false-positive mammogram. Such mammograms require additional testing, sometimes involving a biopsy, ...
Cannabis chemistry: How scientists test pot for potency and safety (video)
2014-04-22
WASHINGTON, April 22, 2014 — Marijuana is in the headlines as more and more states legalize it for medicinal use or decriminalize it entirely. In the American Chemical Society's (ACS') newest Reactions video, we explain the chemistry behind marijuana's high, and investigate what scientists are doing to ensure that legalized weed won't send users on a bad trip. The video is available at http://youtu.be/4ukdUDCE56c
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The American ...
Researchers identify a mechanism linking bariatric surgery to health benefits
2014-04-22
Bariatric surgery has positive effects not only on weight loss but also on diabetes and heart disease. Researchers at the Sahlgrenska Academy and University of Cincinnati have shown that the health benefits are not caused by a reduction in the stomach size but by increased levels of bile acids in the blood. These findings, reported in Nature, indicate that bile acids could be a new target for treating obesity and diabetes.
Previous research from the Sahlgrenska Academy has demonstrated that obesity surgery is the only effective treatment for obesity and obesity-related ...
NeuroPhage discovers GAIM-changing molecules to combat Alzheimer's and related diseases
2014-04-22
Cambridge, MA, April 22, 2014 – Researchers from NeuroPhage Pharmaceuticals, Inc. have engineered a series of molecules with the potential to treat most neurodegenerative diseases that are characterized by misfolded proteins, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases. These molecules are based on what the Company calls a general amyloid interaction motif, or GAIM, which recognizes a characteristic common to many toxic, misfolded proteins, not just one type of misfolded protein. This approach provides NeuroPhage with an array of therapeutic targets, so that ...
Sleep disorder linked to brain disease
2014-04-22
Researchers at the University of Toronto say a sleep disorder that causes people to act out their dreams is the best current predictor of brain diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
"Rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) is not just a precursor but also a critical warning sign of neurodegeneration that can lead to brain disease," says associate professor and lead author Dr. John Peever. In fact, as many as 80 to 90 per cent of people with RBD will develop a brain disease."
As the name suggests, the disturbance occurs during the rapid-eye-movement (REM) ...
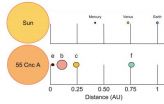
Mysteries of a nearby planetary system's dynamics now are solved
2014-04-22
Mysteries of one of the most fascinating nearby planetary systems now have been solved, report authors of a scientific paper to be published by the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society in its early online edition on 22 April 2014. The study, which presents the first viable model for the planetary system orbiting one the first stars discovered to have planets -- the star named 55 Cancri -- was led by Penn State University graduate student Benjamin Nelson in collaboration with faculty at the Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds at Penn State and ...