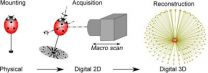
(Press-News.org) Scientists have developed a cost-effective, off-the-shelf system to obtain natural-color 3D models of insects, according to results published April 23, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Chuong Nguyen from CSIRO in Australia, and colleagues.
Scientists studying insects rely on collected specimens that are often shared between scientists through written descriptions, diagrams, and images. These 2D tools are important in understanding and sharing specimens, but they often lack the precise detail of the actual 3D specimen. The authors of this study, interested in understanding the feasibility of digitizing insects for research purposes, created a cost-effective prototype to produce 3D naturally colored digital models of medium-to-large insects (3 to 30mm in length), using off-the-shelf equipment and software. The prototype captures color images from different angles and focal depths using a digital single lens reflex camera and a two-axis turntable. These 2D images are then combined into 3D reconstructions.
The resulting 3D models are compact (around 10 megabytes each), have excellent optical resolution, and can be embedded into documents and web pages, as well as viewed on mobile devices. The authors suggest the system is portable, safe, relatively affordable, complements existing imaging techniques, and reduces the need to handle or ship delicate insect specimens. Furthermore, they hope that this technology opens new opportunities and applications for research data collection, education, art, entertainment, biodiversity assessment, and biosecurity control.
Dr. Nguyen added, "These 3D models represent high quality visualisations of physical specimens that will enable novel solutions to quickly extract, analyse and share rich information. The 3D models are of great value for biodiversity discovery, species identification, quarantine control, and unlocking big data in our biological collections."
INFORMATION:
Citation: Nguyen CV, Lovell DR, Adcock M, La Salle J (2014) Capturing Natural-Colour 3D Models of Insects for Species Discovery and Diagnostics. PLoS ONE 9(4): e94346. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094346
Financial Disclosure: The work is funded by CSIRO OCE Science, CSIRO Tranformational Biology TCP, CSIRO Computational Informatics BSA. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interest Statement: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
PLEASE LINK TO THE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE IN ONLINE VERSIONS OF YOUR REPORT (URL goes live after the embargo ends): http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094346
'Off-the-shelf' equipment used to digitize insects in 3-D
3-D model insects useful for studying, sharing specimens
2014-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stem cells in circulating blood affect cardiovascular health, study finds
2014-04-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that attempts to isolate an elusive adult stem cell from blood to understand and potentially improve cardiovascular health – a task considered possible but very difficult – might not be necessary.
Instead, scientists have found that multiple types of cells with primitive characteristics circulating in the blood appear to provide the same benefits expected from a stem cell, including the endothelial progenitor cell that is the subject of hot pursuit.
"There are people who still dream that the prototypical progenitors for several ...
Scientists discover a new shape using rubber bands
2014-04-24
Cambridge, Mass. – April 23, 2014 – While setting out to fabricate new springs to support a cephalopod-inspired imaging project, a group of Harvard researchers stumbled upon a surprising discovery: the hemihelix, a shape rarely seen in nature.
This made the researchers wonder: Were the three-dimensional structures they observed randomly occurring, or are there specific factors that control their formation? The scientists answered that question by performing experiments in which they stretched, joined, and then released rubber strips. Complemented by numerical simulations ...
Microbes provide insights into evolution of human language
2014-04-24
Big brains do not explain why only humans use sophisticated language, according to researchers who have discovered that even a species of pond life communicates by similar methods.
Dr Thom Scott-Phillips of Durham University led research into Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a type of bacteria common in water and soil, which showed that they communicated in a way that was previously thought to be unique to humans and perhaps some other primates.
The bacteria used combinatorial communication, in which two signals are used together to achieve an effect that is different to the ...
People with mild cognitive impairment may die at higher rate than people without condition
2014-04-23
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic research studying the relationship between death and the two types of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) suggests that people who have these conditions die at a higher rate than people without MCI. The research was released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 66th Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, April 26 to May 3, 2014.
For the study, 862 people with thinking problems and 1,292 with no thinking problems between the ages of 70 and 89 were followed for nearly six years. Over the course of the study, 331 of the ...
People with more education may recover better from traumatic brain injury
2014-04-23
MINNEAPOLIS – People with more years of education may be better able to recover from a traumatic brain injury, according to a study published in the April 23, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
The study examined people with moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries, most of which were from motor vehicle accidents or falls. All were taken to the emergency department and spent time in the hospital after the injury and also for inpatient rehabilitation.
"After these types of injuries, some people are disabled ...
Study examines risk of early death for people with mild cognitive impairment
2014-04-23
PHILADELPHIA – One of the first studies to look at a relationship between death and the two types of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), or problems with memory and thinking abilities, suggests that people who have thinking problems but their memory is still intact might have a higher death rate in a period of six years compared to those who have no thinking or memory problems. The research was released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 66th Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, April 26 to May 3, 2014. The same was suggested in the study for those ...
Marijuana use may increase heart complications in young, middle-aged adults
2014-04-23
Marijuana use may result in cardiovascular-related complications — even death — among young and middle-aged adults, according to a French study reported in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
"In prior research, we identified several remarkable cases of cardiovascular complications as the reasons for hospital admission of young marijuana users," said Émilie Jouanjus, Pharm.D., Ph.D., lead author of the study and a medical faculty member at the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Toulouse in Toulouse, France. "This unexpected finding deserved to be further analyzed, ...
Higher education associated with better recovery from traumatic brain injury
2014-04-23
Better-educated people appear to be significantly more likely to recover from a moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), suggesting that a brain's "cognitive reserve" may play a role in helping people get back to their previous lives, new Johns Hopkins research shows.
The researchers, reporting in the journal Neurology, found that those with the equivalent of at least a college education are seven times more likely than those who didn't finish high school to be disability-free one year after a TBI serious enough to warrant inpatient time in a hospital and rehabilitation ...
Rural microbes could boost city dwellers' health
2014-04-23
The greater prevalence of asthma, allergies and other chronic inflammatory disorders among people of lower socioeconomic status might be due in part to their reduced exposure to the microbes that thrive in rural environments, according to a new scientific paper.
The article, published in the journal Clinical & Experimental Immunology, argues that people living in urban centers who have less access to green spaces may be more apt to have chronic inflammation, a condition caused by immune system dysfunction.
When our immune systems are working properly, they trigger inflammation ...
Princeton release: Not just the poor live hand-to-mouth
2014-04-23
When the economy hits the skids, government stimulus checks to the poor sometimes follow.
Stimulus programs — such as those in 2001, 2008 and 2009 — are designed to boost the economy quickly by getting cash into the hands of people likely to turn around and spend it.
But sending cash to just the very poor may not be the right approach, according to researchers from Princeton University and New York University who analyzed information on the finances of U.S. households from 1989 to 2010.
"What we found is that households that have the lowest liquid wealth — where ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] 'Off-the-shelf' equipment used to digitize insects in 3-D3-D model insects useful for studying, sharing specimens