(Press-News.org) The greater prevalence of asthma, allergies and other chronic inflammatory disorders among people of lower socioeconomic status might be due in part to their reduced exposure to the microbes that thrive in rural environments, according to a new scientific paper.
The article, published in the journal Clinical & Experimental Immunology, argues that people living in urban centers who have less access to green spaces may be more apt to have chronic inflammation, a condition caused by immune system dysfunction.
When our immune systems are working properly, they trigger inflammation to fight off dangerous infections, but the inflammation disappears when the infection is gone. However, a breakdown in immune system function can cause a low level of inflammation to persist indefinitely. Such chronic inflammation can cause a host of health disorders.
"Chronic inflammation can lead to all kinds of problems from irritable bowel syndrome to asthma to allergies and even depression," said Christopher Lowry, an associate professor in the University of Colorado Boulder's Department of Integrative Physiology and a co-author of the paper. "The rise of chronic inflammation and these associated disorders, especially among people living in the cities of developed countries, is troubling."
The two other article co-authors are Graham Rook of UCL (University College London) and Charles Raison of the University of Arizona.
Some scientists have hypothesized that the increase of chronic inflammation in wealthier Western countries is connected to lifestyles that have essentially become too clean. The so-called "hygiene hypothesis" is based on the notion that some microbes and infections interact with the immune system to suppress inflammation and that eliminating exposure to those things could compromise your health.
But the idea that picking up more germs could boost our immune system function does not at first seem to hold up when applied to low-income urbanites, who suffer disproportionately from both infections caused by germs and disorders linked to chronic inflammation. The authors of the new paper say this apparent disconnect is due to a misunderstanding of the hygiene hypothesis.
The authors agree that microbes and some types of infections are important because they can keep the immune system from triggering inflammation when it's not necessary, as happens with asthma attacks and allergic reactions.
But they say the infections that were historically important to immune system development have largely been eliminated in developed countries. The modern diseases we pick up from school, work and other crowded areas today do not actually lead to lower instances of inflammatory disorders.
"The idea that we're too clean—that gives the wrong impression," said Lowry. "You want people to wash their hands because hygiene is important to avoid infections that are harmful."
During our evolutionary history, the human immune system was exposed to microbes and infections in three important ways: commensal microbes were passed to infants from their mothers and other family members; people came into contact with nonpathogenic microbes in the environment; and people lived with chronic infections, such as helminths, which are parasitic worms found in the gut and blood.
In order for those "old infections" to be tolerated in the body for long periods of time, they evolved a mechanism to keep the human immune system from triggering inflammation. Similarly, environmental bacteria, which were abundant and harmless, were tolerated by the immune system.
According to Rook, a professor at UCL, "Helminthic parasites need to be tolerated by the immune system because, although not always harmless, once they are established in the host efforts by the immune system to eliminate them are futile, and merely cause tissue damage."
In contrast, relatively modern "crowd infections," such as measles or chicken pox, cause an inflammatory response. The result is that either the sick person dies or the infection is wiped out by the inflammation and the person becomes immune from having the same infection again in the future.
Collectively, the authors refer to the microbes and old infections that had a beneficial impact on the function of our immune systems as "old friends." Exposure to old friends plays an important role in guarding against inflammatory disorders, the authors said. Because the "old infections" are largely absent from the developed world, exposure to environmental microbes—such as those found in rural environments, like farms and green spaces—has likely become even more important.
The authors say this would explain why low-income urban residents—who cannot easily afford to leave the city for rural vacations—are more likely to suffer from inflammatory disorders. The problem is made worse because people who live in densely populated areas also are more likely to contract crowd infections, which cause more inflammation.
In other words, city dwellers of low socioeconomic status might benefit both from being "cleaner" and "dirtier," depending on the context. Like all people, better hygiene—like washing their hands more frequently, for example—could help them avoid crowd infections while more opportunities to "play in the dirt," like visiting green spaces, could allow their immune systems to come into contact with more beneficial microbes.
"You don't want the crowd infections," said Lowry. "But you do want to find ways to increase your exposure to 'old friends.' "
INFORMATION:
Rural microbes could boost city dwellers' health
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Princeton release: Not just the poor live hand-to-mouth
2014-04-23
When the economy hits the skids, government stimulus checks to the poor sometimes follow.
Stimulus programs — such as those in 2001, 2008 and 2009 — are designed to boost the economy quickly by getting cash into the hands of people likely to turn around and spend it.
But sending cash to just the very poor may not be the right approach, according to researchers from Princeton University and New York University who analyzed information on the finances of U.S. households from 1989 to 2010.
"What we found is that households that have the lowest liquid wealth — where ...
NASA satellites show drought may take toll on Congo rainforest
2014-04-23
A new analysis of NASA satellite data shows Africa's Congo rainforest, the second-largest tropical rainforest in the world, has undergone a large-scale decline in greenness over the past decade.
The study, led by Liming Zhou of University at Albany, State University of New York, shows between 2000 and 2012 the decline affected an increasing amount of forest area and intensified. The research, published Wednesday in Nature, is one of the most comprehensive observational studies to explore the effects of long-term drought on the Congo rainforest using several independent ...
WSU innovation improves drowsy driver detection
2014-04-23
SPOKANE, Wash.—Researchers at Washington State University Spokane have developed a new way to detect when drivers are about to nod off behind the wheel.
Their recently patented technology is based on steering wheel movements—which are more variable in drowsy drivers—and offers an affordable and more reliable alternative to currently available video-based driver drowsiness detection systems.
Van Dongen"Video-based systems that use cameras to detect when a car is drifting out of its lane are cumbersome and expensive," said Hans Van Dongen, research professor at the WSU ...
Study: Iron consumption can increase risk for heart disease
2014-04-23
A new study from the Indiana University School of Public Health-Bloomington has bolstered the link between red meat consumption and heart disease by finding a strong association between heme iron, found only in meat, and potentially deadly coronary heart disease.
The study found that heme iron consumption increased the risk for coronary heart disease by 57 percent, while no association was found between nonheme iron, which is in plant and other non-meat sources, and coronary heart disease.
The study was published online ahead of print in the Journal of Nutrition. Along ...
First size-based chromatography technique for the study of living cells
2014-04-23
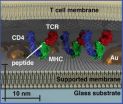
Using nanodot technology, Berkeley Lab researchers have demonstrated the first size-based form of chromatography that can be used to study the membranes of living cells. This unique physical approach to probing cellular membrane structures can reveal information critical to whether a cell lives or dies, remains normal or turns cancerous, that can't be obtained through conventional microscopy.
"We've developed membrane-embedded nanodot array platforms that provide a physical means to both probe and manipulate membrane assemblies, including signaling clusters, while they ...
Hearing quality restored with bionic ear technology used for gene therapy
2014-04-23
VIDEO:
This shows regenerated auditory nerves, after gene therapy.
Click here for more information.
Researchers at UNSW Australia have for the first time used electrical pulses delivered from a cochlear implant to deliver gene therapy, thereby successfully regrowing auditory nerves.
The research also heralds a possible new way of treating a range of neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, and psychiatric conditions such as depression through this novel way of delivering ...
Study shows aspirin can reduce colorectal cancer risks for those with specific gene
2014-04-23
The humble aspirin may have just added another beneficial effect beyond its ability to ameliorate headaches and reduce the risk of heart attacks: lowering colon cancer risk among people with high levels of a specific type of gene.
The extraordinary finding comes from a multi-institutional team that analyzed data and other material from two long-term studies involving nearly 128,000 participants. The researchers found that individuals whose colons have high levels of a specific gene product — 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) RNA — dramatically reduce their ...
Atomic switcheroo explains origins of thin-film solar cell mystery
2014-04-23
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., April 23, 2014 — Treating cadmium-telluride (CdTe) solar cell materials with cadmium-chloride improves their efficiency, but researchers have not fully understood why. Now, an atomic-scale examination of the thin-film solar cells led by the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has answered this decades-long debate about the materials' photovoltaic efficiency increase after treatment.
A research team from ORNL, the University of Toledo and DOE's National Renewable Energy Laboratory used electron microscopy and computational simulations ...
Economics = MC2 -- A portrait of the modern physics startup
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON D.C., April 23, 2014 -- For much of the 20th century, many of the technological innovations that drove U.S. economic growth emerged from "idea factories" housed within large companies -- research units like Bell Labs or Xerox PARC that developed everything from the transistor to the computer mouse.
In recent decades, however, many large high-tech companies have eliminated in-house research programs, turning instead to startup companies as their primary source of breakthrough innovations.
"Small startups have replaced corporate research centers as the drivers ...
Pollutants from coal-burning stoves strongly associated with miscarriages in Mongolia
2014-04-23
Burning coal for domestic heating may contribute to early fetal death according to a new study by experts from The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles and Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia – the coldest capital city in the world.
In a paper published today in the journal BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, researchers report
"alarmingly strong statistical correlations" between seasonal ambient air pollutants and pregnancy loss in Ulaanbaatar (UB), Mongolia.
UB has one of the highest levels of air pollution of all world capitals, with sulfide dioxide and particulate ...