(Press-News.org) OAK RIDGE, Tenn., April 23, 2014 — Treating cadmium-telluride (CdTe) solar cell materials with cadmium-chloride improves their efficiency, but researchers have not fully understood why. Now, an atomic-scale examination of the thin-film solar cells led by the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has answered this decades-long debate about the materials' photovoltaic efficiency increase after treatment.
A research team from ORNL, the University of Toledo and DOE's National Renewable Energy Laboratory used electron microscopy and computational simulations to explore the physical origins of the unexplained treatment process. The results are published in Physical Review Letters (PRL).
Thin-film CdTe solar cells are considered a potential rival to silicon-based photovoltaic systems because of their theoretically low cost per power output and ease of fabrication. Their comparatively low historical efficiency in converting sunlight into energy, however, has limited the technology's widespread use, especially for home systems.
Research in the 1980s showed that treating CdTe thin films with cadmium-chloride significantly raises the cell's efficiency, but scientists have been unable to determine the underlying causes. ORNL's Chen Li, first author on the PRL study, explains that the answer lay in investigating the material at an atomic level.
"We knew that chlorine was responsible for this magical effect, but we needed to find out where it went in the material's structure," Li said. "Only by understanding the structure can we understand what's wrong in this solar cell -- why the efficiency is not high enough, and how can we push it further."
By comparing the solar cells before and after chlorine treatment, the researchers realized that atom-scale grain boundaries were implicated in the enhanced performance. Grain boundaries are tiny defects that that normally act as roadblocks to efficiency, because they inhibit carrier collection which greatly reduces the solar cell power.
Using state of the art electron microscopy techniques to study the thin films' structure and chemical composition after treatment, the researchers found that chlorine atoms replaced tellurium atoms within the grain boundaries. This atomic substitution creates local electric fields at the grain boundaries that boost the material's photovoltaic performance instead of damaging it.
The research team's finding, in addition to providing a long-awaited explanation, could be used to guide engineering of higher-efficiency CdTe solar cells. Controlling the grain boundary structure, says Li, is a new direction that could help raise the cell efficiencies closer to the theoretical maximum of 32 percent light-to-energy conversion. Currently, the record CdTe cell efficiency is only 20.4 percent.
"We think that if all the grain boundaries in a thin film material could be aligned in same direction, it could improve cell efficiency even further," Li said.
The team's research appears as "Grain-Boundary-Enhanced Carrier Collection in CdTe Solar Cells." Coauthors are ORNL's Chen Li, Jonathan Poplawsky, Mark Oxley and Andrew Lupini; University of Toledo's Yelong Wu, Naba Paudel, Wanjian Yin and Yanfa Yan; University of Tennessee's Stephen Pennycook; University of Manchester's Sarah Haigh; University of Oxford's Timothy Pennycook; and NREL's Mowafak Al-Jassim. Li and Oxley hold joint appointments at Vanderbilt University.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy through the SunShot Initiative and the Office of Basic Energy Sciences. The work was sponsored in part by the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council and through a user project supported by ORNL's Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences (CNMS). This research used resources of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center. Yan acknowledges support from the Ohio Research Scholar Program.
CNMS is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, NSRCs, supported by the DOE Office of Science, as premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit http://science.energy.gov/bes/suf/user-facilities/nanoscale-science-research-centers/.
ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy's Office of Science.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
Image: http://www.ornl.gov/Image%20Library/Main%20Nav/ORNL/News/News%20Releases/2014/CdTe_highres.jpg?code=2fb8d37b-bcd7-4c01-a389-152dacfb2d5e
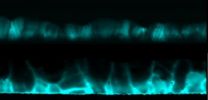
Caption: Cross-sectional electron beam-induced current maps show the difference in cadmium telluride solar cells before (pictured above) and after (below) cadmium chloride treatment. The increased brightness after treatment indicates higher current collection at the grain boundaries.
NOTE TO EDITORS: You may read other press releases from Oak Ridge National Laboratory or learn more about the lab at http://www.ornl.gov/news. Additional information about ORNL is available at the sites below:
Twitter - http://twitter.com/oakridgelabnews
RSS Feeds - http://www.ornl.gov/ornlhome/rss_feeds.shtml
Flickr - http://www.flickr.com/photos/oakridgelab
YouTube - http://www.youtube.com/user/OakRidgeNationalLab
LinkedIn - http://www.linkedin.com/companies/oak-ridge-national-laboratory
Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/Oak.Ridge.National.Laboratory
Atomic switcheroo explains origins of thin-film solar cell mystery
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Economics = MC2 -- A portrait of the modern physics startup
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON D.C., April 23, 2014 -- For much of the 20th century, many of the technological innovations that drove U.S. economic growth emerged from "idea factories" housed within large companies -- research units like Bell Labs or Xerox PARC that developed everything from the transistor to the computer mouse.
In recent decades, however, many large high-tech companies have eliminated in-house research programs, turning instead to startup companies as their primary source of breakthrough innovations.
"Small startups have replaced corporate research centers as the drivers ...
Pollutants from coal-burning stoves strongly associated with miscarriages in Mongolia
2014-04-23
Burning coal for domestic heating may contribute to early fetal death according to a new study by experts from The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles and Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia – the coldest capital city in the world.
In a paper published today in the journal BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, researchers report
"alarmingly strong statistical correlations" between seasonal ambient air pollutants and pregnancy loss in Ulaanbaatar (UB), Mongolia.
UB has one of the highest levels of air pollution of all world capitals, with sulfide dioxide and particulate ...
Superconducting qubit array points the way to quantum computers
2014-04-23
A fully functional quantum computer is one of the holy grails of physics. Unlike conventional computers, the quantum version uses qubits (quantum bits), which make direct use of the multiple states of quantum phenomena. When realized, a quantum computer will be millions of times more powerful at certain computations than today's supercomputers.
A group of UC Santa Barbara physicists has moved one step closer to making a quantum computer a reality by demonstrating a new level of reliability in a five-qubit array. Their findings appear Thursday in the journal Nature.
Quantum ...
Cyber buddy is better than 'no buddy'
2014-04-23
A Michigan State University researcher is looking to give exercise enthusiasts the extra nudge they need during a workout, and her latest research shows that a cyber buddy can help.
The study, which appears in the Games for Health Journal, is the first to indicate that although a human partner is still a better motivator during exercise, a software-generated partner also can be effective.
"We wanted to demonstrate that something that isn't real can still motivate people to give greater effort while exercising than if they had to do it by themselves," said Deborah Feltz, ...
Male or female?
2014-04-23
This news release is available in French and German. Man or woman? Male or female? In humans and other mammals, the difference between sexes depends on one single element of the genome: the Y chromosome. It is present only in males, where the two sexual chromosomes are X and Y, whereas women have two X chromosomes. Thus, the Y is ultimately responsible for all the morphological and physiological differences between males and females.
But this has not always been the case. A very long time ago, the X and Y were identical, until the Y started to differentiate from the ...
Hundreds of genetic mutations found in healthy blood of a supercentenarian
2014-04-23
April 23, 2014 – Genetic mutations are commonly studied because of links to diseases such as cancer; however, little is known about mutations occurring in healthy individuals. In a study published online in Genome Research, researchers detected over 400 mutations in healthy blood cells of a 115-year-old woman, suggesting that lesions at these sites are largely harmless over the course of a lifetime.
Our blood is continually replenished by hematopoietic stem cells that reside in the bone marrow and divide to generate different types of blood cells, including white blood ...
From liability to viability: Genes on the Y chromosome prove essential for male survival
2014-04-23
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (April 23, 2014) – Despite a well-documented history of dramatic genetic decay, the human Y chromosome has over the course of millions of years of evolution managed to preserve a small set of genes that has ensured not only its own survival but also the survival of men. Moreover, the vast majority of these tenacious genes appear to have little if any role in sex determination or sperm production.
Taken together, these remarkable findings—published this week in the journal Nature—suggest that because these Y-linked genes are active across the body, they ...
New target for prostate cancer resistant to anti-hormone therapies
2014-04-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Prostate cancer becomes deadly when anti-hormone treatments stop working. Now a new study suggests a way to block the hormones at their entrance.
Researchers from the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have found that a protein called BET bromodomain protein 4 binds to the hormone androgen receptor downstream of where current therapies work – targeting androgen receptor signaling.
This could mean that when prostate cancer becomes resistant to current treatments, it might remain sensitive to a drug that targets BET bromodomain proteins. ...
Quality control guidelines for genomics studies
2014-04-23
Sequencing an entire human genome is faster and cheaper than ever before, leading to an explosion of studies comparing the genomes of people with and without a given disease. Often clinicians and researchers studying genetic contributions to a certain disease encounter variations that appear to be responsible, only to find other people with the same mutation who don't have the disease or who are affected to a lesser degree.
How do doctors pinpoint the genetic changes that really cause disease? An open-access policy paper to be published Wednesday in Nature proposes guidelines ...
Picky male black widow spiders prefer well-fed virgins
2014-04-23
New University of Toronto Scarborough research shows that male black widow spiders prefer their female mates to be well-fed virgins – a rare example of mate preference by male spiders.
The study, authored by UTSC post-doc Emily MacLeod and Maydianne Andrade, a professor in UTSC's Department of Biological Sciences, found in both controlled field studies and the wild that males overwhelmingly chose to mate with well-fed, unmated females. They also found male black widows can tell whether a potential mate is well-fed and unmated by pheromones released by females.
"This ...