(Press-News.org) A new study from the Indiana University School of Public Health-Bloomington has bolstered the link between red meat consumption and heart disease by finding a strong association between heme iron, found only in meat, and potentially deadly coronary heart disease.
The study found that heme iron consumption increased the risk for coronary heart disease by 57 percent, while no association was found between nonheme iron, which is in plant and other non-meat sources, and coronary heart disease.
The study was published online ahead of print in the Journal of Nutrition. Along with first author Jacob Hunnicutt, a graduate student in the school's Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, the study's co-authors are Ka He and Pengcheng Xun, faculty members in the department.
Hunnicutt said the link between iron intake, body iron stores and coronary heart disease has been debated for decades by researchers, with epidemiological studies providing inconsistent findings. The new IU research, a meta-analysis, examined 21 previously published studies and data involving 292,454 participants during an average 10.2 years of follow-up.
The new study is unique because it looks at the associations of total iron consumption as well as heme and nonheme iron intake in comparison to the risk of coronary heart disease. The only positive association involved the intake of heme iron.
The body treats the two kinds of iron differently. It can better control absorption of iron from vegetable sources, including iron supplements, but not so with iron from meat sources.
"The observed positive association between heme iron and risk of CHD may be explained by the high bioavailability of heme iron and its role as the primary source of iron in iron-replete participants," the researchers wrote in the journal article. "Heme iron is absorbed at a much greater rate in comparison to nonheme iron (37 percent vs. 5 percent). Once absorbed, it may contribute as a catalyst in the oxidation of LDLs, causing tissue-damaging inflammation, which is a potential risk factor for CHD."
Iron stores in the body increase over time. The only way to reduce iron in the body is by bleeding, donating blood or menstruation. Some dietary choices, such as coffee and tea, also can inhibit iron absorption.
INFORMATION:
Hunnicutt can be reached at jnhunnic@indiana.edu. For additional assistance, or for a copy of the study, contact Tracy James at 812-855-0084 or traljame@iu.edu.
Study: Iron consumption can increase risk for heart disease
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First size-based chromatography technique for the study of living cells
2014-04-23
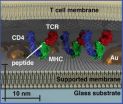
Using nanodot technology, Berkeley Lab researchers have demonstrated the first size-based form of chromatography that can be used to study the membranes of living cells. This unique physical approach to probing cellular membrane structures can reveal information critical to whether a cell lives or dies, remains normal or turns cancerous, that can't be obtained through conventional microscopy.
"We've developed membrane-embedded nanodot array platforms that provide a physical means to both probe and manipulate membrane assemblies, including signaling clusters, while they ...
Hearing quality restored with bionic ear technology used for gene therapy
2014-04-23
VIDEO:
This shows regenerated auditory nerves, after gene therapy.
Click here for more information.
Researchers at UNSW Australia have for the first time used electrical pulses delivered from a cochlear implant to deliver gene therapy, thereby successfully regrowing auditory nerves.
The research also heralds a possible new way of treating a range of neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, and psychiatric conditions such as depression through this novel way of delivering ...
Study shows aspirin can reduce colorectal cancer risks for those with specific gene
2014-04-23
The humble aspirin may have just added another beneficial effect beyond its ability to ameliorate headaches and reduce the risk of heart attacks: lowering colon cancer risk among people with high levels of a specific type of gene.
The extraordinary finding comes from a multi-institutional team that analyzed data and other material from two long-term studies involving nearly 128,000 participants. The researchers found that individuals whose colons have high levels of a specific gene product — 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) RNA — dramatically reduce their ...
Atomic switcheroo explains origins of thin-film solar cell mystery
2014-04-23
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., April 23, 2014 — Treating cadmium-telluride (CdTe) solar cell materials with cadmium-chloride improves their efficiency, but researchers have not fully understood why. Now, an atomic-scale examination of the thin-film solar cells led by the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has answered this decades-long debate about the materials' photovoltaic efficiency increase after treatment.
A research team from ORNL, the University of Toledo and DOE's National Renewable Energy Laboratory used electron microscopy and computational simulations ...
Economics = MC2 -- A portrait of the modern physics startup
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON D.C., April 23, 2014 -- For much of the 20th century, many of the technological innovations that drove U.S. economic growth emerged from "idea factories" housed within large companies -- research units like Bell Labs or Xerox PARC that developed everything from the transistor to the computer mouse.
In recent decades, however, many large high-tech companies have eliminated in-house research programs, turning instead to startup companies as their primary source of breakthrough innovations.
"Small startups have replaced corporate research centers as the drivers ...
Pollutants from coal-burning stoves strongly associated with miscarriages in Mongolia
2014-04-23
Burning coal for domestic heating may contribute to early fetal death according to a new study by experts from The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles and Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia – the coldest capital city in the world.
In a paper published today in the journal BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, researchers report
"alarmingly strong statistical correlations" between seasonal ambient air pollutants and pregnancy loss in Ulaanbaatar (UB), Mongolia.
UB has one of the highest levels of air pollution of all world capitals, with sulfide dioxide and particulate ...
Superconducting qubit array points the way to quantum computers
2014-04-23
A fully functional quantum computer is one of the holy grails of physics. Unlike conventional computers, the quantum version uses qubits (quantum bits), which make direct use of the multiple states of quantum phenomena. When realized, a quantum computer will be millions of times more powerful at certain computations than today's supercomputers.
A group of UC Santa Barbara physicists has moved one step closer to making a quantum computer a reality by demonstrating a new level of reliability in a five-qubit array. Their findings appear Thursday in the journal Nature.
Quantum ...
Cyber buddy is better than 'no buddy'
2014-04-23
A Michigan State University researcher is looking to give exercise enthusiasts the extra nudge they need during a workout, and her latest research shows that a cyber buddy can help.
The study, which appears in the Games for Health Journal, is the first to indicate that although a human partner is still a better motivator during exercise, a software-generated partner also can be effective.
"We wanted to demonstrate that something that isn't real can still motivate people to give greater effort while exercising than if they had to do it by themselves," said Deborah Feltz, ...
Male or female?
2014-04-23
This news release is available in French and German. Man or woman? Male or female? In humans and other mammals, the difference between sexes depends on one single element of the genome: the Y chromosome. It is present only in males, where the two sexual chromosomes are X and Y, whereas women have two X chromosomes. Thus, the Y is ultimately responsible for all the morphological and physiological differences between males and females.
But this has not always been the case. A very long time ago, the X and Y were identical, until the Y started to differentiate from the ...
Hundreds of genetic mutations found in healthy blood of a supercentenarian
2014-04-23
April 23, 2014 – Genetic mutations are commonly studied because of links to diseases such as cancer; however, little is known about mutations occurring in healthy individuals. In a study published online in Genome Research, researchers detected over 400 mutations in healthy blood cells of a 115-year-old woman, suggesting that lesions at these sites are largely harmless over the course of a lifetime.
Our blood is continually replenished by hematopoietic stem cells that reside in the bone marrow and divide to generate different types of blood cells, including white blood ...