(Press-News.org) In the aftermath of war, communities who continue to experience repeated violence could have a major escalation in rates of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and severe distress, suggests new research published in The Lancet Global Health journal.
In 2004, Dr Derrick Silove from the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, and colleagues conducted a survey to estimate the prevalence of common mental disorders among 1022 adults (600 from a rural village and 422 from an urban district) in Timor Leste four years after the end of a long-running and violent war against Indonesian occupation, and again in 2010-11, following a period of prolonged internal conflict.
Interviewers used the Harvard Trauma Questionnaire to assess 16 symptoms of PTSD and the Kessler-10 questionnaire to measure depression and anxiety. The researchers also examined whether poverty, ongoing community conflict, and persisting feelings of injustice contributed to mental illness.
Over the 6 years of follow-up, rates of PTSD increased seven fold (2.3% in 2004 to 16.7% in 2010) and rates of severe distress increased almost three times (5.6% to 15.9%).
"Given that potentially traumatic events were rarer during the internal conflict than during the principal conflict, it seems likely that the effects of recurrent episodes of communal violence on the morale, sense of communal cohesion, and security of the population created a general underlying vulnerability to psychological distress", explains lead author Dr Derrick Silove.*
Interestingly, PTSD was not only linked with experience of violent conflict but also with a range of other stressors. In particular, persisting preoccupations with injustice during two or three periods (the principal conflict 1975-99, internal conflict 2006-7, or the present 2008-10) was linked with a quadrupling of risk for PTSD, which the authors suggest could have been related to the unsatisfactory truth and reconciliation process that followed independence, together with ongoing human rights abuses.
According to Dr Silove, "Our findings suggest that a period of internal conflict can result in a major escalation in mental disorders in post-conflict countries. Mental health services should be enhanced in these settings to meet these increased needs. Our experiences highlight the importance of preventing communal violence, alleviating poverty, and addressing past and ongoing injustices in post-conflict communities to help avert both recurring violence and prevent an increase in mental disorders."*
Writing in a linked Comment, Madelyn Hsiao-Rei Hicks from the University of Massachusetts Medical School, USA, discusses the value of culturally informed research that integrates relevant experiences, sociocultural factors, and political aspects of study populations. She adds, "A further advance would be if studies used in-depth interviews with the probability-sampled respondents of the epidemiological survey. Such interviews would produce detailed information on which to base moderately generalisable and acceptable methods of engagement, treatment, and social healing…For example, if epidemiologists studying conflict-affected populations returned to their survey respondents to explore specific means for achieving justice and reconciliation, a range of informed options could be generated for social reconstitution to prevent the future distress, symptoms, and disability, which Silove and colleagues have shown result from persistent conflict and perceived injustice."
INFORMATION:NOTES TO EDITORS:
This study was funded by Australian National Health and the Medical Research Council
*Quotes direct from author and cannot be found in text of Article
The Lancet Global Health: Recurrent violence linked to substantially higher rates of mental disorders in post-conflict communities
2014-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology: Vitamin D supplements have little effect on risk of falls in older people
2014-04-24
A new meta-analysis, published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology journal, concludes that there is no evidence to suggest that vitamin D supplements prevent falls, and that ongoing trials to test this theory are unlikely to change this result.
The study, by Dr Mark Bolland of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and colleagues, analysed findings from 20 randomised controlled trials which tested the potential of vitamin D supplements to reduce falls, in a total of 29535 people. The findings show that supplements do not reduce falls by 15% or more, meaning that the ...
Citizen scientists match research tool when counting sharks
2014-04-24
Shark data collected by citizen scientists may be as reliable as data collected using automated tools, according to results published April 23, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Gabriel Vianna from The University of Western Australia and colleagues.
Shark populations are declining globally, and scientists lack data to estimate the conservation status of populations for many shark species. Citizen science may be a useful and cost-effective means to increase knowledge of shark populations on coral reefs, but scientists do not yet know enough about how data collected ...
'Off-the-shelf' equipment used to digitize insects in 3-D
2014-04-24
Scientists have developed a cost-effective, off-the-shelf system to obtain natural-color 3D models of insects, according to results published April 23, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Chuong Nguyen from CSIRO in Australia, and colleagues.
Scientists studying insects rely on collected specimens that are often shared between scientists through written descriptions, diagrams, and images. These 2D tools are important in understanding and sharing specimens, but they often lack the precise detail of the actual 3D specimen. The authors of this study, interested in ...
Stem cells in circulating blood affect cardiovascular health, study finds
2014-04-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that attempts to isolate an elusive adult stem cell from blood to understand and potentially improve cardiovascular health – a task considered possible but very difficult – might not be necessary.
Instead, scientists have found that multiple types of cells with primitive characteristics circulating in the blood appear to provide the same benefits expected from a stem cell, including the endothelial progenitor cell that is the subject of hot pursuit.
"There are people who still dream that the prototypical progenitors for several ...
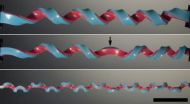
Scientists discover a new shape using rubber bands
2014-04-24
Cambridge, Mass. – April 23, 2014 – While setting out to fabricate new springs to support a cephalopod-inspired imaging project, a group of Harvard researchers stumbled upon a surprising discovery: the hemihelix, a shape rarely seen in nature.
This made the researchers wonder: Were the three-dimensional structures they observed randomly occurring, or are there specific factors that control their formation? The scientists answered that question by performing experiments in which they stretched, joined, and then released rubber strips. Complemented by numerical simulations ...
Microbes provide insights into evolution of human language
2014-04-24
Big brains do not explain why only humans use sophisticated language, according to researchers who have discovered that even a species of pond life communicates by similar methods.
Dr Thom Scott-Phillips of Durham University led research into Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a type of bacteria common in water and soil, which showed that they communicated in a way that was previously thought to be unique to humans and perhaps some other primates.
The bacteria used combinatorial communication, in which two signals are used together to achieve an effect that is different to the ...
People with mild cognitive impairment may die at higher rate than people without condition
2014-04-23
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic research studying the relationship between death and the two types of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) suggests that people who have these conditions die at a higher rate than people without MCI. The research was released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 66th Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, April 26 to May 3, 2014.
For the study, 862 people with thinking problems and 1,292 with no thinking problems between the ages of 70 and 89 were followed for nearly six years. Over the course of the study, 331 of the ...
People with more education may recover better from traumatic brain injury
2014-04-23
MINNEAPOLIS – People with more years of education may be better able to recover from a traumatic brain injury, according to a study published in the April 23, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
The study examined people with moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries, most of which were from motor vehicle accidents or falls. All were taken to the emergency department and spent time in the hospital after the injury and also for inpatient rehabilitation.
"After these types of injuries, some people are disabled ...
Study examines risk of early death for people with mild cognitive impairment
2014-04-23
PHILADELPHIA – One of the first studies to look at a relationship between death and the two types of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), or problems with memory and thinking abilities, suggests that people who have thinking problems but their memory is still intact might have a higher death rate in a period of six years compared to those who have no thinking or memory problems. The research was released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 66th Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, April 26 to May 3, 2014. The same was suggested in the study for those ...
Marijuana use may increase heart complications in young, middle-aged adults
2014-04-23
Marijuana use may result in cardiovascular-related complications — even death — among young and middle-aged adults, according to a French study reported in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
"In prior research, we identified several remarkable cases of cardiovascular complications as the reasons for hospital admission of young marijuana users," said Émilie Jouanjus, Pharm.D., Ph.D., lead author of the study and a medical faculty member at the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Toulouse in Toulouse, France. "This unexpected finding deserved to be further analyzed, ...