(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - Amita Sehgal, PhD, a professor of Neuroscience at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, describes in Cell a circuit in the brain of fruit flies that controls their daily, rhythmic behavior of rest and activity. The new study also found that the fly version of the human brain protein known as corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) is a major coordinating molecule in this circuit. Fly CRF, called DH44, is required for rest/activity cycles and is produced in cells that receive input from the clock cells in the fly brain. In mammals, CRF is secreted rhythmically and it drives the expression of glucocorticoids such as cortisol and is associated with stress and anxiety.
Animal models like flies are helping to fill gaps in current knowledge about how the brain works, notes Sehgal. Indeed, she says, the Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN), initiative, a project of the National Institutes of Health, includes the study of simple animal models, which are expected to provide more detailed insight into brain function.
Though much is known about the cellular and molecular components of the clock, the connections that link clock cells to overt behaviors, such as rest/activity behavior, have not been identified. "This study is essentially a map-of-the-circuitry experiment," says Sehgal, who is also an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). Like humans, flies are active during the day -- walking, flying, feeding and mating -- and spend most of the night asleep.
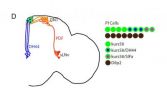
"We conducted a screen for circadian-relevant neurons in the fly brain and found that cells of the pars intercerebralis -- the fly version of the mammalian hypothalamus -- comprise an important component of the circadian output pathway for rest/activity rhythms in flies," Sehgal says. The mammalian hypothalamus is a neuroendocrine structure that regulates sleep, circadian rhythms, feeding and, metabolism.
The Penn team did a random targeting of cells, activating neuronal firing with a transgene designed for this purpose, to see which cells are important in the rest/active behavior. They found that cells in the pars intercerebralis (PI) are essential for rhythmic behavior, and PI cells are connected to the clock cells through a circuit of at least two synapses.
Molecular profiling of PI cells identified the fly version of DH44 as a circadian molecule that is specifically expressed by PI neurons and required for normal rest/activity rhythms in flies. And, when the scientists selectively activated or removed just six PI cells positive for DH44, the fly's activity cycles became irregular. In other words, the flies no longer restricted their sleep to the dark and their activity to the light, but instead showed more random distribution of these behaviors
INFORMATION:
Coauthors are Daniel J. Cavanaugh, Jill D. Geratowski, Julian R. A. Wooltorton, Jennifer M.
Spaethling, Xiangzhong Zheng, and James H. Eberwine, all from Penn, and Clare E. Hector and Erik C. Johnson, from Wake Forest University.
This research as funded in part by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (2R01NS048471) and HHMI.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine has been ranked among the top five medical schools in the United States for the past 17 years, according to U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $392 million awarded in the 2013 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; Chester County Hospital; Penn Wissahickon Hospice; and Pennsylvania Hospital -- the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional affiliated inpatient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region include Chestnut Hill Hospital and Good Shepherd Penn Partners, a partnership between Good Shepherd Rehabilitation Network and Penn Medicine.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2013, Penn Medicine provided $814 million to benefit our community.
Fruit fly study identifies brain circuit that drives daily cycles of rest, activity
Simple animal models provide new insight into basic brain function
2014-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists find way to target cells resistant to chemo
2014-04-24
Scientists from The University of Manchester have identified a way to sensitise cancer cells to chemotherapy - making them more open to treatment.
The study published today in Cell Reports, could pave the way for the development of drugs to target cells that have become resistant to treatment.
The research team made the discovery whilst exploring the possible mechanisms behind resistance to chemotherapy drugs like Paclitaxel, often used to treat breast and colon cancer.
Dr Andrew Gilmore, who led the research team at The University of Manchester, is part of both the ...
New type of protein action found to regulate development
2014-04-24
Johns Hopkins researchers report they have figured out how the aptly named protein Botch blocks the signaling protein called Notch, which helps regulate development. In a report on the discovery, to appear online April 24 in the journal Cell Reports, the scientists say they expect the work to lead to a better understanding of how a single protein, Notch, directs actions needed for the healthy development of organs as diverse as brains and kidneys.
The Johns Hopkins team says their experiments show that Botch uses a never-before-seen mechanism, replacing one chemical group ...
Researchers discover new genetic brain disorder in humans
2014-04-24
A newly identified genetic disorder associated with degeneration of the central and peripheral nervous systems in humans, along with the genetic cause, is reported in the April 24, 2014 issue of Cell.
The findings were generated by two independent but collaborative scientific teams, one based primarily at Baylor College of Medicine and the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the other at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, the Academic Medical Center (AMC) in the Netherlands and the Yale University School of Medicine.
By performing DNA sequencing ...
Scientists reprogram blood cells into blood stem cells in mice
2014-04-24
BOSTON (April 24, 2014)—Researchers at Boston Children's Hospital have reprogrammed mature blood cells from mice into blood-forming hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), using a cocktail of eight genetic switches called transcription factors. The reprogrammed cells, which the researchers have dubbed induced HSCs (iHSCs), have the functional hallmarks of HSCs, are able to self-renew like HSCs, and can give rise to all of the cellular components of the blood like HSCs.
The findings mark a significant step toward one of the most sought-after goals of regenerative medicine: the ...
To mark territory or not to mark territory: Breaking the pheromone code
2014-04-24
LA JOLLA, CA— April 24, 2014 —A team led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has deciphered the surprisingly versatile code by which chemical cues help trigger some of the most basic behaviors in mice.
The findings shed light on the evolution of mammalian behaviors—which include human behaviors—and their underlying brain mechanisms.
"How does an individual respond differently to the environment based on experience? How does it distinguish itself from others? These are some of the fundamental questions that a study like this one helps us address," ...
Genetic legacy from the Ottoman Empire: Single mutation causes rare brain disorder
2014-04-24
An international team of researchers have identified a previously unknown neurodegenerative disorder and discovered it is caused by a single mutation in one individual born during the Ottoman Empire in Turkey about 16 generations ago.
The genetic cause of the rare disorder was discovered during a massive analysis of the individual genomes of thousands of Turkish children suffering from neurological disorders.
"The more we learn about basic mechanisms behind rare forms of neuro-degeneration, the more novel insights we can gain into more common diseases such as Alzheimer's ...
Oops! Researchers find neural signature for mistake correction
2014-04-24
Culminating an 8 year search, scientists at the RIKEN-MIT Center for Neural Circuit Genetics captured an elusive brain signal underlying memory transfer and, in doing so, pinpointed the first neural circuit for "oops" ? the precise moment when one becomes consciously aware of a self-made mistake and takes corrective action.
The findings, published in Cell, verified a 20 year old hypothesis on how brain areas communicate. In recent years, researchers have been pursuing a class of ephemeral brain signals called gamma oscillations, millisecond scale bursts of synchronized ...
Large-scale identification and analysis of suppressive drug interactions
2014-04-24
TORONTO – Baker's yeast is giving scientists a better understanding of drug interactions, which are a major cause of hospitalization and illness world-wide.
When two or more medications are taken at the same time, one can suppress or enhance the effectiveness of the other. Similarly, one drug may magnify the toxicity of another. These types of interactions are a major cause of illness and hospitalization. However, there are severe practical limits on the practical scope of drug studies in humans. Limits come in part from ethics and in part from the staggering expense. ...
Skin layer grown from human stem cells could replace animals in drug and cosmetics testing
2014-04-24
An international team led by King's College London and the San Francisco Veteran Affairs Medical Center (SFVAMC) has developed the first lab-grown epidermis – the outermost skin layer - with a functional permeability barrier akin to real skin. The new epidermis, grown from human pluripotent stem cells, offers a cost-effective alternative lab model for testing drugs and cosmetics, and could also help to develop new therapies for rare and common skin disorders.
The epidermis, the outermost layer of human skin, forms a protective interface between the body and its external ...
Scripps Research Institute scientists find new point of attack on HIV for vaccine development
2014-04-24
LA JOLLA, CA— April 24, 2014 —A team led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) working with the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI) has discovered a new vulnerable site on the HIV virus. The newly identified site can be attacked by human antibodies in a way that neutralizes the infectivity of a wide variety of HIV strains.
"HIV has very few known sites of vulnerability, but in this work we've described a new one, and we expect it will be useful in developing a vaccine," said Dennis R. Burton, professor in TSRI's Department of Immunology and Microbial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Fruit fly study identifies brain circuit that drives daily cycles of rest, activitySimple animal models provide new insight into basic brain function