(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
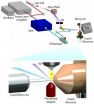
HZB-scientist Emad Aziz, who leads the Joint lab between HZB and Freie Universität Berlin, has developed and installed a new tool to investigate ultrafast dynamics in solutions and at interfaces with the use of ultrashort Laser pulses. Liquid phases are a natural environment for many interesting processes in chemistry and biology, and short light pulses allow insights into electronic and structural dynamics of molecules and molecular complexes. In particular, photoelectron spectroscopy with extreme ultraviolet (XUV) radiation is a powerful method to probe the electron density in a valence shell of a molecular system. In combination with a pump-probe technique, this method enables to reveal mechanisms of molecular processes, which typically occur on the subpicosecond or femtosecond time scale.
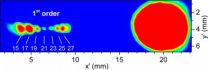
Now Aziz and his team have built a new laser-based tabletop setup which generates XUV light pulses with a duration of 45 femtoseconds. To select specific wavelengths, they implemented special reflection zone plates, developed and fabricated in the HZB-Institute for Nanometre Optics and Technology headed by Alexei Erko. These reflection zone plates achieve monochromatization with extremely high efficiency and minimum temporal pulse distortion.
"In building up this new table-top device and testing it, Jan Metje has achieved one of the major goals of his PhD", his co-supervisor Dr. Igor Kiyan explains. Pulse duration of 45 femtoseconds for monochromatized harmonics is 300 times shorter than the typical pulse duration of synchrotron radiation (15 picoseconds) and is comparable to the pulse length of a free-electron laser (FEL). "Our lab-based experiment has some advantages over FEL's", Aziz points out: "It allows time resolved photo-emission spectroscopy of molecular systems in solutions, so that we can investigate catalytic and energy materials under real conditions as well as the chemistry of natural processes which occur typically in liquid phases and at interfaces. And, last but not least, it is accessible all the time."
INFORMATION: END
New tool for Joint Lab to investigate the chemistry of nature
2014-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harnessing magnetic vortices for making nanoscale antennas
2014-04-30
UPTON, NY—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory are seeking ways to synchronize the magnetic spins in nanoscale devices to build tiny yet more powerful signal-generating or receiving antennas and other electronics. Their latest work, published in Nature Communications, shows that stacked nanoscale magnetic vortices separated by an extremely thin layer of copper can be driven to operate in unison, potentially producing a powerful signal that could be put to work in a new generation of cell phones, computers, and other applications.
The ...
NOAA-led researchers discover ocean acidity is dissolving shells of tiny snails off West Coast
2014-04-30
A NOAA-led research team has found the first evidence that acidity of continental shelf waters off the West Coast is dissolving the shells of tiny free-swimming marine snails, called pteropods, which provide food for pink salmon, mackerel and herring, according to a new paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Researchers estimate that the percentage of pteropods in this region with dissolving shells due to ocean acidification has doubled in the nearshore habitat since the pre-industrial era and is on track to triple by 2050 when coastal waters become 70 ...
Neiker-Tecnalia studies the effects of climate change on Tempranillo grape wines
2014-04-30
Climate change is set to affect the quality of the wines of the Tempranillo grape variety, according to the conclusions of a piece of research conducted by the Basque Institute for Agricultural Research and Development Neiker-Tecnalia, in collaboration with the University of Navarre and the Aula Dei (EEAD) Experimental Station of the National Council for Scientific Research (CSIC). Scientists from these bodies have studied the behaviour of the vines in conditions of climate change; in other words, higher temperature, increased presence of CO2 and greater environmental aridity. ...
7.0T NMR assesses changes in hippocampal neurons in animal models of Alzheimer's disease
2014-04-30
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy can quantitatively analyze in vivo abnormalities of biochemical metabolism within brain tissue in a noninvasive and non-radioactive manner. Compared with 3.0T magnetic resonance spectroscopy, high-field magnetic resonance spectroscopy (≥ 7.0T) exhibits high spatial resolution and density resolution, microscopic imaging of the living body, and obtains both high scanning resolution and result precision within a shorter scan time, thus providing a higher value in clinical diagnosis. In a recent study reported in the Neural Regeneration ...
A researcher from the University of Cádiz discovers 18 new species of molluscs
2014-04-30
Molluscs are invertebrates that make up one of the most numerous groups in the animal kingdom. They are everywhere, from great heights of over 3,000m above sea level to ocean profundities of over 5,000m deep, in polar and tropical waters and they tend to be common elements on coastlines around the world. Within this animal group are found the nudibranchs, characterized among other things, for not having shells and being brightly coloured. This colouring alerts their predators to their toxicity. Within this group, in turn, we can find the Aeolidiidae family.
This family ...
Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder releases dopamine in the brain
2014-04-30
Philadelphia, PA, April 30, 2014 – Some have characterized dopamine as the elixir of pleasure because so many rewarding stimuli – food, drugs, sex, exercise – trigger its release in the brain. However, more than a decade of research indicates that when drug use becomes compulsive, the related dopamine release becomes deficient in the striatum, a brain region that is involved in reward and behavioral control.
New research now published in Biological Psychiatry from the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam suggests that dopamine release is increased in obsessive-compulsive ...
Candid 'insider' views in the NHS could help detect reasons for poor care
2014-04-30
Asking NHS staff about what affects whether they would recommend their organisation for family and friends is an important source of intelligence for improving quality and safety of care, says a new study.
This finding by researchers in the Universities of Leicester, Aberdeen, and Bristol has been published in a paper, 'The friends and family test: a qualitative study of concerns that influence the willingness of English National Health Service staff to recommend their organisation', in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine.
Since 2009, the annual Staff Survey ...
Greater surgeon experience increases likelihood of mitral valve repair vs. replacement
2014-04-30
Toronto, ON, Canada, April 30, 2014 – A new study presenting data from 17 cardiac surgical centers in Virginia, representing 100 surgeons and 99% of cardiac operations performed in the state, demonstrates that, even today, significant variations – among surgeons and hospitals - still exist in the performance of mitral valve repair vs replacement for moderate to severe mitral regurgitation. Significant associations were observed between the propensity for MV repair and both institutional and surgeon annual volume, although increasing surgeon volume appears to be the much ...
CT in the operating room allows more precise removal of small lung cancers
2014-04-30
Toronto, ON, Canada, April 30, 2014 – A new technique that brings CT imaging into the operating room will allow surgeons to precisely demarcate and remove small sub-centimeter lung nodules, leaving as much healthy tissue as possible, according to Raphael Bueno, MD, of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston. His team is presenting the results of this late-breaking research at the 94th AATS Annual Meeting in Toronto, ON, Canada on April 30, 2014.
Lung cancer remains the deadliest cancer and a recent study, the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial, indicated that screening ...
New lab-on-a-chip device overcomes miniaturization problems
2014-04-30
UNSW Australia chemists have invented a new type of tiny lab-on-a-chip device that could have a diverse range of applications, including to detect toxic gases, fabricate integrated circuits and screen biological molecules.
The novel technique developed by the UNSW team involves printing a pattern of miniscule droplets of a special solvent onto a gold-coated or glass surface.
"We use a class of 'green' solvents called ionic liquids, which are salts that are liquid at room temperature. They are non-volatile, so this overcomes one of the main problems in making useful miniaturised ...