(Press-News.org) The rate at which new species evolve is limited by competition for ecological niches, report scientists from the University of Chicago in Nature on April 30. The study, which analyzes the evolutionary and genetic relationships between all 461 songbird species that live in the Himalayan mountains, suggests that as ecological niches within an environment are filled, the formation of new species slows or even stops.
To study what controls the process of speciation, Trevor Price, PhD, professor of ecology and evolution at the University of Chicago, Dhananjai Mohan of the Indian Forest service and their colleagues looked at songbirds in the eastern Himalayas, a region which contains the greatest diversity of songbirds in the world. Thought to have originated from a single species around 50 million years ago, the songbird suborder—which includes swallows, warblers, finches and crows—contains more than 5,000 species, occupies a wide range of climates and possesses extreme variations in body mass, shape and feeding adaptations.
The team collected and sequenced DNA from all 461 species of Himalayan songbirds—including ultra-rare species such as the Bugun liocichla. Of these species, 358 breed within a 10,000 square kilometer area, offering the ability to compare the difference between species in the area and those elsewhere in the Himalayas. The team then created a molecular-based phylogenetic tree that detailed the evolutionary relationships between all the species.
Based on genetic information, the researchers discovered that eastern Himalayan songbirds are, on average, separated from each other by six to seven million years—roughly the same amount of time that humans and chimpanzees have been separated.
"Despite the great diversity of environments and ability for species to move between areas, evolution in eastern Himalayas appears to have slowed to a basic halt," Price said. "Other species have formed elsewhere, such as in China and Siberia, but most have been unable to spread into this region."
The researchers attribute this slowing of evolution to the filling of ecological niches, or exploitable habitats or resources for new species to adapt to. The formation of new species is usually thought to involve three steps. First, a species expands across an environmental range. Then a barrier, such as climate change or a geographic event, causes the species to separate into distinct populations. Lastly, the development of reproductive isolation—the inability to interbreed—finalizes the speciation process. This cycle then repeats, creating the breadth of diversity seen in nature.
Price and his colleagues argue that the expansion of a range cannot occur if there are no ecological niches for a species to expand into. Despite the ability of birds to fly and cross geographic barriers, they cannot persist in regions where they are outcompeted by existing species who occupy available niches. In the eastern Himalayas, the researchers found evidence of this in numerous differences in feeding method and body size that appeared early in the evolutionary history of songbirds. Less dramatic ecological differences, such as living at differing elevations, appeared to form later as the initial adaptive radiation slowed.
"Our argument is that niche filling has stopped species from getting big ranges," Price said. "In the eastern Himalayas, it has become harder and harder for new species to get into that system, and we are quite close to the maximum number of species that can be accommodated. There is little room for more species because niches are increasingly occupied."
This model for diversification stands in stark contrast to previous hypotheses, many of which have focused on the slow development of reproductive isolation as the limiting factor.
In addition, the researchers discovered that the greatest diversity of songbird species were located at around a 2,000 meter elevation—a more temperate region compared to the tropical forest below. They plan to further study this phenomenon on return expeditions.
"It's important to realize just how old and how much incredible genetic diversity are in these mountainous forests," Price adds. "All these species managed to deal with warming, glaciation and cooling without changing very much. It's quite amazing to me think that the next 100 years a lot of these may be gone, when they managed to get through the last 6 million years."
INFORMATION:
The study, "Niche filling slows the diversification of Himalayan songbirds," was funded in part by the National Science Foundation and the National Geographic Society. Additional authors include Daniel Hooper, Caitlyn Buchanan, Ulf Johansson, D. Thomas Tietze, Per Alstrom, Urban Olsson, Mousumi Ghosh-Harihar, Farah Ishtiaq, Sandeep Gupta, Jochen Martens, Bettina Harr and Pratap Singh.
Competition for ecological niches limits the formation of new species
2014-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Initial research: Mango's effects on ulcerative colitis & bone parameters in animal models
2014-04-30
SAN DIEGO, CA – April 30, 2014 – Three new mango-related studies were presented this week at the 2014 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) in San Diego, revealing initial findings on the effects of mango consumption on ulcerative colitis and bone parameters in animal models.
"The mango industry's nutrition research program is committed to advancing our understanding of the role mangos can play as part of a healthy diet," said Megan McKenna, Director of Marketing for the National Mango Board. "These studies provide important insights that ...
Multiple consecutive days of tornado activity spawn worst events
2014-04-30
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Significant tornado outbreaks and especially strong tornadoes are more likely occur within periods of activity lasting three or more days, according to a Purdue University tornado expert.
Jeff Trapp, a professor of earth, atmospheric and planetary sciences, examined 30 years of U.S. weather records and found that an outbreak of 20 or more reported tornadoes had a 74 percent probability of occurring during a period of tornado activity lasting three or more days. During those same periods, a tornado rated 3 or higher on the Enhanced Fujita scale had ...
MS researchers find brain & cognitive reserve protect long-term against cognitive decline
2014-04-30
West Orange, NJ. April 30, 2014. Multiple sclerosis researchers have found that brain reserve and cognitive reserve confer a long-term protective effect against cognitive decline: Sumowski JF, Rocca MA, Leavitt VM, Dackovic J, Mesaros S, Drulovic J, Deluca J, Filippi M. Brain reserve and cognitive reserve protect against cognitive decline over 4.5 years in MS. Neurology. 2014 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000433 [Epub ahead of print]. James Sumowski, PhD, lead author of the article, and John DeLuca, PhD, are at Kessler Foundation. Co-authors are from the Manhattan ...
'US Should significantly reduce rate of incarceration,' says new report
2014-04-30
WASHINGTON -- Given the minimal impact of long prison sentences on crime prevention and the negative social consequences and burdensome financial costs of U.S. incarceration rates, which have more than quadrupled in the last four decades, the nation should revise current criminal justice policies to significantly reduce imprisonment rates, says a new report from the National Research Council.
A comprehensive review of data led the committee that wrote the report to conclude that the costs of the current rate of incarceration outweigh the benefits. The committee recommended ...
Seeing the bedrock through the trees
2014-04-30
University of California, Berkeley, geologist William Dietrich pioneered the application of airborne LIDAR – light detection and ranging – to map mountainous terrain, stripping away the vegetation to see the underlying ground surface.
But that didn't take him deep enough. He still couldn't see what was under the surface: the depth of the soil, the underlying weathered rock and the deep bedrock.
He and geology graduate student Daniella Rempe have now proposed a method to determine these underground details without drilling, potentially providing a more precise way to ...
Hope for better drugs to treat stroke and heart attacks
2014-04-30
An international team of researchers in cooperation with the University of Bonn has taken two "snapshots" of a receptor which are of critical importance for blood coagulation. The scientists now hope to be able to develop novel drugs using these results. These include tailor-made blood-thinning substances for heart attack and stroke patients whose effects are reversible and better controllable than those of current therapies. The researchers are presenting their results in the renowned journal "Nature."
After a cut to the finger, blood platelets come into play: they adhere ...
Should the EU ban on the import of seal products stand?
2014-04-30
Next month, following an appeal by Canada and Norway to overturn the EU ban on the import of seal products, the World Trade Organization (WTO) is expected to announce whether the 2013 decision will be upheld. In an editorial article, a University of Bristol academic, whose research on the animal welfare of the seal hunt has been used in the case, explains why the ban should stand.
The article by Dr Andy Butterworth, Senior Lecturer in Animal Sciences at the University of Bristol's School of Veterinary Sciences and an official observer of the seal hunt is published in ...
Prostate cancer and blood lipids share genetic links
2014-04-30
Numerous studies have suggested a relationship between cardiovascular disease risk factors and prostate cancer. A new study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues in Norway, significantly refines the association, highlighting genetic risk factors associated with low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides as key players and identifying 17 related gene loci that make risk contributions to levels of these blood lipids and to prostate cancer
The findings, published in the April 30, 2014 online issue of ...
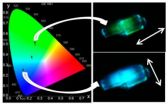
New hybrid material that changes colour according to the direction of the light
2014-04-30
This news release is available in Spanish. The aim with respect to hybrid materials with one organic component and another inorganic one is to combine the best attributes of each one into a single system. Labs across the world are working to develop new hybrid materials for technological applications in nanotechnologies, in particular, and these materials are already being used in lightweight materials for cars, sports equipment, in biomimetic materials, like prostheses, etc.
The hybrid material being sought after by the research group in the Department of Physical ...
Neanderthals were not inferior to modern humans, says CU-Boulder study
2014-04-30
The embargo has been lifted for the article, 'Neandertal Demise: An Archaeological Analysis of the Modern Human Superiority Complex.'
If you think Neanderthals were stupid and primitive, it's time to think again.
The widely held notion that Neanderthals were dimwitted and that their inferior intelligence allowed them to be driven to extinction by the much brighter ancestors of modern humans is not supported by scientific evidence, according to a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Neanderthals thrived in a large swath of Europe and Asia between about ...