(Press-News.org) The present study illustrates, for the hypersonic flows, through the local and marching analysis, the crossover of the mode W and the mode T at O(1) wavenumber and large Görtler number regime. In fact, it is at this wavenumber regime that the instability is most likely to occur. The two approaches are expected to deliver similar results and the marching analysis helps to express the details of the crossover and confirm the result of the local analysis.
In fact the study of Görtler instability goes back to the date of the 1940s. Since Görtler's pioneering investigation on the boundary layer instabilities subjected to the negative curvature in 1940 highlighting the existence of the streamwise-oriented counter-rotating vortices, extensive studies have been carried out on this subject especially in the incompressible flows. These vortices are caused by the imbalance between the centrifugal force and the normal pressure gradient near a concave surface and exhibit a quasi-constant spanwise wavelength.
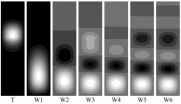
The most distinct difference between the incompressible counterparts is the existence of the trapped-layer mode (mode T) apart from the conventional wall layer mode (mode W) observed in the incompressible cases. The velocity disturbances of the multiple Görtler modes are given below in Figure 1. It is evident that the mode T has its disturbances detached from the wall. As a result of this, the nonlinear development of Görtler vortices in hypersonic boundary layers shows considerable differences. Figure 2 shows the development of the streamwise velocity contours of the Görtler flow up to a fully saturated states. The Mach numbers are 1.5, 3.0, 4.5 and 6.0 respectively. The famous mushroom structures (subsonic and moderate supersonic, e.g., Ma=1.5 and 3.0) are replaced by the bell shapes (hypersonic, e.g., Ma=4.5 and 6.0). This is because the mode T is the most dangerous modal shape in such flows.
To conclude, when considering the flow transition induced by the Görtler instability in hypersonic flows, the mode T highlighted in this article must be considered. Also, with appropriate parameters the mode T and mode W have crossovers. This study is a guidance for future studies of the secondary instability of Görtler vortices and flow transition in hypersonic boundary flows. The readers are also recommended to read the future articles by the authors.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
Jie Ren and Song Fu, "Competition of the multiple Görtler modes in hypersonic boundary layer flows" SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2014(6), 1178-1193
DOI: 10.1007/s11433-014-5454-9
http://phys.scichina.com:8083/sciGe/EN/abstract/abstract508853.shtml
Science China Press Co., Ltd. (SCP) is a scientific journal publishing company of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). For 60 years, SCP takes its mission to present to the world the best achievements by Chinese scientists on various fields of natural sciences researches.
http://www.scichina.com/
Competition of the multiple Gortler modes in hypersonic boundary layer flows
2014-05-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vitamin D deficiency linked to aggressive prostate cancer
2014-05-01
CHICAGO --- African-American and European-American men at high risk of prostate cancer have greater odds of being diagnosed with an aggressive form of the disease if they have a vitamin D deficiency, according to a new study from Northwestern Medicine® and the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC).
Results of the study will be published May 1 in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Vitamin D deficiency could be a biomarker of advanced prostate tumor progression in large segments of the general population," said Adam ...
Extreme sleep durations may affect brain health in later life
2014-05-01
BOSTON, MA – A new research study led by Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) published in The Journal of the American Geriatrics Society in May, shows an association between midlife and later life sleeping habits with memory; and links extreme sleep durations to worse memory in later life. The study suggests that extreme changes in sleep duration from middle age to older age may also worsen memory function.
"Sleep Duration In Midlife and Later Life In Relation to Cognition: The Nurses' Health Study," led by Elizabeth Devore, ScD, instructor in medicine in the Channing ...
New UT Arlington research could improve pharmaceuticals testing
2014-05-01
A UT Arlington chemistry professor, renowned for his work in the area of chemical separations, is leading an effort to find a more accurate way to measure water content in pharmaceuticals – a major quality issue for drug manufacturers.
Daniel W. Armstrong, UT Arlington's Robert A. Welch Chair in Chemistry, says the new technique could be 100 times more sensitive than one of the most popular current methods.
"The analysis for water in many consumer products, including drugs, is one of the most required tests done in the world," said Armstrong. "Current methods have many ...
Playing pool with carbon atoms
2014-04-30
A University of Arizona-led team of physicists has discovered how to change the crystal structure of graphene, more commonly known as pencil lead, with an electric field, an important step toward the possible use of graphene in microprocessors that would be smaller and faster than current, silicon-based technology.
Graphene consists of extremely thin sheets of graphite: when writing with a pencil, graphene sheets slough off the pencil's graphite core and stick to the page. If placed under a high-powered electron microscope, graphene reveals its sheet-like structure ...
Ground breaking technique offers DNA 'Sat Nav' direct to your ancestor's home 1,000 years ago
2014-04-30
Tracing where your DNA was formed over 1,000 years ago is now possible due to a revolutionary technique developed by a team of international scientists led by experts from the University of Sheffield.
The ground breaking Geographic Population Structure (GPS) tool, created by Dr Eran Elhaik from the University of Sheffield's Department of Animal and Plant Sciences and Dr Tatiana Tatarinova from the University of Southern California, works similarly to a satellite navigation system as it helps you to find your way home, but not the one you currently live in – but rather ...
Cutting cancer to pieces: New research on bleomycin
2014-04-30
A variety of cancers are treated with the anti-tumor agent bleomycin, though its disease-fighting properties remain poorly understood.
In a new study, lead author Basab Roy—a researcher at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute—describes bleomycin's ability to cut through double-stranded DNA in cancerous cells, like a pair of scissors. Such DNA cleavage often leads to cell death in particular types of cancer cells.
The paper is co-authored by professor Sidney Hecht, director of Biodesign's Center for BioEnergetics. The study presents, for the first time, alternative ...
Infertile women want more support
2014-04-30
VIDEO:
University of Iowa Communication Studies researchers Keli Steuber and Andrew High talk about infertility.
Click here for more information.
Many women coping with infertility count on relatives or close friends for encouragement and assistance. But according to research at the University of Iowa, when it comes to support, women may not be receiving enough—or even the right kind.
"Infertility is a more prevalent issue than people realize. It affects one in six couples, ...
Stem cells from teeth can make brain-like cells
2014-04-30
University of Adelaide researchers have discovered that stem cells taken from teeth can grow to resemble brain cells, suggesting they could one day be used in the brain as a therapy for stroke.
In the University's Centre for Stem Cell Research, laboratory studies have shown that stem cells from teeth can develop and form complex networks of brain-like cells. Although these cells haven't developed into fully fledged neurons, researchers believe it's just a matter of time and the right conditions for it to happen.
"Stem cells from teeth have great potential to grow into ...
Salk Institute study identifies novel regulator of key gene expression in cancer
2014-04-30
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies have identified a key genetic switch linked to the development, progression and outcome of cancer, a finding that may lead to new targets for cancer therapies.
The switch, a string of nucleotides dubbed a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), does not code for proteins like regular RNA. Instead, the scientists found, this particular lncRNA acts as an on/off switch for a key gene whose excessive activity is tied to inflammation and cancer, COX-2.
The COX-2 gene mediates inflammation, which in most cases helps our ...
New revolutionary sensor links pressure to color change
2014-04-30
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Imagine an automobile crash test that uses test dummies painted all over with a substance that can change color according to the levels of stress that various parts of the dummies' bodies will endure. Such a "color map" could provide vital information to engineers designing safer automobiles.
Or imagine baseball gloves that when worn show the batters if they are using the appropriate amount of pressure to grip their bats, resulting in better performance.
New technology developed at the University of California, Riverside may now make the above and ...