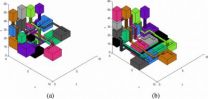
(Press-News.org) When you get sick, your physician may take a sample of your blood, send it to the lab and wait for results. In the near future, however, doctors may be able to run those tests almost instantly on a piece of plastic about the size of credit card.
These labs-on-a-chip would not only be quick—results are available in minutes—but also inexpensive and portable. They could be used miles from the nearest medical clinic to test for anything from HIV to diabetes. But as powerful as they may be, they could be far better, says Shiyan Hu, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at Michigan Technological University.
Generally, a lab-on-a-chip (LOC) can run no more than a test or two. That's because the chips are designed manually, says Hu. If the LOC were made using computer-aided design, you could run dozens of tests with a single drop of blood.
"In a very short time, you could test for many conditions," he said. "This really would be an entire lab on a chip."
With PhD student Chen Liao, Hu has taken the first step. "We have developed software to design the hardware," he said. Their work focuses on routing the droplet of blood or other fluid through each test on the chip efficiently while avoiding any chip contamination.
"It has taken us four years to do the software, but to manufacture the LOC would be inexpensive," Hu said. "The materials are very cheap, and the results are more accurate than a conventional lab's."
Ultimately, Hu aims to fabricate their own biochip using their software.
INFORMATION:
Their work was featured on the cover of the March edition of IEEE Transactions on Nanobiosciences and described in the article "Physical-Level Synthesis for Digital Lab-On-a-Chip Considering Variation, Contamination, and Defect." Liao was partially supported by an A. Richard Newton Graduate Scholarship, awarded by the Design Automation Conference.
A lab in your pocket
Using CAD to load dozens of tests on a lab-on-a-chip
2014-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pushing the boundaries of stem cells
2014-05-07
(NEW YORK – May 7) Adults suffering from diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood-related disorders may benefit from life-saving treatment commonly used in pediatric patients. Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified a new technique that causes cord blood (CB) stems cells to generate in greater numbers making them more useful in adult transplantation.
The study, published in the May issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation, looked at ways to expand the number of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in the laboratory required ...
NASA telescopes coordinate best-ever flare observations
2014-05-07
VIDEO:
Watch the movie to see the wealth of colorful NASA observations of an X-class flare on March 29 -- the most comprehensively observed flare, ever.
BROADCAST QUALITY: http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011522/....
Click here for more information.
On March 29, 2014, an X-class flare erupted from the right side of the sun... and vaulted into history as the best-observed flare of all time. The flare was witnessed by four different NASA spacecraft and one ground-based ...
Glutamate imaging better than MR spectroscopy in first 3 hours after ischemic stroke
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 5, 2014—Glutamate imaging reveals ischemic lesions in the first 3 hours after stroke that are not distinguishable in T1-weighted and T2-weighted imaging.
Researchers using chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST), an emerging MRI technology, have found that using glutamate with CEST shows high spatial resolution in vivo. The finding has the potential to speed diagnosis—and, therefore, treatment—in the critical first hours after a stroke.
"I have been interested in glutamate imaging since its inception," said researcher Zhuozhi Dai of Second Affiliated ...
New study examines premature menopause and effects on later life cognition
2014-05-07
Premature menopause is associated with long-term negative effects on cognitive function, suggests a new study published today (7 May) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (BJOG).
The average age of menopause is around 50 years in the Western World. Premature menopause refers to menopause at or before 40 years of age, this could be due to a bilateral ovariectomy, (surgically induced menopause)or non-surgical loss of ovarian function (sometimes referred to as 'natural' menopause).
The study, based on a sample of 4868 women, used cognitive tests ...
Image-guided peritoneal dialysis catheter placement significantly reduces complications
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 7, 2014— Patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis catheter placement via fluoroscopy and ultrasound-guidance experienced significantly fewer complications at 1 year post-insertion than did patients whose catheters were placed laparoscopically.
The first of two study groups received catheters using fluoroscopy and ultrasound guidance under conscious sedation by interventional radiologists. In the second group, the catheters were inserted using laparoscopy under general anesthesia by surgeons.
"Our results showed that the overall complications at 1 ...
Iterative reconstruction techniques reduce radiation dose for pediatric brain CT
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 7, 2014—A study conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School found that estimated radiation doses are substantially lower for pediatric CT exams of the brain that used an adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique (ASIR) compared to those that did not use ASIR. The researchers found that the brain and salivary gland doses were much lower for ASIR-enabled exams compared to those without ASIR technique. However, no differences in the estimated organ doses were found for the thyroid gland, skeleton, and eye lenses across ...
Nonscreened patients with breast cancer need more treatment than screened patients
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 6, 2014—Screening 40- to 49-year-old women for breast cancer has additional benefits beyond the proven decrease in mortality rate. Patients screened with mammography are statistically less likely to undergo chemotherapy, avoiding the associated toxic morbidities. Screening mammography also helps identify a subset of patients at increased risk of breast cancer by diagnosing high-risk lesions.
The majority of high-risk lesions identified in a retrospective chart review were found in screened patients. Identifying patients at high risk may allow for the ...
Overestimation of radiation exposure may keep women from critical screening
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 5, 2014—Misinformation and misunderstanding about the risks associated with ionizing radiation create heightened public concern and fear, and may result in avoidance of screening mammography that can detect early cancers.
In a study to determine the baseline understanding of the radiation associated with mammography among patients presenting for initial or follow-up imaging, women were asked to rate the amount of radiation received in a single mammogram as being significantly less, slightly less, about the same, slightly more, or significantly more compared ...
EARTH Magazine: Naturally occurring methane found in groundwater in New York
2014-05-07
Alexandria, Va. – Since hydraulic fracturing operations began in the Marcellus Shale region, debate has raged over whether drilling operations are causing high levels of methane in drinking-water wells. But few systematic scientific studies have been published to date, so it's unknown if high methane levels are natural or the result of contamination from nearby gas wells. Now, a new study is adding some much-needed baseline data for methane levels in groundwater in New York. The results suggest that at least in some cases methane occurs at naturally high levels in groundwater.
Read ...
NASA watching year's first tropical low headed for southwestern Mexico
2014-05-07
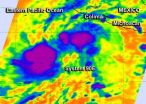
There's a tropical low pressure area in the Eastern Pacific Ocean today, about 8 days before the official Eastern Pacific hurricane season begins. NOAA's National Hurricane Center is giving it a 50 percent chance of becoming a tropical depression in the next two days, and NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead to gather infrared data on it.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over developing tropical low pressure system 90E on May 8 at 08:41 UTC (4:41 a.m. EDT) and infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard, showed that some of the thunderstorms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
[Press-News.org] A lab in your pocketUsing CAD to load dozens of tests on a lab-on-a-chip