(Press-News.org) Leptin-dependent regulation of reproduction
Individuals that lack the adipose-derived hormone leptin fail to complete puberty and are infertile. Leptin-deficient mice recapitulate human phenotypes; however, it is not clear how leptin and leptin signaling impact the reproductive axis. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Vincent Prevot and colleagues at INSERM U837 evaluated leptin deficient animals and determined that leptin acts directly on neurons in the preoptic region of the hypothalamus that synthesize nitric oxide to regulate peripheral levels of leutinizing hormone (LH), which is essential for reproduction. Administration of leptin increased neuronal production of nitric oxide synthase, while deletion or pharmacological inhibition of NOS blocked leptin-induced LH release in mice. Mathematical models indicated that leptin action in the preoptic region leads to a build-up of NO that reaches a level that is critical for the induction and release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and subsequent LH secretion by the pituitary gland. This study demonstrates that leptin communicates the status of peripheral energy stores to GnRH-releasing neurons via the preoptic hypothalamus to regulate fertility.
TITLE:
Leptin-dependent neuronal NO signaling in the preoptic hypothalamus facilitates reproduction
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Vincent Prevot
Inserm U837, Lille, FRA
Phone: +33 612-90-38-76; E-mail: vincent.prevot@inserm.fr
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/65928
Female susceptibility to CNS autoimmunity linked to sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that is defined by extensive neuronal demyelination and enhanced blood brain barrier (BBB) permeability. There is a strong sex bias in MS patients, with 3 to 4 female patients for every affected male. The female bias is recapitulated in SLJ mice with experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE), a commonly used MS model. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Robyn Klein and colleagues at Washington University performed whole transcriptome analysis of transcripts collected from EAE-susceptible CNS regions in naïve SJL mice and determined that female SJL mice express dramatically higher levels of the sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor S1PR2 compared to male animals. Expression and activity of S1PR2 were associated with endothelial barrier dysfunction, which enhanced BBB permeability and the loss of immune privilege. Pharmacological inactivation of S1PR2 signaling attenuated BBB permeability and EAE severity. Importantly, female MS patients also exhibited increased expression of S1PR2 in the CNS vasculature during periods of MS-associated CNS autoimmunity, indicating that S1PR2 may be a suitable therapeutic target in humans.
TITLE:
Enhanced sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 expression underlies female CNS autoimmunity susceptibility
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Robyn S. Klein
Washington University, Saint Louis, MO, USA
Phone: 314 286 2140; E-mail: rklein@dom.wustl.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/73408
IMMUNOLOGY
TITLE:
Decreased RORC-dependent silencing of prostaglandin receptor EP2 induces autoimmune Th17 cells
AUTHOR CONTACT:
David A. Hafler
Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA
Phone: 2037856351; E-mail: david.hafler@yale.edu
Or
David M. Kofler
Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA
Phone: 203.785.5947; Fax: 203.785.2238; E-mail: david.kofler@yale.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/72973
ONCOLOGY
TITLE:
Dynamic Treg interactions with intratumoral APCs promote local CTL dysfunction
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Thorsten Mempel
Massachusetts General Hospital & Harvard Medical School, Charlestown, MA, USA
Phone: 617-724-4596; E-mail: tmempel@mgh.harvard.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/66375
TITLE
Inhibition of ER stress–associated IRE-1/XBP-1 pathway reduces leukemic cell survival
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Chih-Chi Andrew Hu
H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute, Tampa, FL, USA
Phone: 813-745-4167; E-mail: chih-chi.hu@moffitt.org
Or
Juan R. Del Valle
H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute, Tampa, FL, USA
Phone: 813.745.4167; Fax: 813.745.1328; Email: Juan.DelValle@moffitt.org
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/73448
TITLE:
Combined MEK and JAK inhibition abrogates murine myeloproliferative neoplasm
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Jing Zhang
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, USA
Phone: 608-263-1147; E-mail: zhang@oncology.wisc.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/74182
NEPHROLOGY
TITLE:
KLF4-dependent epigenetic remodeling modulates podocyte phenotypes and attenuates proteinuria
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Hiroyuki Sasamura
Keio University, Tokyo, JPN
Phone: 81-3-5363-3796; Fax: 81-3-3359-2745; E-mail: sasamura@a8.keio.jp
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/69557
NEUROSCIENCE
TITLE:
Neural peptidase endothelin-converting enzyme 1 regulates endothelin 1–induced pruritus
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Martin Steinhoff
UCD (University College Dublin), Dublin, IRL
Phone: +353 1 716 6261; Fax: +353 1 716 6265; E-mail: Martin.Steinhoff@ucd.ie
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/67323
INFORMATION: END
JCI online ahead of print table of contents for May 8, 2014
2014-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Regenerating plastic grows back after damage
2014-05-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Looking at a smooth sheet of plastic in one University of Illinois laboratory, no one would guess that an impact had recently blasted a hole through it.
Illinois researchers have developed materials that not only heal, but regenerate. Until now, self-repairing materials could only bond tiny microscopic cracks. The new regenerating materials fill in large cracks and holes by regrowing material.
Led by professor Scott White, the research team comprises professors Jeffry S. Moore and Nancy Sottos and graduate students Brett Krull, Windy Santa Cruz and ...
Extinct kitten-sized hunter discovered
2014-05-08
A Case Western Reserve University student and his mentor have discovered an ancient kitten-sized predator that lived in Bolivia about 13 million years ago—one of the smallest species reported in the extinct order Sparassodonta.
Third-year undergraduate student Russell Engelman and Case Western Reserve anatomy professor Darin Croft made the finding by analyzing a partial skull that had been in a University of Florida collection more than three decades.
The researchers report their finding in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology online at: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02724634.2013.827118#.U2p8-S8njhM.
"The ...
Fueling aviation with hardwoods
2014-05-08
A key challenge in the biofuels landscape is to get more advanced biofuels—fuels other than corn ethanol and vegetable oil-based biodiesel—into the transportation pool. Utilization of advanced biofuels is stipulated by the Energy Independence and Security Act; however, current production levels lag behind proposed targets. Additionally, certain transportation sectors, such as aviation, are likely to continue to require liquid hydrocarbon fuels in the long term even as light duty transportation shifts to alternative power sources. A multi-university team lead by George ...
Chemotherapy timing is key to success
2014-05-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- MIT researchers have devised a novel cancer treatment that destroys tumor cells by first disarming their defenses, then hitting them with a lethal dose of DNA damage.
In studies with mice, the research team showed that this one-two punch, which relies on a nanoparticle that carries two drugs and releases them at different times, dramatically shrinks lung and breast tumors. The MIT team, led by Michael Yaffe, the David H. Koch Professor in Science, and Paula Hammond, the David H. Koch Professor in Engineering, describe the findings in the May 8 online ...
Climate change may worsen summertime ozone pollution
2014-05-08
Ozone pollution across the continental United States will become far more difficult to keep in check as temperatures rise, according to new research results.
The study shows that Americans face the risk of a 70 percent increase in unhealthy summertime ozone levels by 2050.
The results appear online this week in a paper in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, published by the American Geophysical Union.
The work was funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Warmer temperatures and other changes in the atmosphere ...
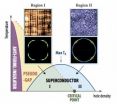
Scientists find solution to 2 long-standing mysteries of cuprate superconductivity
2014-05-08
UPTON, NY—Scientists seeking to understand the intricacies of high-temperature superconductivity—the ability of certain materials to carry electrical current with no energy loss—have been particularly puzzled by a mysterious phase that emerges as charge carriers are added that appears to compete with superconductivity. It's also been a mystery why, within this "pseudogap" phase, the movement of superconducting electrons appears to be restricted to certain directions. So exploring the pseudogap and whether and how it affects the movement of electrons has been a pivotal challenge. ...
'Rice theory' explains north-south China cultural differences, study shows
2014-05-08
A new cultural psychology study has found that psychological differences between the people of northern and southern China mirror the differences between community-oriented East Asia and the more individualistic Western world – and the differences seem to have come about because southern China has grown rice for thousands of years, whereas the north has grown wheat.
"It's easy to think of China as a single culture, but we found that China has very distinct northern and southern psychological cultures and that southern China's history of rice farming can explain why people ...
Exploring the magnetism of a single atom
2014-05-08
Magnetic devices like hard drives, magnetic random access memories (MRAMs), molecular magnets, and quantum computers depend on the manipulation of magnetic properties. In an atom, magnetism arises from the spin and orbital momentum of its electrons. 'Magnetic anisotropy' describes how an atom's magnetic properties depend on the orientation of the electrons' orbits relative to the structure of a material. It also provides directionality and stability to magnetization. Publishing in Science, researchers led by EPFL combine various experimental and computational methods to ...
Plant hormone has dual role in triggering flower formation, Penn study finds
2014-05-08
Flowers aren't just pretty to look at, they are how plants reproduce. In agricultural plants, the timing and regulation of flower formation has economic significance, affecting a crop's yield.
A new paper by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania published in the journal Science has revealed that a plant hormone once believed to promote flower formation in annual plants also plays a role in inhibiting flowers from forming. The dual role of this hormone, gibberellin, could be exploited to produce higher-yielding crop plants.
The study was led by Nobutoshi Yamaguchi ...
GaitTrack app makes cellphone a medical monitor for heart and lung patients
2014-05-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — By simply carrying around their cellphones, patients who suffer from chronic disease could soon have an accurate health monitor that warns their doctors when their symptoms worsen.
GaitTrack, an app developed by researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the U. of I. at Chicago, turns a smartphone into a sophisticated medical device. Unlike other apps that merely count steps, GaitTrack uses eight motion parameters to perform a detailed analysis of a person's gait, or walking pattern, which can tell physicians much about a patient's ...