(Press-News.org) Biomedical engineering researchers have developed an anti-cancer drug delivery method that essentially smuggles the drug into a cancer cell before triggering its release. The method can be likened to keeping a cancer-killing bomb and its detonator separate until they are inside a cancer cell, where they then combine to destroy the cell.
"This is an efficient, fast-acting way of delivering drugs to cancer cells and triggering cell death," says Dr. Ran Mo, lead author of a paper on the work and a postdoctoral researcher in the joint biomedical engineering program at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. "We also used lipid-based nanocapsules that are already in use for clinical applications, making it closer to use in the real world."
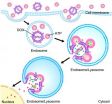
The technique uses nanoscale lipid-based capsules, or liposomes, to deliver both the drug and the release mechanism into cancer cells. One set of liposomes contains adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP), the so-called "energy molecule." A second set of liposomes contains an anti-cancer drug called doxorubicin (Dox) that is embedded in a complex of DNA molecules. When the DNA molecules come into contact with high levels of ATP, they unfold and release the Dox. The surface of the liposomes is integrated with positively charged lipids or peptides, which act as corkscrews to introduce the liposomes into cancer cells.
As the liposomes are absorbed into a cancer cell, they are sealed off from the rest of the cell in an endosome – a compartment that walls off all foreign material that gets into a cell.
The environment inside an endosome is acidic, which causes the Dox liposomes and ATP liposomes to fuse together, as well as to the wall of the endosome itself.
Meanwhile, two other things are happening simultaneously. First, the ATP liposomes spill their ATP into the Dox liposomes, releasing the Dox from its DNA cage. Second, the walls of the Dox liposomes create an opening in the endosome, spilling their Dox-rich contents into the surrounding cell – leading to cell death.
In a mouse model, the researchers found that the new technique significantly decreased the size of breast cancer tumors compared to treatment that used Dox without the nanoscale liposomes.
"This work is somewhat similar to previous research we've done with polymer-based nanogels – but there is a key difference," says Dr. Zhen Gu, senior author of the paper and an assistant professor in the joint biomedical engineering program. "The difference is that this liposome-based technique allows us to introduce additional ATP into the cancer cell, releasing the drug more quickly.
"Being able to adjust ATP levels is important because some cancer cells are ATP deficient," Gu adds. "But this technique would work even in those environments."
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy by ATP-Mediated Liposomal Drug Delivery," is published online in Angewandte Chemie. The paper was co-authored by Tianyue Jiang, a Ph.D. student in the joint biomedical engineering program. The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health under grant 1UL1TR001111 and funding from NC State and UNC-Chapel Hill.
New method sneaks drugs into cancer cells before triggering release
2014-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nation's data capital poised to advance leadership position in big data
2014-05-09
WASHINGTON—The Northern Virginia Technology Council (NVTC), the George Washington University (GW), and Attain, LLC, today released a research report conducted by Chmura Economics & Analytics highlighting the depth and breadth of big data experience, expertise and assets in Northern Virginia and the Potomac region.
The report "Big Data and Analytics in Northern Virginia and the Potomac Region" concludes that the area—dubbed the nation's data capital—is a natural leader in the evolving field of big data and analytics. With a concentration of data analytics businesses and ...
Long-term childhood poverty contributes to young adult obesity rates
2014-05-09
A new study from the University of Houston Department of Health and Human Performance (HHP) finds childhood poverty reaches into the lives of white, Hispanic and African-American young adult women, contributing to their propensity to be overweight and obese.
"We know that having a low socioeconomic status during childhood contributes to children being overweight or obese," said HHP's Daphne Hernandez, who also is an executive board member of the UH Texas Obesity Research Center. "We've found a connection between the long-term exposure to poverty during childhood and ...
Forty is not too old or too late to start endurance training
2014-05-09
Amsterdam, 9 May. A study of healthy senior men has found that "relatively intensive" endurance exercise confers benefits on the heart irrespective of the age at which they began training.(1) The benefits were evident and comparable in those who had started training before the age of 30 or after the age of 40. As a result, said the investigators, 40 is not too old to start endurance training.
The study, which was performed in France, was reported today at the EuroPRevent congress 2014 in Amsterdam by David Matelot, from the Inserm 1099 unit in Rennes, France.
The study ...
Salt needed: Tolerance lessons from a dead sea fungus
2014-05-09
Despite its name, the Dead Sea does support life, and not just in the sense of helping visitors float in its waters. Algae, bacteria, and fungi make up the limited number of species that can tolerate the extremely salty environment at the lowest point on Earth.
Some organisms thrive in salty environments by lying dormant when salt concentrations are very high. Other organisms need salt to grow. To learn which survival strategy the filamentous fungus Eurotium rubrum uses, a team of researchers led by Eviatar Nevo from the University of Haifa in Israel, Igor Grigoriev ...
States opting out of Medicaid leave 1.1 million community health center patients without health insurance
2014-05-09
WASHINGTON, DC and NEW YORK (May 9, 2014)— An estimated 1.1 million community health center patients are left without the benefits of health coverage simply because they live in one of 24 states that have opted out of the Medicaid expansion, a key part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), according to a new report.
The research, by the Geiger Gibson/RCHN Community Health Foundation Research Collaborative at Milken Institute School of Public Health (Milken Institute SPH) at the George Washington University also shows that the vast majority (71 percent) of the 1.1 million ...
Implantable device to beat high blood pressure
2014-05-09
An implantable device that reduces blood pressure by sending electrical signals to the brain has been created by a group of researchers in Germany.
The device has successfully reduced the blood pressure in rats by 40 per cent without any major side effects, and could offer hope for a significant proportion of patients worldwide who do not respond to existing medical treatment for the condition.
The first results have been published today, 9 May, in IOP Publishing's Journal of Neural Engineering.
The device consists of 24 individual electrodes that are integrated into ...
Study shows short bursts of intense exercise before meals control blood sugar better than 1 continuous 30 minute session
2014-05-09
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) indicates that brief bursts of intense exercise before meals (termed exercise 'snacking' by the study authors) helps control blood sugar in people with insulin resistance more effectively than one daily 30-minute session of moderate exercise. The research was conducted by exercise science and medicine researchers, including Monique Francois and Associate Professor James Cotter from the University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
The study used a cross-over design, ...
From age 30 onwards, inactivity has greatest impact on women's lifetime heart disease risk
2014-05-09
From the age of 30 onwards, physical inactivity exerts a greater impact on a woman's lifetime risk of developing heart disease than the other well-known risk factors, suggests research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
This includes overweight, the finding show, prompting the researchers to suggest that greater effort needs to be made to promote exercise.
The researchers wanted to quantify the changing contribution made to a woman's likelihood of developing heart disease across her lifetime for each of the known top four risk factors in Australia: ...
Frequent arguments with family and friends linked to doubling in death risk in middle age
2014-05-09
Frequent arguments with partners, relatives, or neighbours may boost the risk of death from any cause in middle age, suggests research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Men and those not in work seemed to be the most vulnerable, the findings indicate.
The evidence suggests that supportive social networks and strong relationships are good for general health and wellbeing, but the authors wanted to find out if the stressors inherent in family relationships and friendships had any impact on the risk of death from any cause.
They therefore ...
Hurricanes Katrina and Rita may have caused up to half of recorded stillbirths in worst hit areas
2014-05-09
Hurricanes Katrina and Rita may have been responsible for up to half of all recorded stillbirths in the worst hit areas, suggests research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
And the true fetal death toll may even be higher, because of the displacement of people whose homes and way of life were destroyed, suggest the authors.
Hurricane Katrina struck the state of Louisiana, USA, on August 29 2005, followed by Hurricane Rita a month later on September 24. Katrina was the costliest natural disaster in American history, while Rita was the ...