Hospitals recover from recession, some financial issues remain
2014-05-12
(Press-News.org) The recent economic recession affected hospitals across the nation, regardless of financial status, but following the rebound, financially weak and safety-net hospitals continue to struggle, according to health researchers.
"Poor financial outcomes [for hospitals] could lead to poor care," said Naleef Fareed, assistant professor of health policy and administration, Penn State. "This is an issue that needs attention as health care reform moves forward."
Fareed and colleagues used data from both the American Hospital Association Annual Survey and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to analyze how different groups of hospitals fared financially during the recession, and where these groups stand as health care reform continues in the United States.
"The effect of the recession wasn't permanent," said Fareed. "Hospitals recovered from the recession, but those that were initially financially weak before the recession remained in a precarious condition through 2011."
The researchers looked at nearly 3,000 privately owned hospitals from 2006 through 2011. Included in the study were both for-profit and nonprofit hospitals, as well as safety-net and non-safety-net hospitals.
"A safety-net hospital provides an unusually high amount of care to the poor and vulnerable population," said Fareed. He pointed out that many factors could be linked with a hospital being a safety net.
At the beginning of the study period, more than half of the hospitals were considered financially strong while about a quarter were financially weak. The remaining hospitals fell in the "financially mixed" category. All three of these categories of hospitals experienced a financial dip in 2008, but by 2011 financial status was comparable to the 2006 baseline for all three.
About 28 percent of the safety-net hospitals were financially weak in 2006. While their financial performance dipped in 2008, these institutions rebounded by 2011. However, the financial gap between the safety-net hospitals and the non-safety-net hospitals continues to widen in terms of their total profit.
"In many ways, our findings could be interpreted as showing that hospitals' cup is half empty or that it is half full," the researchers wrote in the May issue of Health Affairs. "On the one hand, financially weak and safety-net hospitals continue to keep their doors open. On the other hand, these institutions remain in precarious financial positions that could compromise their ability to invest in innovations or quality improvement activities that may provide value for patients."
Looking toward the future, Fareed and colleagues note that it is critical to monitor the state of hospitals, especially financially weak and safety-net hospitals, to assess how the Affordable Care Act affects the care they deliver and the populations they serve.
INFORMATION:
Gloria J. Bazzoli, professor of health administration, Virginia Commonwealth University, and Teresa M. Waters, professor of preventive medicine, University of Tennessee, also worked on this research.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality supported this research.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Man's best friend shares similar 'albino' gene
2014-05-12
Michigan State University researchers have identified a genetic mutation in Doberman pinschers that causes albinism in the breed, a discovery that has eluded veterinarians and breeders worldwide up until now.
Paige Winkler, a doctoral student in the College of Veterinary Medicine, co-led the study with Joshua Bartoe, an assistant professor in the Department of Small Animal Clinical Sciences, and discovered a mutated gene that is associated with a form of albinism in humans.
"What we found was a gene mutation that results in a missing protein necessary for cells to ...
Against the current with lava flows
2014-05-12
This news release is available in German.
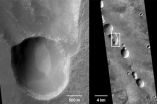
An Italian astronomer in the 19th century first described them as 'canali' – on Mars' equatorial region, a conspicuous net-like system of deep gorges known as the Noctis Labyrinthus is clearly visible. The gorge system, in turn, leads into another massive canyon, the Valles Marineris, which is 4,000 km long, 200 km wide and 7 km deep. Both of these together would span the US completely from east to west.
As these gorges, when observed from orbit, resemble terrestrial canyons formed by water, most researchers assumed that ...
Drug therapy for allergy moves forward
2014-05-12
Researchers have identified several target molecules which are suitable for the development of new allergy drugs. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the most prestigious journal in the field of allergology, has recently published an extensive review article on the prospects of drug therapy for allergy. Completed in a large-scale EU project, the lead author of the review article is Professor Ilkka Harvima of the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital.
Immediate allergic reactions and allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis, asthma ...
Role of pro-urokinase in neuronal apoptosis and revascularization after ACI
2014-05-12
Among the drugs used for acute ischemic stroke, recombinant tissue plasminogen activator is widely accepted internationally. In China, urokinase has been widely used for thrombolysis after acute ischemic stroke. Pro-urokinase is the precursor of urokinase. Compared with urokinase, pro-urokinase has greater ability to dissolve thrombus and is safer to use. However, most countries do not recognize urokinase for thrombolytic treatment after acute ischemic stroke, which has not been approved for clinical use. Dr. Wenli Hu and team from Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical ...
Unusual neural connection between injured cingulum and brainstem in a SAH patients
2014-05-12
The cingulum is an important pathway for cholinergic innervation for the cerebral cortex. Many studies have reported connections between the cholinergic nuclei, especially between the cholinergic nuclei in the basal forebrain and those in the brainstem via the fornix and thalamus. However, little is known about the connection between cholinergic nuclei in the basal forebrain and cholinergic nuclei in the brainstem via the cingulum. Even no study on this phenomenon after cerebral hemorrhage has been reported. Dr. Sung Ho Jang and team from College of Medicine, Yeungnam University ...
Molecular regulation of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
2014-05-12
Oligodendrocyte lineage gene 1 (Olig1) plays a key role in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage and myelin repair. miRNA-9 is involved in the occurrence of many related neurological disorders. Bioinformatics analysis demonstrated that miRNA-9 complementarily, but incompletely, bound oligodendrocyte lineage gene 1, but whether miRNA-9 regulates oligodendrocyte lineage gene 1 remains poorly understood. Dr. Lijun Yang and co-workers from Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University in China prepared whole brain slices from a rat model of oxygen-glucose deprivation and ...
Unmanned air vehicle flow separation control using dielectric barrier discharge plasma at high wind
2014-05-12
Plasma technology based on Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) has been widely demonstrated to be a novel active flow control method. In order to make the plasma flow control technology more practical, the plasma authority must be improved at high wind speed. Dr. ZHANG Xin and his group from School of Aeronautic, Northwestern Polytechnical University set out to tackle this problem. After 2-years of innovative research, they have developed a novel plasma actuator to improve the plasma authority at high wind speed. They found that the novel plasma actuator acting on the surface ...
Dopamine turns worker ants into warrior queens
2014-05-12
VIDEO:
When an H. saltator colony's queen dies, the female workers engage in ritual fights to establish dominance. Ultimately, a small group of workers establishes dominance and become a cadre of...
Click here for more information.
The ritualized fighting behavior of one ant species is linked to increases in dopamine levels that trigger dramatic physical changes in the ants without affecting their DNA, according to research from North Carolina State University, Arizona State ...
Major breakthrough in understanding Prader-Willi Syndrome, a parental imprinting disorder
2014-05-12
Scientists at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have reported a major breakthrough in understanding the molecular basis for Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), perhaps the most studied among the class of diseases that involves defects in parental imprinting.
The work, described in the latest online edition of the prestigious journal Nature Genetics, was led by Prof. Nissim Benvenisty, the Herbert Cohn Professor of Cancer Research and director of the Stem Cell Unit at the Alexander Silberman Institute of Life Sciences at the Hebrew University; and his PhD student Yonatan Stelzer. ...
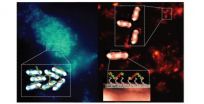
Hijacking bacteria's natural defenses to trap and reveal pathogens
2014-05-12
The breakthrough, published in the journal Nature Materials, could offer an easier way of detecting pathogenic bacteria outside of a clinical setting and could be particularly important for the developing world, where access to more sophisticated laboratory techniques is often limited.
The research was led by Professor Cameron Alexander, Head of the Division of Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering and EPSRC Leadership Fellow in the University's School of Pharmacy, building on work by PhD student Peter Magennis. Professor Alexander said: "Essentially, we have hijacked ...