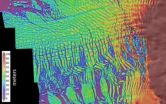
(Press-News.org) National Science Foundation- (NSF) funded researchers at the University of Washington have concluded that Antarctica's fast-moving Thwaites Glacier will likely disappear in a matter of centuries, potentially raising sea level by more than a half-a-meter (two feet).
Data gathered by NSF-funded airborne radar, detailed topography maps and computer modeling was used to make the determination.
The glacier acts as an ice dam, stabilizing and regulating movement toward the sea of the massive West Antarctic Ice Sheet. The ice sheet contains enough ice to cause another 3 to 4 meters (10 to 13 feet) of global sea level rise.
"There's been a lot of speculation about the stability of marine ice sheets, and many scientists suspected that this kind of behavior is under way," said Ian Joughin, a glaciologist at the university's Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the first author on the paper. " This study provides a more quantitative idea of the rates at which the [ice sheet] collapse could take place."
The paper's co-authors are Benjamin Smith, a physicist at APL, and Brooke Medley, a former University of Washington doctoral student, now at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.
While the word "collapse" implies a sudden change, the fastest scenario based on the data, the researchers said, is 200 years, and the longest is more than 1,000 years.
The findings are published in the May 16 edition of the journal Science.
The new discovery is among a series of significant findings that derive from research funded by NSF during the International Polar Year (IPY) 2007-2009, during which scientists from more than 60 nations focused their efforts on research in the Arctic and Antarctic. NSF was the lead U.S. agency for the IPY
The research was funded by two NSF grants: one awarded to the Center for the Remote Sensing of Ice Sheets (CReSIS) at the University of Kansas; the other, a collaborative IPY grant, Constraining the Mass-Balance Deficit of the Amundsen Coast's Glaciers, to Joughin and his colleagues.
NASA also supported the research through grant NNX09AE47G.
The new study used airborne radar, developed by CReSIS to peer down through the thick ice and map the topography of the underlying bedrock. The shape of the underlying bedrock controls the ice sheet's long-term stability. The mapping was done as part of NASA's Operation IceBridge, a series of overflights of the ice by a P-3 research aircraft, and included other instruments to measure the height of the ice sheet's rapidly thinning surface. In some places Thwaites Glacier has been losing tens of feet, or several meters, of elevation per year.
While the timescales for a collapse of the ice sheet are in question, such a collapse may be inevitable, the researchers said.
"Previously, when we saw thinning we didn't necessarily know whether the glacier could slow down later, spontaneously or through some feedback," Joughin said. "In our model simulations it looks like all the feedbacks tend to point toward it actually accelerating over time; there's no real stabilizing mechanism we can see."
Earlier warnings of collapse had been based on a simplified model of ice sitting in an inward-sloping basin. The topography around Antarctica, however, is complex.
The researchers combined the IceBridge and CReSIS data with their own satellite measurements of ice-surface speeds. Their computer model was able to reproduce the glacier's ice loss during the past 18 years, and they ran the model forward under different amounts of ocean-driven melting.
The place where the glacier meets land, the grounding line, now sits on a shallow ridge at a depth of about 600 meters (2,000 feet) below asea level. Results show that as the ice edge retreats into the deeper part of the bay, the ice face will become steeper and, like a towering pile of sand, the fluid glacier will become less stable and collapse out toward the sea.
"Once it really gets past this shallow part, it's going to start to lose ice very rapidly," Joughin said.
The study considered future scenarios using faster or slower melt rates depending on the amount of future warming. The fastest melt rate led to the early stages lasting 200 years, after which the rapid-stage collapse began. The slowest melt rate kept most of the ice for more than a millennium before the onset of rapid collapse. The most likely scenarios may be between 200 and 500 years, Joughin said.
"All of our simulations show it will retreat at less than a millimeter of sea level rise per year for a couple of hundred years, and then, boom, it just starts to really go," Joughin said.
Researchers did not model the more chaotic rapid collapse, but the remaining ice is expected to disappear within a few decades.
INFORMATION:
Airborne radar surveys and data-based models indicate West Antarctic Ice Sheet collapse is underway
Discovery is latest outcome of NSF-funded International Polar Year research
2014-05-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Henry Ford researchers identify genetic factors that may aid survival from brain cancer
2014-05-12
DETROIT – A Henry Ford Hospital research team has identified specific genes that may lead to improved survival of glioblastoma, the most common and deadly form of cancerous brain tumor.
The molecular data is expected to aid further research into genes that either help or impede the survival of patients diagnosed with the tumor, which can invade and rapidly grow in any part of the human brain.
"Studies such as ours that help define molecular alterations associated with short-term survival likely will help define the reasons why our current treatments don't succeed in these ...
Researchers find a new gene expression mechanism of PRRS virus
2014-05-12
MANHATTAN, Kan. — A collaborative study involving Kansas State University researchers has discovered a new gene expression mechanism in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, or PRRS, virus — an important swine pathogen that costs the U.S. pork industry more than $600 million a year. The discovery provides a new avenue for scientists to explore strategies to control and prevent the disease.
Ying Fang, Ph.D., associate professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology at Kansas State University, led a study that looked at the unique gene expression mechanism of ...
Hospitals ranked on complications after hip and knee replacement surgeries
2014-05-12
With an aging population comes an increase in hip and knee joint replacement surgeries, totaling almost one million procedures per year in the United States. To provide better information on the outcomes of these surgeries, help inform patient choice, and improve the quality of the nation's hospitals, a team of Yale School of Medicine researchers have developed a measure for hospitals based on the complications following their patients' hip and knee replacements.
The team published an article in the May issue of the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery showing there are ...
Dartmouth scientists identify genetic blueprint for cancerous tumors of the appendix
2014-05-12
Using next generation DNA sequencing, Dartmouth scientists have identified potentially actionable mutations in cancers of the appendix. Their study, "Molecular Profiling of Appendiceal Epithelial Tumors Using Massively Parallel Sequencing to Identify Somatic Mutations," was published in the journal Clinical Chemistry today. When specific mutations for a cancer type are identified, patients can be treated with chemotherapy or other targeted agents that work on those mutations.
Little is known about the molecular biology of two types of appendix tumors, low-grade appendiceal ...
Ames Lab creates multifunctional nanoparticles for cheaper, cleaner biofuel
2014-05-12
The U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory has created a faster, cleaner biofuel refining technology that not only combines processes, it uses widely available materials to reduce costs.
Ames Laboratory scientists have developed a nanoparticle that is able to perform two processing functions at once for the production of green diesel, an alternative fuel created from the hydrogenation of oils from renewable feedstocks like algae.
The method is a departure from the established process of producing biodiesel, which is accomplished by reacting fats and oils with alcohols.
"Conventionally, ...
Mount Sinai researchers identify changes that may occur in neural circuits due to addiction
2014-05-12
A research team from the Friedman Brain Institute of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has published evidence that shows that subtle changes of inhibitory signaling in the reward pathway can change how animals respond to drugs such as cocaine. This is the first study to demonstrate the critical links between the levels of the trafficking protein, the potassium channels' effect on neuronal activity and a mouse's response to cocaine. Results from the study are published in the peer-reviewed journal Neuron on May 7, 2014.
The authors investigated the role of ...
Corn dwarfed by temperature dip suitable for growing in mines, caves
2014-05-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Lowering temperatures for two hours each day reduces the height of corn without affecting its seed yield, a Purdue study shows, a technique that could be used to grow crops in controlled-environment facilities in caves and former mines.
Raising the crops in isolated and enclosed environments would help prevent genetically modified pollen and seed from escaping into the ecosystem and crossing with wild plants.
Cary Mitchell, professor of horticulture, said the technique could be particularly useful for growing transgenic crops to produce high-value ...
INFORMS study: Online buzz forecasts new product performance months before product release
2014-05-12
Companies can significantly improve the forecasting accuracy of forthcoming products' performance by mining online consumer buzz prior to product release, according to a study being published by Marketing Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS).
Social media attention to a firm's forthcoming products also influences its stock price, the study shows.
Pre-Release Buzz Evolution Patterns and New Product Performance is by Guiyang Xiong and Sundar Bharadwaj, professors at Terry College of Business at the University ...
Potential cure for captive amphibians with chytrid fungus
2014-05-12
Researchers at Vanderbilt University have identified an alternative to a sometimes toxic therapy that protects frogs in zoos from a deadly fungal infection that has been destroying the amphibian populations worldwide. Their research is published ahead of print in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
The fungal disease, chytridiomycosis, has been decimating frogs all over the world. At present, nothing can help amphibians in the wild, but zoos currently rely on the often-toxic itraconazole to eradicate the disease from infected amphibians they wish to acquire.
To ...
UBC scientists find new way to mobilize immune system against viruses
2014-05-12
University of British Columbia scientists have uncovered an intricate chain reaction in the body's immune system and have used the knowledge to develop a new treatment against harmful viruses.
Viral pandemics, such as the coronavirus that caused the deadly SARS outbreak in 2002, have caused hundreds of deaths in Canada, yet effective anti-viral drugs are rare.
A key element to this natural immune response is an antiviral protein in the blood called Interferon alpha. Like soldiers, Interferon alpha is quickly deployed by the body to fight viruses and removed just as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
[Press-News.org] Airborne radar surveys and data-based models indicate West Antarctic Ice Sheet collapse is underwayDiscovery is latest outcome of NSF-funded International Polar Year research