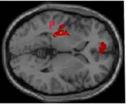
(Press-News.org) Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that is often used to help improve the level of consciousness in patients with disorder of consciousness (DOC). However, the responses to stimulation of acupoints in patients with DOC are not fully understood. Hao Zhang and colleagues from China Rehabilitation Research Center found that acupuncture at the Yongquan acupoints induced stronger neuronal activity than acupuncture at the sham acupoints shown on positron emission tomography (PET). These researchers believe that acupuncture at the Yongquan acupoints may increase synaptic activity in some areas of the brain. The putamen, cingulate cortex, frontal lobe and cerebellum are involved in conscious thought. This may explain the mechanism by which acupuncture at the Yongquan acupoints results in improvement of patients with DOC. These finding have been published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 5, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: " Neuronal activation by acupuncture at Yongquan (KI1) and sham acupoints in patients with disorder of consciousness: a positron emission tomography study," by Hao Zhang1, Xinting Sun1, Sujuan Liu2, Yingmao Chen3, Feng Ling4 (1 Department of Neurorehabilitation, China Rehabilitation Research Center, Beijing, China; 2 Department of Hyperbaric Oxygen, Fuxing Hospital, Beijing, China; 3 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China; 4 Department of Neurosurgery, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China)
Zhang H, Sun XT, Liu SJ, Chen YM, Ling F. Neuronal activation by acupuncture at Yongquan (KI1) and sham acupoints in patients with disorder of consciousness: a positron emission tomography study. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(5):500-501.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Neuronal activation by acupuncture at Yongquan and sham acupoints for DOC: A PET study
2014-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Effect of repeated-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation at the Guangming point on EEGs
2014-05-16
In a recent study reported in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 5, 2014), repeated-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation was administered to healthy people at the left Guangming (GB37) and a mock point, and calculated the sample entropy of electroencephalogram signals using nonlinear dynamics. Additionally, researchers compared electroencephalogram sample entropy of signals in response to visual stimulation before, during, and after repeated-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation at the Guangming. Results showed that repeated-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation ...
New treatment targeting versatile protein may protect brain cells in Parkinson's disease
2014-05-16
In Parkinson's disease (PD), dopamine-producing nerve cells that control our movements waste away. Current treatments for PD therefore aim at restoring dopamine contents in the brain. In a new study from Lund University, researchers are attacking the problem from a different angle, through early activation of a protein that improves the brain's capacity to cope with a host of harmful processes. Stimulating the protein, called Sigma-1 receptor, sets off a battery of defence mechanisms and restores lost motor function. The results were obtained in mice, but clinical trials ...
Domesticated animals provide vital link to emergence of new diseases
2014-05-16
Research at the University of Liverpool suggests pets and other domesticated animals could provide new clues into the emergence of infections that can spread between animals and humans.
The study showed that the number of parasites and pathogens shared by humans and animals is related to how long animals have been domesticated.
The findings suggest that although wild animals may be important for the transmission of new diseases to humans, humanity's oldest companions – livestock and pets such as cattle and dogs provide the vital link in the emergence of new diseases.
Using ...
Tricking the uncertainty principle
2014-05-16
Caltech researchers have found a way to make measurements that go beyond the limits imposed by quantum physics.
Today, we are capable of measuring the position of an object with unprecedented accuracy, but quantum physics and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle place fundamental limits on our ability to measure. Noise that arises as a result of the quantum nature of the fields used to make those measurements imposes what is called the "standard quantum limit." This same limit influences both the ultrasensitive measurements in nanoscale devices and the kilometer-scale ...
Mothers' sleep, late in pregnancy, affects offspring's weight gain as adults
2014-05-16
Poor-quality sleep during the third trimester of pregnancy can increase the odds of weight gain and metabolic abnormalities in offspring once they reach adulthood, according to a new study published online May 8, 2014, in the journal Diabetes.
The researchers linked the excess weight and changes in metabolism to epigenetic modifications that reduce expression of the gene for adiponectin—a hormone that helps regulate several metabolic processes, including glucose regulation. Lower levels of adiponectin correlate with increased body fat and reduced activity.
"Disrupted ...
Water pipe smoking causes significant exposure to nicotine and cancer-causing agents
2014-05-16
PHILADELPHIA — Young adults who smoked water pipes in hookah bars had elevated levels of nicotine, cotinine, tobacco-related cancer-causing agents, and volatile organic compounds (VOC) in their urine, and this may increase their risk for cancer and other chronic diseases, according to a study published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"This study reports systemic intake of tobacco-specific nitrosamines and VOCs after a typical water pipe-smoking session in a hookah bar setting, thus making the ...
War and peace (of mind)
2014-05-16
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Naval Health Research Center have found that mindfulness training – a combination of meditation and body awareness exercises – can help U.S. Marine Corps personnel prepare for and recover from stressful combat situations.
The study, published in the May 16, 2014 online issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry, suggests that incorporating meditative practices into pre-deployment training might be a way to help the U.S. military reduce rising rates of stress-related health conditions, including ...
Male infertility linked to mortality in study led by Stanford researcher
2014-05-16
STANFORD, Calif. — Men who are infertile because of defects in their semen appear to be at increased risk of dying sooner than men with normal semen, according to a study led by a researcher at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Men with two or more abnormalities in their semen were more than twice as likely to die over a roughly eight-year period as men who had normal semen, the study found.
Smoking and diabetes — either of which doubles mortality risk — both get a lot of attention, noted the study's lead author, Michael Eisenberg, MD, PhD, assistant professor ...
Magnets and kids: A dangerous duo
2014-05-16
Cincinnati, OH, May 16, 2014 -- Magnet ingestions by children have received increasing attention over the past 10 years. With the growing availability of new and stronger neodymium-iron-boron magnets being sold as "toys," there has been an increase of cases of ingestion, resulting in serious injury and, in some cases, death. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers studied the trends of magnetic ingestions at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), Canada's largest children's hospital.
Matt Strickland, MD, and colleagues ...
Study reveals 1 in 10 16-year-olds surveyed have considered self-harm
2014-05-16
One in ten 16-year-olds surveyed in a new study by Queen's University and the University of Ulster have considered self-harm or taking an overdose.
The results of the annual Young Life and Times (YLT) survey, which are published today (Friday 16 May) during Mental Health Awareness Week, also found that almost a third of 16-year-olds questioned had experienced serious personal, emotional or mental health problems at some point in the past year.
1,367 16-year-olds across Northern Ireland took part in the 2013 survey undertaken by ARK, a joint initiative by Queen's University ...