(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON D.C., May 20, 2014 -- The long life of lithium ion batteries makes them the rechargeable of choice for everything from implantable medical devices to wearable consumer electronics. But lithium ion batteries rely on liquid chemistries involving lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, creating flame risks that would be avoided if the cells were completely solid-state.
Now a team of researchers at Tohoku University in Japan has created a new type of lithium ion conductor for future batteries that could be the basis for a whole new generation of solid-state batteries. It uses rock salt Lithium Borohydride (LiBH4), a well-known agent in organic chemistry laboratories that has been considered for batteries before, but up to now has only worked at high temperatures or pressures.
In the journal APL Materials, from AIP Publishing, the researchers describe how they doped a cubic lattice of KI molecules with the LiBH4. This allowed them to stabilize the high-pressure form of Lithium borohydride and make a solid solution at normal atmospheric pressure that was stable at room temperature.
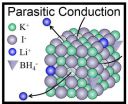
In making the new technology, the team made the peculiar discovery that the Li+ ions functioned like pure Li+ ion conductors, even though they were just doping the KI lattices. This is the reverse of the normal doping technique, in which a small amount of stabilizing element would be added to an ionic conductor abundant in Lithium.
"In other words, LiBH4 is a sort of 'parasite' but not a host material," said Hitoshi Takamura who led the research at Tohoku University. He and his colleagues have called this mechanism "parasitic conduction" and have suggested that it could be broadly applied in the search for new batteries -- anywhere that small amounts of Li+ ions could be used to dope an oxide, sulfide, halide or nitride host material.
"This work suggests the potential of this mechanism in the ongoing search for the perfect material for use in solid state batteries," added Takamura. "The urgency of this quest has been abundantly clear after the grounding of so many aircraft in recent months."
INFORMATION:
The article "Synthesis of Rock-Salt Type Lithium Borohydride and Its Peculiar Li+ Ion Conduction Properties" is authored by R. Miyazaki, H. Maekawa and H. Takamura. It will be published in the journal APL Materials on May 20, 2014 (DOI: 10.1063/1.4876638). After that date, it may be accessed at: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/aplmater/2/5/10.1063/1.4876638
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Materials is a new open access journal featuring original research on significant topical issues within the field of materials science. See: http://aplmaterials.aip.org
New lithium battery created in Japan
Using a parasitic conduction mechanism, technology described in the journal 'APL Materials' promises safer batteries in the future
2014-05-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reading privacy policy lowers trust
2014-05-20
Website privacy policies are almost obligatory for many online services, but for anyone who reads these often unwieldy documents, trust in the provider is more commonly reduced than gained, according to US researchers.
Almost every commercial website, social network, search engine and banking site has a privacy policy. Indeed, these and countless other sites that scrape personal information via forms, logins and tracking cookies are obliged by law in some parts of the world to post a document online giving details of how they protect any personal data you give the site ...
Can mobile phones cause allergic reactions?
2014-05-20
New Rochelle, NY, May 20, 2014—Studies have identified mobile phones and related devices as sources of metal sensitization and potential causes of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). Despite efforts to control allergen release in phones, many phones on the market release levels of metals, such as nickel and chromium, which are sufficient to induce ACD, according to an article in Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology ...
Climate change brings mostly bad news for Ohio
2014-05-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio— Scientists delivered a mostly negative forecast for how climate change will affect Ohioans during the next year or so, and well beyond.
Researchers report that the projected increase in precipitation and the associated runoff will likely lead to a larger-than-average bloom of harmful blue-green algae in Lake Erie this summer. In addition, the development of an El Niño over the Pacific later this year may result in a very dry 2015 in Ohio. But Ohio may fare better than its neighbors in one respect: While drought and high temperatures are expected to shrink ...
NIH researchers discover key factor in early auditory system development
2014-05-20
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have uncovered a molecule in an animal model that acts as a key player in establishing the organization of the auditory system. The molecule, a protein known as Bmp7, is produced during embryonic development and acts to help sensory cells find their ultimate position on the tonotopic map, which is the fundamental principle of organization in the auditory system. The tonotopic map groups sensory cells by the sound frequencies that stimulate them. The study is the first to identify one of the molecular mechanisms that determines ...
Is there really cash in your company's trash?
2014-05-20
This news release is available in French. One company's trash can be another's treasure.
Take Marmite. Made from a by-product of commercial beer production, the yeast-based spread has topped toast throughout the Commonwealth for decades. By recuperating the waste product from one company, another was able to thrive.
Environmental concerns are at the forefront of government policy, so the time is right for companies worldwide to adopt this type of resource exchange, known as industrial symbiosis (IS).
A new study by Concordia University researcher Raymond Paquin ...
Engineers build world's smallest, fastest nanomotor
2014-05-20
VIDEO:
Cockrell School of Engineering assistant professor Donglei (Emma) Fan and her mechanical engineering team have built the fastest, smallest nanomotor to date. The team's nanomotor could enable controlled drug delivery...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at the Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin have built the smallest, fastest and longest-running tiny synthetic motor to date. The team's nanomotor is an important step toward ...
Program to reduce behavior problems boosts math, reading, NYU Steinhardt study shows
2014-05-20
A program aimed at reducing behavior problems in order to boost academic achievement has improved performance in math and reading among low-income kindergartners and first graders, according to a study by researchers at New York University's Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development.
Their findings, which appear in the Journal of Educational Psychology, point to the value of well-designed interventions to improve education, the study's authors say.
"Supporting young low-income children so they can reach their potential in the classroom and beyond ...
Professors' super waterproof surfaces cause water to bounce like a ball
2014-05-20
In a basement lab on BYU's campus, mechanical engineering professor Julie Crockett analyzes water as it bounces like a ball and rolls down a ramp.
This phenomenon occurs because Crockett and her colleague Dan Maynes have created a sloped channel that is super-hydrophobic, or a surface that is extremely difficult to wet. In layman's terms, it's the most extreme form of water proof.
Engineers like Crockett and Maynes have spent decades studying super-hydrophobic surfaces because of the plethora of real-life applications. And while some of this research has resulted in ...
Termite genome lays roadmap for 'greener' control measures
2014-05-20
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A team of international researchers has sequenced the genome of the Nevada dampwood termite, providing an inside look into the biology of the social insect and uncovering new genetic targets for pest control.
Michael Scharf, a Purdue University professor of entomology who participated in the collaborative study, said the genome could help researchers develop control strategies that are more specific than the broad-spectrum chemicals conventionally used to treat termite infestations.
"The termite genome reveals many unique genetic targets that can ...
Fairy circles apparently not created by termites after all
2014-05-20
This news release is available in German. Leipzig. For several decades scientists have been trying to come up with an explanation for the formation of the enigmatic, vegetation-free circles frequently found in certain African grassland regions. Now researchers have tested different prevailing hypotheses as to their respective plausibility. For the first time they have carried out a detailed analysis of the spatial distribution of these fairy circles – and discovered a remarkably regular and spatially comprehensive homogenous distribution pattern. This may best be explained ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] New lithium battery created in JapanUsing a parasitic conduction mechanism, technology described in the journal 'APL Materials' promises safer batteries in the future