(Press-News.org) NGC 3590 is a small open cluster of stars around 7500 light-years from Earth, in the constellation of Carina (The Keel). It is a gathering of dozens of stars loosely bound together by gravity and is roughly 35 million years old.
This cluster is not just pretty; it is very useful to astronomers. By studying this particular cluster — and others nearby — astronomers can explore the properties of the spiral disc of our galaxy, the Milky Way. NGC 3590 is located in the largest single segment of a spiral arm that can be seen from our position in the galaxy: the Carina spiral feature.
The Milky Way has multiple spiral arms, long curved streams of gas and stars stretching out from the galactic centre. These arms — two major star-filled arms, and two less populated minor arms — are each named after the constellations in which they are most prominent [1]. The Carina spiral feature is seen from Earth as a patch of sky heavily populated with stars, in the Carina-Sagittarius minor arm.
The name of this arm — Carina, or The Keel — is quite appropriate. These spiral arms are actually waves of piled up gas and stars sweeping through the galactic disc, triggering sparkling bursts of star formation and leaving clusters like NGC 3590 in their wake. By finding and observing young stars like those in NGC 3590, it is possible to determine the distances to the different parts of this spiral arm, telling us more about its structure.
Typical open clusters can contain anything from a few tens to a few thousands of stars, and provide astronomers with clues about stellar evolution. The stars in a cluster like NGC 3590 are born at around the same time from the same cloud of gas, making these clusters perfect test sites for theories on how stars form and evolve.
This image from the Wide Field Imager (WFI) on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at La Silla, shows the cluster and the gas clouds surrounding it, which glow in orange and red hues due to the radiation coming from nearby hot stars. WFI's large field of view also captures a colossal number of background stars.
To obtain this image, multiple observations were made using different filters to capture the different colours of the scene. This image was created by combining images taken in the visible and infrared parts of the spectrum, and a special filter that collected only light coming from glowing hydrogen.
INFORMATION:
Notes
[1] These four arms are named the Carina-Sagittarius, Norma, Scutum-Centaurus, and Perseus arms.
More information
ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world's most productive ground-based astronomical observatory by far. It is supported by 15 countries: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope, the world's most advanced visible-light astronomical observatory and two survey telescopes. VISTA works in the infrared and is the world's largest survey telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope is the largest telescope designed to exclusively survey the skies in visible light. ESO is the European partner of a revolutionary astronomical telescope ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. ESO is currently planning the 39-metre European Extremely Large optical/near-infrared Telescope, the E-ELT, which will become "the world's biggest eye on the sky".
Links
Photos of the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/search/?adv=&subject_name=mpg
Photos from the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/search/?adv=&facility=15
Photos of La Silla: http://www.eso.org/public/images/archive/category/lasilla/
Contacts
Richard Hook
ESO, Public Information Officer
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6655
Cell: +49 151 1537 3591
Email: rhook@eso.org
A star cluster in the wake of Carina
2014-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows iron from melting ice sheets may help buffer global warming
2014-05-21
A newly-discovered source of oceanic bioavailable iron could have a major impact our understanding of marine food chains and global warming. A UK team has discovered that summer meltwaters from ice sheets are rich in iron, which will have important implications on phytoplankton growth. The findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications on 21st May, 2014*.
It is well known that bioavailable iron boosts phytoplankton growth in many of the Earth's oceans. In turn phytoplankton capture carbon – thus buffering the effects of global warming. The plankton also feed ...
More maternal mental health surveillance is needed, suggests new study
2014-05-21
Maternal depression is more common at four years following childbirth than at any other time in the first 12 months after childbirth, and there needs to be a greater focus on maternal mental health, suggests a new study published today (21 May) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
The study using data from 1507 women from six public hospitals in Melbourne, Australia, examines the prevalence of maternal depression from early pregnancy to four years postpartum. The researchers identify the possible risk factors for depressive symptoms at four ...
Molecule linked to aggressive pancreatic cancer offers potential clinical advances
2014-05-21
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — Mayo Clinic researchers have discovered an enzyme they say is tightly linked to how aggressive pancreatic cancer will be in a patient.
They say the study, published in Molecular Cancer Research, provides key insights into the most aggressive form of the disease, which is one of the deadliest human cancers.
It also offers a number of possible future clinical advances, such as a way to gauge outcome in individual patients, and insight into potential therapy to shut down activity of the enzyme, known as Rac1b.
"The implication from our research is ...
A quicker way to determine who's faking it on the Internet
2014-05-21
Researchers at the University of Montreal have developed an improved chemical analysis method that is more efficient and faster in detecting counterfeit medicines, which have skyrocketed in recent years. The method was developed and tested in a study by Philippe Lebel, Alexandra Furtos and Karen Waldron of the university's Department of Chemistry. It identifies and quantifies the various compounds present in a pharmaceutical product, in a fifth of the time it takes governmental services to do the same job. "Fake drugs are a scourge for public health," says Lebel. Once a ...
Compound reverses symptoms of Alzheimer's disease in mice, SLU research shows
2014-05-21
ST. LOUIS -- A molecular compound developed by Saint Louis University scientists restored learning, memory and appropriate behavior in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, according to findings in the May issue of the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
The molecule also reduced inflammation in the part of the brain responsible for learning and memory.
The paper, authored by a team of scientists led by Susan Farr, Ph.D., research professor of geriatrics at Saint Louis University, is the second mouse study that supports the potential therapeutic value of an antisense compound ...
Vitamin E in canola and other oils hurts lungs
2014-05-20
CHICAGO --- A large new Northwestern Medicine® study upends our understanding of vitamin E and ties the increasing consumption of supposedly healthy vitamin E-rich oils -- canola, soybean and corn – to the rising incidence of lung inflammation and, possibly, asthma.
The new study shows drastically different health effects of vitamin E depending on its form. The form of Vitamin E called gamma-tocopherol in the ubiquitous soybean, corn and canola oils is associated with decreased lung function in humans, the study reports. The other form of Vitamin E, alpha-tocopherol, ...
Researchers test whether Red Queen hypothesis makes species resilient
2014-05-20
In Lewis Carroll's 1871 classic novel Through the Looking Glass, the Red Queen tells Alice: "Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place."
Over the years, evolutionary biologists have used the Red Queen's statement to refer to the "Red Queen" hypothesis, which describes how living organisms, including humans, manage to survive in a changing environment by adapting through sexual reproduction. According to a University of Iowa researcher, the hypothesis is supported.
In a paper published in the journal Biology Letters, lead author ...
Shale development generally helps local government coffers
2014-05-20
Oil and gas development from shale fields has generally helped the public finances of local communities, providing new revenues and resources that usually -- but not always -- outweigh the increased demand for public services and other costs, according to a new analysis from two Duke University researchers.
Daniel Raimi and Richard Newell gathered data from communities surrounding 10 oil and gas "plays" from September 2013 through February 2014, traveling to Arkansas, Colorado, Louisiana, Montana, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, Texas and Wyoming to interview local officials ...
'Supermodel' mouse reveals mechanisms that regulate metabolism, researchers find
2014-05-20
DALLAS – May 20, 2014 – A lean "Supermodel" mouse type has revealed the potentially critical role played by a largely unknown gene that regulates metabolism, findings that could provide new insight into diseases ranging from diabetes to obesity, a new study by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers suggests.
The Supermodel mouse's phenotype – the physical characteristics that result from its gene makeup – include being very small in size, with an unusual body form caused by abnormal distribution of fat, said Dr. Zhe Chen, Assistant Professor of Biophysics, and ...
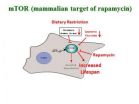
Research explains action of drug that may slow aging and related disease
2014-05-20
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A proven approach to slow the aging process is dietary restriction, but new research in the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University helps explain the action of a drug that appears to mimic that process – rapamycin.
Rapamycin, an antibiotic and immunosuppressant approved for use about 15 years ago, has drawn extensive interest for its apparent ability – at least in laboratory animal tests – to emulate the ability of dietary restriction in helping animals to live both longer and healthier.
However, this medication has some drawbacks, including ...