(Press-News.org) When University of Illinois Associate Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Hyunjoon Kong, graduate student Cartney Smith, and colleagues set out to improve MR imaging (MRI), they turned current contrast agent technology on its head—or rather, they turned it inside out. The new compound they designed in collaboration with Illinois' Roger Adams Professor of Chemistry Steven C. Zimmerman is not only more effective, but also self-assembling. Kong is also a member of the Regenerative Biology and Tissue Engineering research theme at the Institute for Genomic Biology.
When doctors perform an MRI, they administer a contrast agent: a chemical that, when injected into the bloodstream or ingested by the patient just before the MRI, improves the clarity of structures or organs in the resulting image. One common class of contrast agent, often used for imaging of blood vessels and internal bleeding, contains gadolinium, a rare-earth metal.
Recently, biomedical researchers have found ways to increase the effectiveness of certain contrast agents by associating them with nanoparticles. The contrast agent being used is packaged inside or bonded to the surface of microscopic particles, which can be designed to target certain regions of the body or prolong the agent's activity.
Researchers are now exploring the multipurpose use of nanoparticles. If particles could be loaded with several types of contrast agents or dyes instead of one, or a contrast agent along with another type of diagnostic aid or a medication, doctors could more efficiently test for and treat conditions, and limit the number of injections received by patients.
Just like toddlers sharing a new toy, though, compounds packaged together into a nanoparticle cannot always play well together. For example, contrast agents may bind to other chemicals, reducing their effectiveness. In addition, when contrast agents are enclosed inside a nanoparticle, they may not work as well. Attempts to attach agents to the outer surface of nanoparticles via covalent formation are also problematic, as they can negatively affect the activity of the nanoparticles or the compounds that they carry.
Kong, Smith and colleagues tackled these challenges by using interactions between naturally occurring biomolecules as a guide. Many types of proteins are strongly attached to cell membranes not by covalent bonds, but by the sum of multiple weaker forces—the attraction of positive and negative charges, and the tendency of non-polar (oil-like) substances to seek each other and avoid water.
The group hypothesized that the same types of forces could be used to attach a contrast agent to the surface of a type of nanoparticle called a liposome, which resembles a little piece of cell membrane in the shape of a tiny bubble. The researchers designed a "fastener" molecule, DTPA-chitosan-g-C18, that is charged, attracting it to the liposome and binding it to the contrast agent gadolinium. A nonpolar region anchors it to the liposome membrane.
In a series of experiments reported in a recent ACS Nano article (DOI: 10.1021/nn4026228), Kong and others demonstrated that their fastener molecule readily inserted itself into the membrane of pre-made liposomes. Gadolinium stably associated with the modified nanoparticles in solution, and experiments in animal models showed that these nanoparticles produced clear diagnostic images.
"The strategy works like Velcro on a molecular level to adhere functional units to the outer leaflet of a liposome," said Smith, who was first author on the study. "This work represents a new material design strategy that is scalable and easily implemented. The development of improved contrast agents has the potential to directly impact patients' lives by detecting damaged blood vessels."
One of the difficulties of working with liposomes is their tendency to degrade inside the body. When the fastener-loaded liposomes degraded, some of the efficacy of the gadolinium was lost. In a second study published in Langmuir (DOI: 10.1021/la500412r), Kong and Smith developed a process for chemically cross-linking the components of the nanoparticle that prolonged the life of the nanoparticles in biological conditions.
INFORMATION:
The work reported in ACS Nano was a collaboration among Kong, Smith, Zimmerman, and others at the University of Illinois, as well as Dr. Sanjay Misra and researchers at the Mayo Clinic. Both studies were supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health, as well as the University of Illinois Center for Advanced Study.
Illinois researchers combine weak chemical forces to strengthen novel imaging technology
A new nanoparticle design, inspired by cell membranes, has led to clearer MRI images and paved the way for better diagnostic tools
2014-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study reveals corporate social responsibility can lead to better customer service
2014-05-21
Currently accepted wisdom in the corporate world is that in order to motivate frontline employees who serve customers, corporations need to increase their salary, make them feel more positive about the company, or give them more explicit instructions on how to interact with customers. A new study led by Drexel University's Daniel Korschun, PhD, an assistant professor at the LeBow College of Business, examines how frontline employees respond to corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities such as charitable giving, environmental programs and ethical practices. The study ...
New guidelines and technology needed for placement of feeding tubes in pediatric patients
2014-05-21
Universal guidelines and improvements in technology are needed to reduce injuries and deaths from improper placement of nasogastric feeding tubes in pediatric patients, according to a comprehensive review of published literature.
The review, conducted by the New Opportunities for Verification of Enteral Tube Location (NOVEL) Work Group Project of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) found that while the bedside placement of a nasogastric feeding tube is a common procedure conducted by nurses, incorrect placement can have serious and ...
New, fossil-fuel-free process makes biodiesel sustainable
2014-05-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new fuel-cell concept, developed by an Michigan State University researcher, will allow biodiesel plants to eliminate the creation of hazardous wastes while removing their dependence on fossil fuel from their production process.
The platform, which uses microbes to glean ethanol from glycerol and has the added benefit of cleaning up the wastewater, will allow producers to reincorporate the ethanol and the water into the fuel-making process, said Gemma Reguera, MSU microbiologist and one of the co-authors.
"With a saturated glycerol market, traditional ...
Risky alcohol use in male-dominated industries
2014-05-21
New Rochelle, NY, May 21, 2014—The workplace can provide an ideal environment to implement support, well-being, and testing interventions aimed at reducing risky alcohol use among men. By targeting male-dominated industries, in particular, alcohol screening and prevention efforts may be effective in reducing alcohol use, according to a Review article in Journal of Men's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Men's Health website.
A team of Australian researchers led by Nicole Lee, ...
Phase III clinical trial shows image fusion-guided biopsy significantly improves accuracy of prostate
2014-05-21
NEW HYDE PARK, NY – A recent study by investigators from LIJ Medical Center demonstrated that using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in men with an elevated prostate specific antigen (PSA) resulted in a prostate cancer detection rate that was twice as high as data reported in the March 1999 Prostate journal that analyzed men undergoing the standard 12-core biopsy with an elevated PSA. Physicians in the recent trial used a targeted approach to evaluate prostate cancer that combines MR imaging and transrectal ultrasound fusion guided prostate biopsy.
Given the limitations ...
Carnegie Mellon, Microsoft Research automate privacy compliance for big data systems
2014-05-21
PITTSBURGH—Web services companies, such as Facebook, Google and Microsoft, all make promises about how they will use personal information they gather. But ensuring that millions of lines of code in their systems operate in ways consistent with privacy promises is labor-intensive and difficult. A team from Carnegie Mellon University and Microsoft Research, however, has shown these compliance checks can be automated.
The researchers developed a prototype automated system that is now running on the data analytics pipeline of Bing, Microsoft's search engine. According to ...
Funny River Fire, Alaska
2014-05-21
According to the Alaskan Division of Forestry the Funny River fire was very active overnight (May 20) because of low humidity. Currently the fire is estimated to be near 7,000 acres and has reached Tustumena Lake. It is spreading east and west along the shore, is 10 miles long, and is about a mile wide with broadening at the lake shore. There have been no evacuations or reports of any structures lost.
Early this morning (May 21), flame lengths of 125 feet with erratic fire behavior were reported. Winds for today are forecasted to remain out of the north keeping the fire ...
A faster track to the tools that track disease
2014-05-21
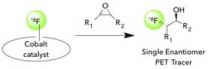
Radioactivity is usually associated with nuclear fallout or comic-book spider bites, but in very small amounts it can be a useful tool for diagnosing diseases.
Small molecules containing a radioactive isotope of fluorine called "18F radiotracers" are used to detect and track certain diseases in patients. Once injected into the body, these molecules accumulate in specific targets, such as tumors, and can be visualized by their radioactive tag on a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. The 18F tags quickly decay so no radioactivity remains after about a day.
But there ...
PMS may spell menopause symptoms later -- but not hot flashes
2014-05-21
CLEVELAND, Ohio (May 21, 2014)—Having premenstrual syndrome (PMS) before menopause does not mean women will be troubled by hot flashes afterward. But they may face more menopause complaints other than hot flashes, such as trouble with memory and concentration, finds a new study published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
The research team at the Helsinki University Central Hospital and Folkhälsan Research Institute in Helsinki, Finland, are the first to show a link between PMS and a worse quality of life after menopause. They ...
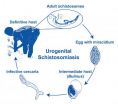
Scientist uncovers links connecting environmental changes with spike in infectious disease
2014-05-21
National Museum of Natural History scientist Bert Van Bocxlaer and an international team of researchers revealed that anthropogenic changes in Africa's Lake Malaŵi are a driving force behind the increase of urogenital schistosomiasis, a debilitating tropical disease caused by parasitic flatworms. Scientists estimate that 250 million people are affected by schistosomiasis worldwide, and 600 million more are at risk of contracting it. In some villages along the shorelines of Lake Malaŵi, 73 percent of the people and up to 94 percent of the schoolchildren are infected ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
[Press-News.org] Illinois researchers combine weak chemical forces to strengthen novel imaging technologyA new nanoparticle design, inspired by cell membranes, has led to clearer MRI images and paved the way for better diagnostic tools